Abstract
Purpose
To compare the perioperative and functional outcomes of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) and thulium laser enucleation of the prostate (ThuLEP) for the treatment of large-volume benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) (> 80 ml).
Methods
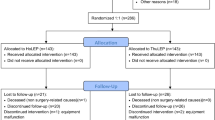
A total of 116 consecutive patients with BPH were randomized to be treated surgically with either HoLEP (n = 58) or ThuLEP (n = 58), following the classical three-lobe enucleation technique. Follow-up was assessed at 1, 3, 6, 12 and 18 months after surgery.
Results
At 18 months, the lower urinary tract symptom index was improved significantly in both groups compared with the baseline values. The operative time (78.4 ± 8.0 vs. 71.4 ± 6.4 min) and enucleation time (61.2 ± 5.4 vs. 56.4 ± 8.4 min) were significantly shorter for ThuLEP compared to HoLEP (both p < 0.001). There were no significant differences between the two groups regarding morcellation time, resected weight, hemoglobin decrease, catheter time and hospital stay (p > 0.05). The HoLEP and ThuLEP groups had equivalent International Prostate Symptom Scores (3 [3–3] vs. 3 [3–3], p = 0.776), quality of life (1 [1–2] vs. 2 [1–2], p = 0.809), Qmax (25.3 ± 4.8 ml/s vs. 24.7 ± 4.4 ml/s, p = 0.470), postvoid residual urine (PVR) (6.1 [2.6–20.8] vs. 7.7 [3.1–22.8] ml, p = 0.449) and PSA (0.84 ± 0.32 vs. 0.90 ± 0.34 ml, p = 0.309) at 18 months postoperatively.
Conclusion
Both HoLEP and ThuLEP relieve lower urinary tract symptoms in a comparable way with high efficacy and safety. ThuLEP was statistically superior to HoLEP in operation time and enucleation time, although the differences were clinically negligible.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker B, Herrmann TRW, Gross AJ, Netsch C (2018) Thulium vapoenucleation of the prostate versus holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for the treatment of large volume prostates: preliminary 6-month safety and efficacy results of a prospective randomized trial. World J Urol 36(10):1663–1671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2321-8
Naspro R, Suardi N, Salonia A, Scattoni V, Guazzoni G, Colombo R, Cestari A, Briganti A, Mazzoccoli B, Rigatti P, Montorsi F (2006) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus open prostatectomy for prostates > 70 g: 24-month follow-up. Eur Urol 50(3):563–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2006.04.003
Cornu JN, Ahyai S, Bachmann A, de la Rosette J, Gilling P, Gratzke C, McVary K, Novara G, Woo H, Madersbacher S (2015) A systematic review and meta-analysis of functional outcomes and complications following transurethral procedures for lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from benign prostatic obstruction: an update. Eur Urol 67(6):1066–1096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.06.017
Yang Z, Wang X, Liu T (2013) Thulium laser enucleation versus plasmakinetic resection of the prostate: a randomized prospective trial with 18-month follow-up. Urology 81(2):396–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2012.08.069
Elshal AM, Elkoushy MA, El-Nahas AR, Shoma AM, Nabeeh A, Carrier S, Elhilali MM (2015) GreenLight laser (XPS) photoselective vapo-enucleation versus holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized controlled study. J Urol 193(3):927–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2014.09.097
Wu G, Hong Z, Li C, Bian C, Huang S, Wu D (2016) A comparative study of diode laser and plasmakinetic in transurethral enucleation of the prostate for treating large volume benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized clinical trial with 12-month follow-up. Lasers Med Sci 31(4):599–604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-1883-1
Bach T, Wendt-Nordahl G, Michel MS, Herrmann TR, Gross AJ (2009) Feasibility and efficacy of Thulium:YAG laser enucleation (VapoEnucleation) of the prostate. World J Urol 27(4):541–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-008-0370-0
Herrmann TR, Bach T, Imkamp F, Georgiou A, Burchardt M, Oelke M, Gross AJ (2010) Thulium laser enucleation of the prostate (ThuLEP): transurethral anatomical prostatectomy with laser support Introduction of a novel technique for the treatment of benign prostatic obstruction. World J Urol 28(1):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-009-0503-0
Gravas S, Bachmann A, Reich O, Roehrborn CG, Gilling PJ, De La Rosette J (2011) Critical review of lasers in benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). BJU Int 107(7):1030–1043. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09954.x
Xia SJ, Zhuo J, Sun XW, Han BM, Shao Y, Zhang YN (2008) Thulium laser versus standard transurethral resection of the prostate: a randomized prospective trial. Eur Urol 53(2):382–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2007.05.019
Saredi G, Pacchetti A, Pirola GM, Martorana E, Berti L, Scroppo FI, Marconi AM (2016) Impact of thulium laser enucleation of the prostate on erectile, ejaculatory and urinary functions. Urol Int 97(4):397–401. https://doi.org/10.1159/000446829
Gilling PJ, Kennett K, Das AK, Thompson D, Fraundorfer MR (1998) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) combined with transurethral tissue morcellation: an update on the early clinical experience. J Endourol 12(5):457–459. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.1998.12.457
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien P-A (2004) Classification of surgical complications. Ann Surg 240(2):205–213. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae
Mamoulakis C, Efthimiou I, Kazoulis S, Christoulakis I, Sofras F (2011) The modified Clavien classification system: a standardized platform for reporting complications in transurethral resection of the prostate. World J Urol 29(2):205–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-010-0566-y
