Abstract
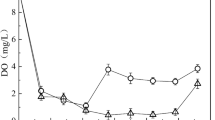
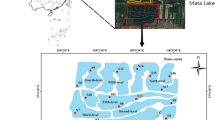
Sediments and surface water were sampled in a tide flat in the Huiquan Bay, Qingdao, China in January 2004 to simulate the exchange of NH4-N/NO3-N/PO 3−4 between sediments and surface water. A working system was designed with which samples were shaken at 60, 120 and 150 revolutions per minute (r/min). Experiment results show that NH4-N concentration in water at shaking rate of 60 r/min decreased gradually, while at 120 r/min increased gradually. In resuspension, fine-grained sediments contributed most NH4-N to the seawater, followed by medium-grained and coarse-grained sediments. The NO3-N concentration in water had a negative relation with the shaking rate; the medium-grained sediments contributed more NO3-N to seawater than the coarse-and fine-grained sediments. The PO 3−4 concentration is positively related with the shaking rate, the fine-grained sediments were the main N and P contributor to the seawater, followed by medium-and coarse-grained sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fanning, K. A., K. L. Carder and P. R. Betzer, 1982. Sediment resuspension by coastal water: a potential mechanism for nutrent re-cycling on the ocean’s margins. Deep-Sea Research, Part A 29: 953–965.
Hou, L. J., M. Li and S. Y. Xu, 2003. Effect of environmental factors on phosphorus release from sediments in urban reaches of Suzhou Creek. Shanghai Enviromental Sciences 22(4): 258–260.
Li, Y., D. N. Wu and Y. X. Xue, 1998. A development sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in the sediments and its environmental geochemical significance. Marine Environmental Science 17(1): 15–20.
Liu, W, Z. L. Chen, J. Wang, J. Liu, D. Q. Wang and X. Z. Zhang, 2004. Cycling characters of inorganic nitrogen between water and sediment of river in a small town. Journal of Agro-Enviroment Science 23(3): 520–524.
Ma, H. B., J. M. Song, X. X. Lü and H. M. Yuan, 2003. Nitrogen forms and their functions in recycling of the Bohai Sea sediments. Geochimica 32(1): 48–53.
Ma, Y., X. Y. Shen and D. H. Lin, 2000. Study on phosphorus releasing from sediment in South Lake Taihu. Shanghai Enviromental Science 19(8): 391–393.
Morin, J. and J. W. Morse, 1999. Ammonium release from resuspended sediments in the Laguna Madre estuary. Marine Chemistry 60: 75–83.
Qian, C. P., Z. L. Chen, L. Z. Hu and H. G. Deng, 2003. Effects of sediment resuepension on nitrogen and phosphate exchange at the sediment-water interface in east chongming tidal flat. Enviroment Science 24(5): 114–119.
Song, J. M., 1997. Chemistry of Sediment-Sea Water Interface of the China Seas. China Ocean Press, Beijing.
Thomsen, L., G. Graf, V. Martens and E. Steen, 1994. An instrument for sampling water from the benthic boundary layer. Continental Shelf Research 14: 871–882.
Vangriesheim, A. and A. Khripounoff, 1990. Nwar-bottom particle concentration and flux: temporal variations observed with sediment traps and nephelometer on the Meriadzek Terrace, Bay of Biscay. Progress in Oceanography 24: 103–116.
Wainright, S. C., 1987. Stimulation of heterotrophic microplankton production by resuspended marine sediments. Science 238: 1 710–1 712.
Wainright, S. C., 1990. Sediment-to-water fluxes of particulate material and microbes by resuspension and their contribution to the planktonic food web. Marine Ecology Progress Series 62: 271–281.
Wang, Y. C., G. J. Wan, C. Q. Yin and R. G. Huang, 2002. Distribution of total, exchangeable and fixed nitrogen in the sediments of two lakes in Guizhou Province. Journal of Lake Science 14(4): 301–309.
Wu, F. C., G. J. Wan and R. G. Huang, 1996. Biogeochemical processes of nutrition elements at the sediment-water interface of lakes I: Nitrogen cycling and its environmental impacts. Acta Mineralogica Sinica 16(4): 403–409. (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu, G. W. and B. Q. Qing, 2003. Chemical sequential extraction of phosphorus in lake sediments. Journal of Agro-Environment Science 22(2): 350–352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported funded by the knowledge Innovation Key Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KZCX1-SW-01-08) and the National Key Project for Basic Research of China (Contract No. 2007CB407305)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Song, J., Guo, Z. et al. The release behavior of inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus in sediment during disturbance. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 26, 197–202 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-008-0197-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-008-0197-y