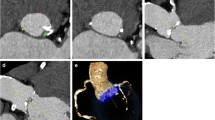
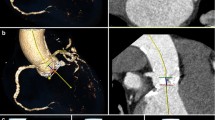
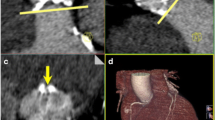
Abstract
Objectives
To compare image quality and radiation dose of pre-transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) aortoiliofemoral CT angiography (AICTA) provided by standard vs. dual-energy mode with reduced iodine load protocols.
Methods
One hundred and sixty-one patients underwent a two-step CTA protocol before TAVI including cardiac CTA with injection of 65 mL of iodinated contrast agent (ICA), immediately followed by AICTA. From this second acquisition, the following three different patient groups were identified: Group 1: 52 patients with standard AICTA (60 mL ICA, 100 kVp, mA automodulation); Group 2: 48 patients with dual-energy AICTA with 50 % iodine load reduction (30 mL ICA, fast kVp switching, 600 mA); Group 3: 61 patients with an identical protocol to Group 2, but exposed to 375 mA. The qualitative/subjective image quality (13-point score) and quantitative/objective image quality (contrast attenuation and image noise) were evaluated. The radiation dose was recorded.
Results
There was no significant difference in non-diagnostic images between the three protocols. Contrast attenuation, signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio were significantly higher, whereas noise was significantly lower in the standard protocol (all P < 0.05). The radiation dose was lower in the dual-energy protocol at 375 mA (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Dual-energy AICTA before TAVI results in a reduction of iodine load while maintaining sufficient diagnostic information despite increased noise.
Key Points
• Dual-energy AICTA before TAVI results in a 50 % reduction of iodine load.
•The reduction of iodine load maintains sufficient image quality despite increased noise.
• Using 375 mA in dual-energy mode results in a reduction of radiation dose.
• A high tube current setting (600 mA) should be used in overweight patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AICTA:
-
Aortoiliofemoral CT angiography.
- BMI:
-
Body Mass Index.
- CA:
-
Contrast Attenuation.
- CNR:
-
Contrast to Noise Ratio.
- CTA:
-
CT Angiography
- CTDIvol :
-
CT Dose Index.
- DLP:
-
Dose Length Product.
- ICA:
-
Iodinated Contrast Agent.
- keV:
-
Kiloelectron Volts.
- kVp:
-
Kilovolt Peak.
- PACS:
-
Picture Archiving and Communication system.
- SNR:
-
Signal to Noise Ratio.
- TAVI:
-
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation.
References
Iung B, Baron G, Butchart EG et al (2003) A prospective survey of patients with valvular heart disease in Europe: The Euro Heart Survey on Valvular Heart Disease. Eur Heart J 24:1231–1243
Cribier A, Eltchaninoff H, Bash A et al (2002) Percutaneous transcatheter implantation of an aortic valve prosthesis for calcific aortic stenosis: first human case description. Circulation 106:3006–3008
Cribier A, Eltchaninoff H, Tron C et al (2006) Treatment of calcific aortic stenosis with the percutaneous heart valve: mid-term follow-up from the initial feasibility studies: the French experience. J Am Coll Cardiol 47:1214–1223
Gilard M, Eltchaninoff H, Iung B et al (2012) Registry of transcatheter aortic-valve implantation in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med 366:1705–1715
Iung B, Baron G, Tornos P, Gohlke-Bärwolf C, Butchart EG, Vahanian A (2007) Valvular heart disease in the community: a European experience. Curr Probl Cardiol 32:609–661
Leipsic J, Gurvitch R, Labounty TM et al (2011) Multidetector computed tomography in transcatheter aortic valve implantation. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 4:416–429
Tops LF, Wood DA, Delgado V et al (2008) Noninvasive evaluation of the aortic root with multislice computed tomography implications for transcatheter aortic valve replacement. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 1:321–330
Wood DA, Tops LF, Mayo JR et al (2009) Role of multislice computed tomography in transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Am J Cardiol 103:1295–1301
Holmes DR, Mack MJ, Kaul S et al (2012) 2012 ACCF/AATS/SCAI/STS Expert Consensus Document on Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J Am Coll Cardiol 59:1200–1254
Achenbach S, Delgado V, Hausleiter J, Schoenhagen P, Min JK, Leipsic JA (2012) SCCT expert consensus document on computed tomography imaging before transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI)/transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 6:366–380
Holmes DR Jr, Mack MJ (2011) Transcatheter valve therapy: a professional society overview from the American College of Cardiology Foundation and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Ann Thorac Surg 92:380–389
American College of Radiology Manual on Contrast Media Version 9. Available from: http://www.acr.org/~/media/ACR/Documents/PDF/QualitySafety/Resources/Contrast%20Manual/2013_Contrast_Media.pdf. Published 2013
Thomsen HS (2007) European Society of Urogenital Radiology guidelines on contrast media application. Curr Opin Urol 17:70–76
Coursey CA, Nelson RC, Boll DT et al (2010) Dual-Energy Multidetector CT: How Does It Work, What Can It Tell Us, and When Can We Use It in Abdominopelvic Imaging? Radiographics 30:1037–1055
