Abstract
Objectives
To predict epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation status in lung adenocarcinoma using MR-based radiomics signature of brain metastasis and explore the optimal MR sequence for prediction.
Methods
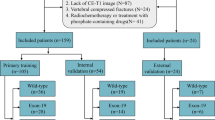
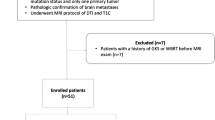
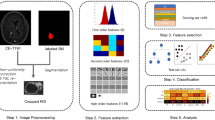
Data from 52 patients with brain metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma (28 with mutant EGFR, 24 with wild-type EGFR) were retrospectively reviewed. Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging (T1-CE), T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (T2-FLAIR), T2WI, and DWI sequences were selected for radiomics features extraction. A total of 438 radiomics features were extracted from each MR sequence. All sequences were randomly divided into training and validation cohorts. The least absolute shrinkage selection operator was used to select informative features, a radiomics signature was built with the logistic regression model of the training cohort, and the radiomics signature performance was evaluated using the validation cohort and an independent testing data set.
Results
The radiomics signature built on 9 selected features showed good discrimination in both the training and validation cohorts for T2-FLAIR. The radiomics signature of T2-FLAIR yielded an AUC of 0.987, a classification accuracy of 0.991, sensitivity of 1.000, and specificity of 0.980 in the validation cohort. The AUC was 0.871 in the independent testing data set. The AUCs of our radiomics signature to differentiate exon 19 and exon 21 mutations were 0.529, 0.580, 0.645, and 0.406 for T1-CE, T2-FLAIR, T2WI, and DWI, respectively.
Conclusions
We developed a T2-FLAIR radiomics signature that can be used as a noninvasive auxiliary tool for predicting EGFR mutation status in lung adenocarcinoma, which is helpful to guide therapeutic strategies.
Key Points
• MR-based radiomics signature of brain metastasis may help predict EGFR mutation status in lung adenocarcinoma, especially using T2-FLAIR.
• Nine radiomics features extracted from T2-FLAIR sequence strongly correlate with EGFR mutation status.
• Radiomics features reflect tumor heterogeneity through potential changes in tissue morphology caused by EGFR mutation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACC:
-
Classification accuracy
- ARMS-PCR:
-
Amplification refractory mutation system–polymerase chain reaction
- ctDNA:
-
Circulating tumor DNA
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- KPS:
-
Karnofsky Scores
- LASSO:
-
Least absolute shrinkage selection operator
- NGS:
-
Next-generation sequencing technology
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- SEN:
-
Sensitivity
- SPE:
-
Specificity
- T1-CE:
-
Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging
- T2-FLAIR:
-
T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
- TE:
-
Echo time
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- TR:
-
Repetition time
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A et al (2020) Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70:145–164
Riihimäki M, Hemminki A, Fallah M et al (2014) Metastatic sites and survival in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 86:78–84
Achrol AS, Rennert RC, Anders C et al (2019) Brain metastases. Nat Rev Dis Primers 5:5
Yang JJ, Zhou C, Huang Y et al (2017) Icotinib versus whole-brain irradiation in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer and multiple brain metastases (BRAIN): a multicentre, phase 3, open-label, parallel, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med 5:707–716
Reungwetwattana T, Nakagawa K, Cho BC et al (2018) CNS response to osimertinib versus standard epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2018.78.3118:Jco2018783118
Mok TS, Wu YL, Ahn MJ et al (2017) Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med 376:629–640
Luo J, Shen L, Zheng D (2014) Diagnostic value of circulating free DNA for the detection of EGFR mutation status in NSCLC: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 4:6269
Qiu M, Wang J, Xu Y et al (2015) Circulating tumor DNA is effective for the detection of EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 24:206–212
Merker JD, Oxnard GR, Compton C et al (2018) Circulating tumor DNA analysis in patients with cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology and College of American Pathologists Joint Review. J Clin Oncol 36:1631–1641
Wu SG, Rao MY, Zhou J et al (2015) Distribution of metastatic disease in the brain in relation to the hippocampus: a retrospective single-center analysis of 6064 metastases in 632 patients. Oncotarget 6:44030–44036
Takano K, Kinoshita M, Takagaki M et al (2016) Different spatial distributions of brain metastases from lung cancer by histological subtype and mutation status of epidermal growth factor receptor. Neuro Oncol 18:716–724
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278:563–577
