Abstract
Objectives
To introduce a novel percutaneous technique to stop blood entry at the lesser aortic arch curvature by coil embolisation in type Ia endoleak after TEVAR.
Methods
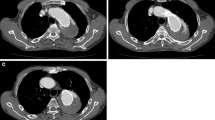
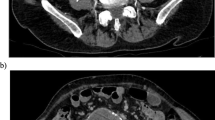
A 61-year-old Marfan patient presented with type Ia endoleak of the aortic arch and a growing aortic arch pseudoaneurysm after TEVAR. Multiple preceding operations and interventions made an endovascular approach unsuccessful. Direct percutaneous puncture of the aneurysmal sac would have cured the sign, but not the cause of blood entry at the lesser curvature of the aortic arch. Direct CT-guided percutaneous puncture of the blood entry site in the aortic arch with fluoroscopically guided coil embolisation using detachable extra-long coils was successfully performed.
Results
Three weeks after the intervention, the patient developed fever because of superinfection of the pseudoaneurysm. The blood cultures and CT-guided mediastinal aspirate were sterile. After intravenous administration of antibiotics, the fever disappeared and the patient recovered. Six-month follow-up showed permanent closure of the endoleak and a shrinking aneurysmal sac.
Conclusions
Direct percutaneous puncture of the aortic arch at the blood entry site of a thoracic type Ia endoleak after TEVAR and double-chimney stent-grafts with coil embolisation of the wedge-shaped space between the lesser aortic curvature and the stent-graft is possible.
Key Points
• Endoleaks after thoracic endovascular aortic repair are common in 15-30 %.
• Most endoleaks can be treated by endovascular means.
• Direct percutaneous endoleak repair is described as a bail-out option.
• Direct percutaneous aortic arch coil embolisation of type 1a endoleak is possible.
• Antibiotic prophylaxis should be administered case by case, considering individual risk factors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Girdauskas E, Kuntze T, Borger MA, Falk V, Mohr FW (2008) Distal aortic reinterventions after root surgery in Marfan patients. Ann Thorac Surg 86:1815–1819
Waterman AL, Feezor RJ, Lee WA et al (2012) Endovascular treatment of acute and chronic aortic pathology in patients with Marfan syndrome. J Vasc Surg 55:1234–1240
Parmer SS, Carpenter JP, Stavropoulos SW et al (2006) Endoleaks after endovascular repair of thoracic aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 44:447–452
Preventza O, Wheatley GH 3rd, Ramaiah VG et al (2008) Management of endoleaks associated with endovascular treatment of descending thoracic aortic diseases. J Vasc Surg 48:69–73
Day CP, Buckenham TM, Laing AD (2011) Embolization of proximal type 1 endoleak using N-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate after endovascular repair of the thoracic aorta: two case reports. J Vasc Interv Radiol 22:105–107
Bangard C, Gawenda M, Lackner K (2008) Transarterial occlusion of type 1 endoleak of the aortic arch by coil embolization and thrombin injection after endovascular therapy of retrograde Stanford A dissection. RöFo 180:926–928
Katada Y, Kondo S, Takahashi S et al (2013) Direct percutaneous puncture embolization of type II endoleaks using a coaxial technique. J Endovasc Ther 20:34–38
Krueger K, Zaehringer M, Gawenda M, Brunkwall J, Lackner K (2003) Successful treatment of a type-II endoleak with percutaneous CT-guided thrombin injection in a patient after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Eur Radiol 13:1748–1749
Uthoff H, Katzen BT, Gandhi R, Peña CS, Benenati JF, Geisbüsch P (2012) Direct percutaneous sac injection for postoperative endoleak treatment after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 56:965–972
Riesenman PJ, Farber MA, Mauro MA, Selzman CH, Feins RH (2007) Aortoesophageal fistula after thoracic endovascular aortic repair and transthoracic embolization. J Vasc Surg 46:789–791
Venkatesan AM, Kundu S, Sacks D et al (2010) Practice guidelines for adult antibiotic prophylaxis during vascular and interventional radiology procedures. Written by the Standards of Practice Committee for the Society of Interventional Radiology and Endorsed by the Cardiovascular Interventional Radiological Society of Europe and Canadian Interventional Radiology Association [corrected]. J Vasc Interv Radiol 21:1611–1630
Acknowledgments
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Christopher Bangard. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. No complex statistical methods were necessary for this article. Institutional Review Board approval was not required because retrospective data are presented. Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board. Methodology: retrospective, observational, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bangard, C., Franke, M., Pfister, R. et al. Thoracic type Ia endoleak: direct percutaneous coil embolization of the aortic arch at the blood entry site after TEVAR and double-chimney stent-grafts. Eur Radiol 24, 1430–1434 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3143-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3143-8