Reich O, Gratzke C, Stief CG (2006) Techniques and long-term results of surgical procedures for BPH. Eur urol 49(6):970–978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2005.12.072(discussion 978)
Elkoushy MA, Elhilali MM (2016) Management of benign prostatic hyperplasia larger than 100 ml: simple open enucleation versus transurethral laser prostatectomy. Curr Urol Rep 17(6):44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-016-0601-7
Bach T, Netsch C, Haecker A, Michel MS, Herrmann TR, Gross AJ (2010) Thulium:YAG laser enucleation (VapoEnucleation) of the prostate: safety and durability during intermediate-term follow-up. World J Urol 28(1):39–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-009-0461-6
Becker B, Orywal AK, Gross AJ, Netsch C (2019) Thulium vapoenucleation of the prostate (ThuVEP) for prostates larger than 85 ml: long-term durability of the procedure. Lasers Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-019-02760-1
Bach T, Huck N, Wezel F, Hacker A, Gross AJ, Michel MS (2010) 70 vs 120 W thulium:yttrium-aluminium-garnet 2 microm continuous-wave laser for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic ex vivo evaluation. BJU Int 106(3):368–372. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.09059.x
Netsch C, Bach T, Pohlmann L, Herrmann T, Gross AJ (2012) Comparison of 120-200 W 2 mum thulium:yttrium–aluminum–garnet vapoenucleation of the prostate. J Endourol 26(3):224–229. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2011.0173
Kyriazis I, Swiniarski PP, Jutzi S, Wolters M, Netsch C, Burchardt M, Liatsikos E, Xia S, Bach T, Gross AJ, Herrmann TR (2015) Transurethral anatomical enucleation of the prostate with Tm:YAG support (ThuLEP): review of the literature on a novel surgical approach in the management of benign prostatic enlargement. World J Urol 33(4):525–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-015-1529-0
Netsch C, Becker B, Tiburtius C, Moritz C, Becci AV, Herrmann TRW, Gross AJ (2017) A prospective, randomized trial comparing thulium vapoenucleation with holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic obstruction: perioperative safety and efficacy. World J Urol 35(12):1913–1921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-017-2071-z
Zhang F, Shao Q, Herrmann TR, Tian Y, Zhang Y (2012) Thulium laser versus holmium laser transurethral enucleation of the prostate: 18-month follow-up data of a single center. Urology 79(4):869–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2011.12.018
Tinmouth WW, Habib E, Kim SC, Kuo RL, Paterson RF, Terry CL, Elhilali M, Lingeman JE (2005) Change in serum prostate specific antigen concentration after holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: a marker for completeness of adenoma resection? J Endourol 19(5):550–554. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2005.19.550
Pirola GM, Saredi G, Codas Duarte R, Bernard L, Pacchetti A, Berti L, Martorana E, Carcano G, Badet L, Fassi-Fehri H (2018) Holmium laser versus thulium laser enucleation of the prostate: a matched-pair analysis from two centers. Ther Adv Urol 10(8):223–233. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756287218779784
Placer J, Salvador C, Planas J, Trilla E, Lorente D, Celma A, Lopez MA, Morote J (2015) Effects of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate on sexual function. J Endourol 29(3):332–339. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2014.0502
Briganti A, Naspro R, Gallina A, Salonia A, Vavassori I, Hurle R, Scattoni E, Rigatti P, Montorsi F (2006) Impact on sexual function of holmium laser enucleation versus transurethral resection of the prostate: results of a prospective, 2-center, randomized trial. J Urol 175(5):1817–1821. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(05)00983-3
Carmignani L, Bozzini G, Macchi A, Maruccia S, Picozzi S, Casellato S (2015) Sexual outcome of patients undergoing thulium laser enucleation of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Asian J Androl 17(5):802–806. https://doi.org/10.4103/1008-682X.139255
Nam JK, Kim HW, Lee DH, Han JY, Lee JZ, Park SW (2015) Risk factors for transient urinary incontinence after holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. World J Men’s Health 33(2):88–94. https://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2015.33.2.88
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the staff at Xiangya Hospital of Central South University for their support in generating this manuscript. The authors would like to give particular thanks to the 116 patients who agreed to this study and completed the follow-up survey. Finally, the authors would like to thank National Natural Science Foundation of China for its support.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China 81770758 (to L.W.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ and LW contribute to conception and design. ZO, WH, RW, MM and LC contribute to acquisition of data. XP and ZO contribute to analysis of data. JZ contributes to drafting the article. JZ, XZ, RX, SJ, LQ and LW contribute to revising it critically for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants/or animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Institutional Review Board approval for this study was obtained from the Ethical Committee of Xiangya Hospital Central South University on 31 January 2016.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Ou, Z., Zhang, X. et al. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus thulium laser enucleation of the prostate for the treatment of large-volume prostates > 80 ml: 18-month follow-up results. World J Urol 38, 1555–1562 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-02945-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-02945-x