Zhang Y, Oikonomou A, Wong A, Haider MA, Khalvati F (2017) Radiomics-based prognosis analysis for non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep 7:46349
Rizzo S, Botta F, Raimondi S et al (2018) Radiomics: the facts and the challenges of image analysis. Eur Radiol Exp 2:36
Wu J, Tha KK, Xing L, Li R (2018) Radiomics and radiogenomics for precision radiotherapy. J Radiat Res 59:i25–i31
Taguchi N, Oda S, Yokota Y et al (2019) CT texture analysis for the prediction of KRAS mutation status in colorectal cancer via a machine learning approach. Eur J Radiol 118:38–43
Oh JE, Kim MJ, Lee J et al (2020) Magnetic resonance-based texture analysis differentiating KRAS mutation status in rectal cancer. Cancer Res Treat 52:51–59
Yang L, Dong D, Fang M et al (2018) Can CT-based radiomics signature predict KRAS/NRAS/BRAF mutations in colorectal cancer? Eur Radiol 28:2058–2067
Tu W, Sun G, Fan L et al (2019) Radiomics signature: a potential and incremental predictor for EGFR mutation status in NSCLC patients, comparison with CT morphology. Lung Cancer 132:28–35
Li Z, Mao Y, Li H, Yu G, Wan H, Li B (2016) Differentiating brain metastases from different pathological types of lung cancers using texture analysis of T1 postcontrast MR. Magn Reson Med 76:1410–1419
Liu Y, Liu X, Xu L et al (2018) Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of treatment efficacy and prognosis for brain metastases in lung cancer patients after radiotherapy: a preliminary study. Thorac Cancer 9:865–873
Herlidou-Même S, Constans JM, Carsin B et al (2003) MRI texture analysis on texture test objects, normal brain and intracranial tumors. Magn Reson Imaging 21:989–993
Liu Z, Zhang XY, Shi YJ et al (2017) Radiomics analysis for evaluation of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 23:7253–7262
Yotsukura M, Yasuda H, Shigenobu T et al (2017) Clinical and pathological characteristics of EGFR mutation in operable early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 109:45–51
Liu Y, Kim J, Balagurunathan Y et al (2016) Radiomic features are associated with EGFR mutation status in lung adenocarcinomas. Clin Lung Cancer 17:441–448.e446
Mei D, Luo Y, Wang Y, Gong J (2018) CT texture analysis of lung adenocarcinoma: can radiomic features be surrogate biomarkers for EGFR mutation statuses. Cancer Imaging 18:52
Digumarthy SR, Padole AM, Gullo RL, Sequist LV, Kalra MK (2019) Can CT radiomic analysis in NSCLC predict histology and EGFR mutation status? Medicine (Baltimore) 98:e13963
Segal E, Sirlin CB, Ooi C et al (2007) Decoding global gene expression programs in liver cancer by noninvasive imaging. Nat Biotechnol 25:675–680
Koay EJ, Lee Y, Cristini V et al (2018) A visually apparent and quantifiable CT imaging feature identifies biophysical subtypes of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 24:5883–5894
Grossmann P, Stringfield O, El-Hachem N et al (2017) Defining the biological basis of radiomic phenotypes in lung cancer. Elife 6:22
Siegelin MD, Borczuk AC (2014) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung adenocarcinoma. Lab Invest 94:129–137
Jin Y, Li JP, Tang LY et al (2011) Protein expression and significance of VEGF, EGFR and MMP-9 in non-small cell lung carcinomas. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 12:1473–1476
Huang SF, Liu HP, Li LH et al (2004) High frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations with complex patterns in non-small cell lung cancers related to gefitinib responsiveness in Taiwan. Clin Cancer Res 10:8195–8203
Brattström D, Wester K, Bergqvist M et al (2004) HER-2, EGFR, COX-2 expression status correlated to microvessel density and survival in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Acta Oncol 43:80–86
Qi Y, Cui X, Han M et al (2020) Radiomics analysis of lung CT image for the early detection of metastases in patients with breast cancer: preliminary findings from a retrospective cohort study. Eur Radiol 30:4545–4556
Xu J, Cui X, Wang B et al (2020) Texture analysis of early cerebral tissue damage in magnetic resonance imaging of patients with lung cancer. Oncol Lett 19:3089–3100
Ng F, Kozarski R, Ganeshan B, Goh V (2013) Assessment of tumor heterogeneity by CT texture analysis: can the largest cross-sectional area be used as an alternative to whole tumor analysis? Eur J Radiol 82:342–348
Funding
This study has received funding by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (ID: 81670046) and State Key Laboratory of Computer Architecture (ICT, CAS) (ID: CARCHA202002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Mingyong Han.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• retrospective
• diagnostic or prognostic study
• performed at one institution
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 246 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Wang, B., Wang, Z. et al. Radiomics signature of brain metastasis: prediction of EGFR mutation status. Eur Radiol 31, 4538–4547 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07614-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07614-x