Abstract
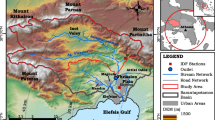
The conceptual rainfall-runoff model TOPMODEL is used to simulate runoffs of the Meishan and Nianyushan catchments during the summers of 1998 and 1999 in the GAME/HUBEX (GEWEX Asia Monsoon Experiment/HUAIHE River Basin Experiment) project. The rainfall distributions are estimated by weather radar and rain gauge networks according to different methods. Observed and simulated runoffs are compared and analyzed for both catchments. Results show that (1) the runoff of the catchment is best simulated by radar data combined with rain gauge network data from inside the catchment, and (2) the rainfall estimated by radar adjusted by a few rain gauges outside the catchment can be used to simulate runoff equally as well as using the dense rain gauge network alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borga, M., E. N. Anagnostou, and E. Frank, 2000: On the use of real-time radar rainfall estimates for flood prediction in mountainous basins. J. Geophys. Res., 105 (D5), 2269–2280.
Beven, K. J., M. J. Kirkby, N. Schofield, and A. F. Tagg, 1984: Testing a physically-based flood forecasting model (TOPMODEL) for three U. K. catchments. J. Hydrol., 69, 119–143.
Freer, J., and K. Beven, 1996: Application of a generalized TOPMODEL to the small Ringelbach catchment, Vosges, France. Water Resour. Res., 32(7), 2147–2159.
Guo Fang, Liu Xinren, and Ren Liliang, 2000: A topography-based hydrological model: TOPMODEL and its widened application. Advances in Water Science, 11(3), 296–301. (in Chinese)
Li Jiantong, Yang Weisheng, Guo Lin, Chen Zemian, 2000: A study of improving precision of measuring regional precipitation in optimum interpolation method. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 24(2), 263–270.
Liu Xiaoyang, Mao Jietai, Zhu Yuanjing, and Li Jiren, 2002: Radar rainfall estimation and its application on runoff simulation over SHIGUANHE catchments. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 38(3), 342–349.
Pessoa, M. L., L. B. Rafael, and R. W. Earle, 1993: Use of weather radar for flood forecasting in the Sieve River basin: A sensitivity analysis. J. Appl. Meteor., 32, 462–475.
Sun, X., R. G. Mein, T. D. Keenan, and J. F. Elliott, 2000: Flood estimation using radar and rain gauge data. J.Hydrol., 239, 4–18.
Valeo, C., and S. M. A. Moin, 2000: Variable source area modeling in urbanizing watersheds. J. Hydrol., 228, 68–81.
Verworn, H. R., 1991: “Hydrological elevance of radar rainfall data. Hydrological Applications of Weather Radar, Eds., E. Horwood, New York, 531–542.
Wyss, J., E. R. Williams, and R. L. Bras., 1990: Hydrologic modelling of New England river basins using radar rainfall data. J. Geophys. Res., 95(D3), 2143–2152.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiaoyang, L., Jietai, M., Yuanjing, Z. et al. Runoff simulation using radar and rain gauge data. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 20, 213–218 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-003-0006-7
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-003-0006-7