Kalva SP, Sahani DV, Hahn PF, Saini S (2006) Using the K-edge to improve contrast conspicuity and to lower radiation dose with a 16-MDCT: a phantom and human study. J Comput Assist Tomogr 30:391–397
Yuan R, Shuman WP, Earls JP et al (2012) Reduced iodine load at CT pulmonary angiography with dual-energy monochromatic imaging: comparison with standard CT pulmonary angiography–a prospective randomized trial. Radiology 262:290–297
Delesalle M-A, Pontana F, Duhamel A et al (2013) Spectral Optimization of Chest CT Angiography with Reduced Iodine Load: Experience in 80 Patients Evaluated with Dual-Source, Dual-Energy CT. Radiology 267:256–266
The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. Available from http://nuclear.com/archive/2012/12/04/ML12338A682.pdf
Authors on behalf of the ICRP, Cousins C, Miller DL, Bernardi G et al (2013) ICRP PUBLICATION 120: Radiological Protection in Cardiology. Ann ICRP 42:1–125
Singh S, Kalra MK, Gilman MD et al (2011) Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique for radiation dose reduction in chest CT: a pilot study. Radiology 259:565–573
Loewe C, Becker CR, Berletti R et al (2010) 64-Slice CT angiography of the abdominal aorta and abdominal arteries: comparison of the diagnostic efficacy of iobitridol 350 mgI/ml versus iomeprol 400 mgI/ml in a prospective, randomized, double-blind multi-center trial. Eur Radiol 20:572–583
Lehmann EL, D'Abrera HJ (1975) Nonparametrics: Statistical methods based on ranks. Holden-Day, Oxford
Bruce RJ, Djamali A, Shinki K, Michel SJ, Fine JP, Pozniak MA (2009) Background fluctuation of kidney function versus contrast-induced nephrotoxicity. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192:711–718
Mack MJ, Brennan JM, Brindis R et al (2013) Outcomes following transcatheter aortic valve replacement in the United States. JAMA J Am Med Assoc 310:2069–2077
Bagur R, Webb JG, Nietlispach F et al (2009) Acute kidney injury following transcatheter aortic valve implantation: predictive factors, prognostic value, and comparison with surgical aortic valve replacement. Eur Heart J 31:865–874
Tang K, Wang L, Li R, Lin J, Zheng X, Cao G (2012) Effect of low tube voltage on image quality, radiation dose, and low-contrast detectability at abdominal multidetector CT: phantom study. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:130–169
Sigal-Cinqualbre AB, Hennequin R, Abada HT, Chen X, Paul J-F (2004) Low-Kilovoltage Multi-Detector Row Chest CT in Adults: Feasibility and Effect on Image Quality and Iodine Dose. Radiology 231:169–174
Nakaura T, Awai K, Oda S et al (2011) Low-kilovoltage, high-tube-current MDCT of liver in thin adults: pilot study evaluating radiation dose, image quality, and display settings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:1332–1338
Matsumoto K, Jinzaki M, Tanami Y, Ueno A, Yamada M, Kuribayashi S (2011) Virtual monochromatic spectral imaging with fast kilovoltage switching: improved image quality as compared with that obtained with conventional 120-kVp CT. Radiology 259:257–262
Wuest W, Anders K, Schuhbaeck A et al (2012) Dual source multidetector CT-angiography before Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) using a high-pitch spiral acquisition mode. Eur Radiol 22:51–58
Plank F, Friedrich G, Bartel T et al (2012) Benefits of high-pitch 128-slice dual-source computed tomography for planning of transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Ann Thorac Surg 94:1961–1966
Joshi SB, Mendoza DD, Steinberg DH et al (2009) Ultra-low-dose intra-arterial contrast injection for iliofemoral computed tomographic angiography. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2:1404–1411
Nietlispach F, Leipsic J, Al-Bugami S, Masson J-B, Carere RG, Webb JG (2009) CT of the ilio-femoral arteries using direct aortic contrast injection: proof of feasibility in patients screened towards percutaneous aortic valve replacement. Swiss Med Wkly 139:458
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Annick Troniou for her invaluable assistance.
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Pr. Jean-Nicolas Dacher, MD, PhD. The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies: Pr. Jean-Nicolas Dacher is consultant for GE HealthCare. No other conflict of interest is to disclose. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. Dr. Michael Bubenheim kindly provided statistical advice for this manuscript. One of the authors (Michael Bubenheim) has significant statistical expertise. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board. Methodology: retrospective, diagnostic or prognostic study.
This work was presented at the Annual Meeting of the European Society of Cardiac Radiology in London (October 2013). It has been selected for presentation within the EPOS highlighted poster presentations session and has received a Certificate of Merit Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubourg, B., Caudron, J., Lestrat, JP. et al. Single-source dual-energy CT angiography with reduced iodine load in patients referred for aortoiliofemoral evaluation before transcatheter aortic valve implantation: impact on image quality and radiation dose. Eur Radiol 24, 2659–2668 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3263-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3263-1