Abstract
Objective:
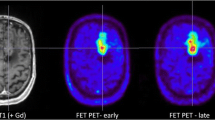
The management of non-contrast-enhancing brain tumours largely depends on biopsy, which allows a differentiation of low-grade gliomas (LGG) from high-grade gliomas (HGG). The aim of this study was to compare positron emission tomography using 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose (FDG-PET) and O-(2-[18F]-fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine (FET-PET) in terms of providing target regions for biopsies.
Materials and methods:
Fifteen consecutive patients with newly diagnosed brain tumours (n = 11) or suspected recurrence of a known LGG (n = 4), in whom MRI demonstrated no contrast enhancement, were studied by both FET-PET and FDG-PET. FET-PET, FDG-PET and MRI data were fused, and then transferred to the neurosurgical navigation system, prior to neurosurgical interventions.
Results:
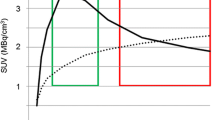
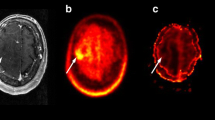
Histology showed HGG (WHO grade III) in 6/15 and LGG (WHO grade II) in 9/15 patients. FET-PET revealed an increased intratumoural tracer uptake in 8/9 LGG and in 5/6 HGG. FDG-PET depicted hypermetabolic spots in 2/9 LGG and in 4/6 HGG. In 6 patients we observed an increased intratumoural uptake of both tracers. In 4 of them, the area of highest FET accumulation in the tumour corresponded to the focus of increased FDG uptake.
Conclusions:
FET-PET appears to be superior to FDG-PET for biopsy planning in non-contrast-enhancing brain tumours. FDG-PET does not provide any additional information in this issue.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glantz MJ, Burger PC, Herndon JE, Friedman AH, Cairncross JG, Vick NA, Schold SC Jr (1991) Influence of the type of surgery on the histologic diagnosis in patients with anaplastic gliomas. Neurology 41:1741–1744
Brucher JM (1993) Neuropathological diagnosis with stereotactic biopsies. Possibilities, difficulties and requirements. Acta Neurochir 124:37–39
DeAngelis LM (2001) Brain tumors. N Engl J Med 344:114–123
Watanabe M, Tanaka R, Takeda N (1992) Magnetic resonance imaging and histopathology of cerebral gliomas. Neuroradiology 34:463–469
Byrne TN (1994) Imaging of gliomas. Semin Oncol 21:162–171
Ginsberg LE, Fuller GN, Hashmi M, Leeds NE, Schomer DF (1998) The significance of lack of MR contrast enhancement of supratentorial brain tumors in adults: histopathological evaluation of a series. Surg Neurol 49:436–440
Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Martinez AJ (1993) Unreliability of contemporary neurodiagnostic imaging in evaluating suspected adult supratentorial (low-grade) astrocytoma. J Neurosurg 79:533–536
Barker FG 2nd, Chang SM, Huhn SL, Davis RL, Gutin PH, McDermott MW, Wilson CB, Prados MD (1997) Age and the risk of anaplasia in magnetic resonance-nonenhancing supratentorial cerebral tumors. Cancer 80:936–941
Scott JN, Brasher PM, Sevick RJ, Rewcastle NB, Forsyth PA (2002) How often are nonenhancing supratentorial gliomas malignant? A population study. Neurology 59:947–949
Francavilla TL, Miletich RS, Di Chiro G, Patronas NJ, Rizzoli HV, Wright DC (1989) Positron emission tomography in the detection of malignant degeneration of low-grade gliomas. Neurosurgery 24:1–5
Goldman S, Levivier M, Pirotte B, Brucher JM, Wikler D, Damhaut P, Stanus E, Brotchi J, Hildebrand J (1996) Regional glucose metabolism and histopathology of gliomas. A study based on positron emission tomography-guided stereotactic biopsy. Cancer 78:1098–1106
Herholz K, Pietrzyk U, Voges J, Schroder R, Halber M, Treuer H, Sturm V, Heiss WD (1993) Correlation of glucose consumption and tumor cell density in astrocytomas. A stereotactic PET study. J Neurosurg 79:853–858
Wong TZ, van der Westhuizen GJ, Coleman RE (2002) Positron emission tomography imaging of brain tumors. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 12:615–626
Chung JK, Kim YK, Kim SK, Lee YJ, Paek S, Yeo JS, Jeong JM, Lee DS, Jung HW, Lee MC (2002) Usefulness of 11C-methionine PET in the evaluation of brain lesions that are hypo- or isometabolic on 18F-FDG-PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 29:176–182
