Abstract
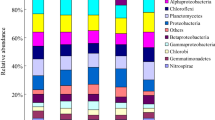
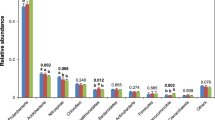
We investigated the effect of long-term fertilization on bacterial abundance, composition, and diversity in paddy soil. The experiment started in 1990 in Taoyuan Agro-ecosystem Research Station in China (111°33′ E, 28°55′ N). The molecular approaches including real-time quantitative PCR, terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism, and clone library construction were employed using 16S rRNA gene as genetic marker. Application of inorganic fertilizers did not affect bacterial abundance, and rice straw incorporation combined with inorganic fertilizers significantly (P < 0.05) increased bacterial abundance with shifts in bacterial community composition. Among phylogenetic groups, γ-Proteobacteria was responsive to all fertilization regimes while Acidobacteria was relatively stable to fertilization practices. Inorganic fertilizer mainly affected γ-Proteobacteria and δ-Proteobacteria, while rice straw incorporation influenced β-Proteobacteria and Verrucomicrobia. Therefore, long-term fertilization can affect abundance and composition of bacterial communities in paddy soil.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asakawa S, Kimura M (2008) Comparison of bacterial community structures at main habitats in paddy field ecosystem based on DGGE analysis. Soil Biol Biochem 40:1322–1329
Asari N, Ishihara R, Nakajima Y, Kimura M, Asakawa S (2007) Succession and phylogenetic composition of eubacterial communities in rice straw during decomposition on the surface of paddy field soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 53:56–65
Bell T, Newman JA, Silverman BW, Turner SL, Lilley AK (2005) The contribution of species richness and composition to bacterial services. Nature 436:1157–1160
Bittman B, Forge TA, Kowalenko CG (2005) Responses of the bacterial and fungal biomass in a grassland soil to multi-year applications of dairy manure slurry and fertilizer. Soil Biol Biochem 37:613–623
Bronick CJ, Lai R (2005) Soil structure and management: a review. Geoderma 124:3–22
Burke DJ, Kretzer AM, Rygiewicz PZ, Topa MA (2006) Soil bacterial diversity in a loblolly pine plantation: influence of ectomycorrhizas and fertilization. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 57:409–419
Bünemann EK, Bossio DA, Smithson PC, Frossard E, Oberson A (2004) Microbial community composition and substrate use in a highly weathered soil as affected by crop rotation and P fertilization. Soil Biol Biochem 36:889–901
Cardinale BJ, Srivastava DS, Duffy JE, Wright JP, Downing AL, Sankaran M, Jouseau C (2006) Effects of biodiversity on the functioning of trophic groups and ecosystems. Nature 443:989–992
Ceja-Navarro JA, Rivera-Orduna FN, Patino-Zuniga L, Vila-Sanjurjo A, Crossa J, Govaerts B, Dendooven L (2010) Phylogenetic and multivariate analyses to determine the effects of different tillage and residue management practices on soil bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3685–3691
Chen Z, Luo X, Hu R, Wu M, Wu J, Wei W (2010) Impact of long-term fertilization on the composition of denitrifier communities based on nitrite reductase analyses in a paddy soil. Microb Ecol 60:850–861
Clegg CD, Lovell RDL, Hobbus PJ (2003) The impact of grassland management regime on the community structure of selected bacterial groups in soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 43:263–270
Costa AL, Paixão SM, Caçador I, Carolino M (2007) CLPP and EEA profiles of microbial communities in salt marsh sediments. J Soil Sediment 7:418–425
Da Silva KRA, Salles JF, Seldin L, van Elsas JD (2003) Application of a novel Paenibacillus-specific PCR-DGGE method and sequence analysis to assess the diversity of Paenibacillus spp. in the maize rhizosphere. J Microbiol Methods 54:213–231
Dandie CE, Miller MN, Burton DL, Zebarth BJ, Trevors JT, Goyer C (2007) Nitric oxide reductase-targeted real-time PCR quantification of denitrifier populations in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4250–4258
Dunbar J, Ticknor LO, Kuske CR (2001) Phylogenetic specificity and reproducibility and new method for analysis of terminal restriction fragment profiles of 16S rRNA genes from bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:190–197
Enwall K, Nyberg K, Bertilsson S, Cederlund H, Stenstrom J, Hallin S (2007) Long-term impact of fertilization on activity and composition of bacterial communities and metabolic guilds in agricultural soil. Soil Biol Biochem 39:106–115
Esperschütz J, Gattinger A, Mäder P, Schloter M, Fliessbach A (2007) Response of soil microbial biomass and community structures to conventional and organic farming systems under identical crop rotations. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 61:26–37
