Abstract
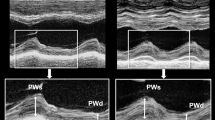
Diastolic wall strain (DWS) was reported as a simple and feasible echocardiographic index in assessing left ventricular (LV) diastolic stiffness. We sought to evaluate whether DWS predicts age-related cardiovascular events. Patients referred for transthoracic echocardiogram, those with preserved LV ejection fraction and no clinical heart failure were studied. Cardiovascular events were ascertained using Framingham criteria (myocardial infarction, coronary insufficiency, stroke, transient ischemic attack, congestive heart failure, or cardiovascular death). DWS was calculated with a validated formula. Cox proportional hazards modeling was used to assess the risk of cardiovascular events. Of a total number of 962 patients (mean age 60.9 ± 14.9 years, 48.0% men), 69 (7.2%) developed at least 1 cardiovascular event during a mean follow-up of 43 ± 32 months. After adjusting for cardiovascular comorbidities in a multivariable model, low DWS (≦ 0.33) was a significant independent predictor of cardiovascular events [hazard ratio (HR): 1.87, 95% confidential interval (CI) 1.04–3.36, P = 0.04]. Echocardiographic assessment of DWS may help in identifying the patients at increased risk for future age-related cardiovascular events.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsang TS, Barnes ME, Gersh BJ, Takemoto Y, Rosales AG, Bailey KR, Seward JB (2003) Prediction of risk for first age-related cardiovascular events in an elderly population: the incremental value of echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 42:1199–1205
Redfield MM, Jacobsen SJ, Burnett JC Jr, Mahoney DW, Bailey KR, Rodeheffer RJ (2003) Burden of systolic and diastolic ventricular dysfunction in the community: appreciating the scope of the heart failure epidemic. JAMA 289:194–202
Tsang TS, Gersh BJ, Appleton CP, Tajik AJ, Barnes ME, Bailey KR, Oh JK, Leibson C, Montgomery SC, Seward JB (2002) Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction as a predictor of the first diagnosed nonvalvular atrial fibrillation in 840 elderly men and women. J Am Coll Cardiol 40:1636–1644
Ommen SR, Nishimura RA, Appleton CP, Miller FA, Oh JK, Redfield MM, Tajik AJ (2000) Clinical utility of Doppler echocardiography and tissue Doppler imaging in the estimation of left ventricular filling pressures: a comparative simultaneous Doppler-catheterization study. Circulation 102:1788–1794
Takeda Y, Sakata Y, Higashimori M, Mano T, Nishio M, Ohtani T, Hori M, Masuyama T, Kaneko M, Yamamoto K (2009) Noninvasive assessment of wall distensibility with the evaluation of diastolic epicardial movement. J Card Fail 15:68–77
Yamamoto K, Sakata Y, Ohtani T, Takeda Y, Mano T (2009) Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circ J 73:404–410
Li VW, Cheuk DK, Cheng FW, Yang JY, Yau JP, Ho KK, Li CK, Li RC, Yuen HL, Ling AS, Chan GC, Cheung YF (2017) Myocardial stiffness as assessed by diastolic wall strain in adult survivors of childhood leukaemias with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 18:451–458
Ohtani T, Mohammed SF, Yamamoto K, Dunlay SM, Weston SA, Sakata Y, Rodeheffer RJ, Roger VL, Redfield MM (2012) Diastolic stiffness as assessed by diastolic wall strain is associated with adverse remodelling and poor outcomes in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur Heart J 33:1742–1749
Soyama Y, Mano T, Goda A, Sugahara M, Masai K, Masuyama T (2017) Prognostic value of diastolic wall strain in patients with chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Heart Vessels 32:68–75
Kamimura D, Suzuki T, Hall ME, Wang W, Winniford MD, Shah AM, Rodriguez CJ, Butler KR, Mosley TH (2018) Diastolic wall strain is associated with incident heart failure in African Americans: Insights from the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. J Cardiol 71:477–483
McKee PA, Castelli WP, McNamara PM, Kannel WB (1971) The natural history of congestive heart failure: the Framingham study. N Engl J Med 285:1441–1446
Arnlov J, Evans JC, Meigs JB, Wang TJ, Fox CS, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, D'Agostino RB, Vasan RS (2005) Low-grade albuminuria and incidence of cardiovascular disease events in nonhypertensive and nondiabetic individuals: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 112:969–975
Levitzky YS, Pencina MJ, D'Agostino RB, Meigs JB, Murabito JM, Vasan RS, Fox CS (2008) Impact of impaired fasting glucose on cardiovascular disease: the Framingham Heart Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 51:264–270
Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA, Kuznetsova T, Lancellotti P, Muraru D, Picard MH, Rietzschel ER, Rudski L, Spencer KT, Tsang W, Voigt JU (2015) Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 16:233–270
Devereux RB, Alonso DR, Lutas EM, Gottlieb GJ, Campo E, Sachs I, Reichek N (1986) Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular hypertrophy: comparison to necropsy findings. Am J Cardiol 57:450–458
Vasan RS, Levy D (2000) Defining diastolic heart failure: a call for standardized diagnostic criteria. Circulation 101:2118–2121
Liu YW, Lee WH, Lin CC, Huang YY, Lee WT, Lee CH, Tsai LM, Chen JH, Tsai WC (2014) Left ventricular diastolic wall strain and myocardial fibrosis in treated hypertension. Int J Cardiol 172:e304–e306
Heeringa J, van der Kuip DA, Hofman A, Kors JA, van Rooij FJ, Lip GY, Witteman JC (2007) Subclinical atherosclerosis and risk of atrial fibrillation: the rotterdam study. Arch Intern Med 167:382–387
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C), 26461096, from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (Tokyo, Japan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsujimoto, S., Miyasaka, Y., Suwa, Y. et al. Diastolic wall strain as a predictor of age-related cardiovascular events in patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. Heart Vessels 34, 784–792 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-018-1311-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-018-1311-5