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. PNAS 103:626–631
Freitag TE, Chang L, Clegg CD, Prosser JI (2005) Influence of inorganic nitrogen management regime on the diversity of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in agricultural grassland soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8323–8334
Gelsomino A, Keijzer-Wolters A, Cacco G, van Elsas JD (1999) Assessment of bacterial community structure in soil by polymerase chain reaction and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. J Microbiol Methods 38:1–15
Gong W, Yan X, Wang J, Hu T, Gong Y (2009) Long-term manure and fertilizer effects on soil organic matter fractions and microbes under a wheat–maize cropping system in northern China. Geoderma 149:318–324
Gu Y, Zhang X, Tu S, Lindström K (2009) Soil microbial biomass, crop yields, and bacterial community structure as affected by long-term fertilizer treatments under wheat–rice cropping. Eur J Soil Biol 45:239–246
He JZ, Zheng Y, Chen CR, He YQ, Zhang LM (2008) Microbial composition and diversity of an upland red soil under long-term fertilization treatments as revealed by culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches. J Soils Sediments 8:349–358
Islam R, Trivedi P, Madhaiyan M, Seshadri S, Lee G, Yang Y, Kim M, Han G, Singh Chauban P, Sa T (2010) Isolation, enumeration and characterization of diazotrophic bacteria from paddy soil sample under long-term fertilizer management experiment. Biol Fertil Soils 46:261–269
Kikuchi H, Watanabe T, Jia ZJ, Kimura M, Asakawa S (2007) Molecular analyses reveal stability of bacterial communities in bulk soil of a Japanese paddy field: estimation by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of 16S rRNA genes amplified from DNA accompanied with RNA. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 53:448–458
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Lehtovirta LE, Prosser JI, Nicol GW (2009) Soil pH regulates the abundance and diversity of group 1.1c Crenarchaeota. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:367–376
Liou R, Huang S, Lin C, Chen S (2003) Methane emission from fields with three various rice straw treatments in Taiwan paddy soils. J Environ Sci Health B 38:511–527
Liu M, Feng H, Chen X, Huang Q, Jiao J, Zhang B, Li H (2009) Organic amendments with reduced chemical fertilizer promote soil microbial development and nutrient availability in a subtropical paddy field: the influence of quantity, type and application time of organic amendments. Appl Soil Ecol 42:166–175
Marschner P, Yang CH, Lieberei R, Crowley DE (2001) Soil and plant specific effects on bacterial community composition in the rhizosphere. Soil Biol Biochem 33:1437–1445
Marschner P, Kandeler E, Marschner B (2003) Structure and function of the soil microbial community in a long-term fertilizer experiment. Soil Biol Biochem 35:453–461
Marschner P, Crowley D, Yang CH (2004) Development of specific rhizosphere bacterial communities in relation to plant species, nutrition and soil type. Plant Soil 261:199–208
Melero S, Madejon E, Herencia JF, Ruiz JC (2008) Effect of implementing organic farming on chemical and biochemical properties of an irrigated loam soil. Agron J 100:136–144
Nakayama N, Okabe A, Toyota K, Kimura M, Asakawa S (2006) Phylogenetic distribution of bacteria isolated from the floodwater of a Japanese paddy field. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 52:305–312
Nemergut DR, Townsend AR, Sattin SR, Freeman KR, Fierer N, Neff JC, Bowman WD, Schadt CW, Weintraub MN, Schmidt SK (2008) The effects of chronic nitrogen fertilization on alpine tundra soil microbial communities: implications for carbon and nitrogen cycling. Environ Microbiol 10:3093–3105
Noll M, Matthies D, Frenzel P, Derakshani M, Liesack W (2005) Succession of bacterial community structure and diversity in a paddy soil oxygen gradient. Environ Microbiol 7:382–395
Ogilvie LA, Hirsch PR, Johnston AQB (2008) Bacterial diversity of the broadbalk ‘classical’ winter wheat experiment in relation to long-term fertilizer inputs. Microbiol Ecol 56:525–537
Okabe A, Oike H, Toyota K, Kimura M (2000) Comparison of phospholipids fatty acid composition in floodwater and plow layer soil during the rice cultivation period in a Japanese paddy field. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 46:893–904
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. In: USDA Circular No. 939. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC, p 19
Parrent JL, Vilgalys R (2007) Biomass and compositional responses of ectomycorrhizal fungal hyphae to elevated CO2 and nitrogen fertilization. New Phytol 176:164–174
Qiu QF, Noll M, Abraham WR, Lu YH, Conrad R (2008) Applying stable isotope probing of phospholipid fatty acids and rRNA in a Chinese rice field to study activity and composition of the methanotrophic bacterial communities in situ. ISME J 2:602–614
Roesch LFW, Fulthorpe RR, Riva A, Casella G, Hadwin AKM, Kent AD, Daroub SH, Camargo FAO, Farmerie WG, Triplett EW (2007) Pyrosequencing enumerates and contrasts soil microbial diversity. ISME J 1:283–290
Rousk J, Brookes PC, Baath E (2010) Investigating the mechanisms for the opposing pH relationships of fungal and bacterial growth in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 42:926–934
Rui J, Peng J, Lu Y (2009) Succession of bacterial populations during plant residue decomposition in rice field soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4879–4886
Saha S, Prakash V, Kundu S, Kumar N, Minna BL (2008) Soil enzymatic activity as affected by long term application of farm yard manure and mineral fertilizer under a rainfed soybean–wheat system in N–W Himalaya. Eur J Soil Biol 44:309–315
Sandaa RA, Torsvik V, Enger Φ, Daae FL, Castberg T, Hahn D (2006) Analysis of bacterial communities in heavy metal-contaminated soils at different levels of resolution. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 30:237–251
Sarathchandra SU, Ghani A, Yeates GW, Burch G, Cox NR (2001) Effect of nitrogen and phosphate fertilizers on microbial and nematode diversity in pasture soils. Soil Biol Biochem 33:953–964
Shen JP, Zhang LM, Guo JF, Ray JL, He JZ (2010) Impact of long-term fertilization practices on the abundance and composition of soil bacterial communities in Northeast China. Appl Soil Ecol 46:119–214
Steenwerth KL, Jackson LE, Calderón FJ, Stromberg MR, Scowd KM (2003) Soil microbial community and land use history in cultivated and grassland ecosystems of coastal California. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1599–1611
Sugano A, Tsuchimoto H, Tun CC, Asakawa S, Kimura M (2005) Succession and phylogenetic profile of eubacterial communities in rice straw incorporated into a rice field: estimation by PCR-DGGE analysis. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 51:51–60
Takahashi S, Uenosono S, Ono S (2003) Short- and long-term effects o f rice straw application on nitrogen uptake by crops and nitrogen mineralization under flooded and upland conditions. Plant Soil 251:291–301
Tanahashi T, Murase J, Matsuya K, Hayashi M, Kimura M, Asakawa S (2005) Bacterial communities responsible for the decomposition of rice straw compost in Japanese rice paddy field estimated by DGGE analysis of amplified 16S rDNA and 16S rRNA fragments. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 51:351–360
Tanaka H, Kyaw K, Toyota K, Motobayashi T (2010) Influence of application of rice straw, farmyard manure, and municipal biowastes on nitrogen fixation, soil microbial biomass N, and mineral N in a model paddy microcosm. Biol Fertil Soils 42:501–505
Wasaki J, Rothe A, Kania A, Neumann G, Römheld V, Shinano T, Osaki M, Kandeler E (2005) Root exudation, phosphorus acquisition, and microbial diversity in the rhizosphere of white lupine as affected by phosphorus supply and atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration. J Environ Qual 34:2157–2166
Wessén E, Hallin S, Philippot L (2010) Differential responses of bacterial and archaeal groups at high taxonomical ranks to soil management. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1759–1765
Wu M, Zhang H, Li X, Zhang Y, Su Z, Zhang C (2008) Soil fungistasis and its relations to soil microbial composition and diversity: a case study of a series of soils with different fungistasis. J Environ Sci China 20:871–877
Yadav RL (2003) Assessing on-farm efficiency and economics of fertilizer N, P and K in rice wheat systems of India. Field Crop Res 81:39–51
Zheng Y, Zhang LM, Zheng YM, Di HJ, He JZ (2008) Abundance and community composition of methanotrophs in a Chinese paddy soil under long-term fertilization practices. J Soils Sediments 8:406–414
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-YW-BR-01, KZCX2-YW-T07, and KZCX2-YW-423) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (40771115, 40901125). We thank Prof. Paolo Nannipieri for careful revision of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, M., Qin, H., Chen, Z. et al. Effect of long-term fertilization on bacterial composition in rice paddy soil. Biol Fertil Soils 47, 397–405 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-010-0535-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-010-0535-z