Delbeke D, Meyerowitz C, Lapidus RL, Maciunas RJ, Jennings MT, Moots PL, Kessler RM (1995) Optimal cutoff levels of F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the differentiation of low-grade from high-grade brain tumors with PET. Radiology 195:47–52
Spence AM, Muzi M, Mankoff DA, O'Sullivan SF, Link JM, Lewellen TK, Lewellen B, Pham P, Minoshima S, Swanson K, Krohn KA (2004) 18F-FDG PET of gliomas at delayed intervals: improved distinction between tumor and normal gray matter. J Nucl Med 45:1653–1659
Ishizu K, Nishizawa S, Yonekura Y, Sadato N, Magata Y, Tamaki N, Tsuchida T, Okazawa H, Miyatake S, Ishikawa M et al (1994) Effects of hyperglycemia on FDG uptake in human brain and glioma. J Nucl Med 35:1104–1109
Stockhammer F, Thomale UW, Plotkin M, Hartmann C, von Deimling A (2007) 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake is associated with 1p and 19q loss in WHO grade II gliomas. J Neurosurg 106:633–637
Levivier M, Massager N, Wikler D, Lorenzoni J, Ruiz S, Devriendt D, David P, Desmedt F, Simon S, Van Houtte P, Brotchi J, Goldman S (2004) Use of stereotactic PET images in dosimetry planning of radiosurgery for brain tumors: clinical experience and proposed classification. J Nucl Med 45:1146–1154
Pirotte B, Goldman S, Massager N, David P, Wikler D, Lipszyc M, Salmon I, Brotchi J, Levivier M (2004) Combined use of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose and 11C-methionine in 45 positron emission tomography-guided stereotactic brain biopsies. J Neurosurg 101:476–483
Goldman S, Levivier M, Pirotte B, Brucher JM, Wikler D, Damhaut P, Dethy S, Brotchi J, Hildebrand J (1997) Regional methionine and glucose uptake in high-grade gliomas: a comparative study on PET-guided stereotactic biopsy. J Nucl Med 38:1459–1462
Pirotte B, Goldman S, Massager N, David P, Wikler D, Vandesteene A, Salmon I, Brotchi J, Levivier M (2004) Comparison of 18F-FDG and 11C-methionine for PET-guided stereotactic brain biopsy of gliomas. J Nucl Med 45:1293–1298
Pauleit D, Floeth F, Hamacher K, Riemenschneider MJ, Reifenberger G, Müller HW, Zilles K, Coenen HH, Langen KJ (2005) O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET combined with MRI improves the diagnostic assessment of cerebral gliomas. Brain 128:678–687
Langen KJ, Hamacher K, Weckesser M, Floeth F, Stoffels G, Bauer D, Coenen HH, Pauleit D (2006) O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine: uptake mechanisms and clinical applications. Nucl Med Biol 33:287–294
Weber W, Wester HJ, Grosu AL, Herz M, Dzewas B, Feldmann HJ, Molls M, Stocklin G, Schwaiger M (2000) O-(2-[18F] fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine and L-[methyl-11C] methionine uptake in brain tumours: Initial results of a comparative study. Eur J Nucl Med 27:542–549
Pauleit D, Stoffels G, Bachofner A, Floeth FW, Sabel M, Herzog H, Tellmann L, Jansen P, Reifenberger G, Hamacher K, Coenen HH, Langen KJ (2009) Comparison of (18)F-FET and (18)F-FDG PET in brain tumors. Nucl Med Biol 36:779–787
Bjartmarz H, Rehncrona S (2007) Comparison of accuracy and precision between frame- based and frameless stereotactic navigation for deep brain stimulation electrode implantation. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 85:235–242
McGirt MJ, Villavicencio AT, Bulsara KR, Friedman AH (2003) MRI-guided stereotactic biopsy in the diagnosis of glioma: comparison of biopsy and surgical resection specimen. Surgical neurology 59:277–281, discussion 281-282
Kim JE, Kim DG, Paek SH, Jung HW (2003) Stereotactic biopsy for intracranial lesions: reliability and its impact on the planning of treatment. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145:547–554, discussion 554-555
Muacevic A, Uhl E, Steiger HJ, Reulen HJ (2000) Accuracy and clinical applicability of a passive marker based frameless neuronavigation system. J Clin Neurosci 7:414–418
Messing-Junger AM, Floeth FW, Pauleit D, Reifenberger G, Willing R, Gärtner J, Coenen HH, Langen KJ (2002) Multimodal target point assessment for stereotactic biopsy in children with diffuse bithalamic astrocytomas. Childs Nerv Syst 18:445–449
Floeth FW, Pauleit D, Sabel M, Stoffels G, Reifenberger G, Riemenschneider MJ, Jansen P, Coenen HH, Steiger HJ, Langen KJ (2007) Prognostic value of O-(2-18Ffluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET and MRI in low-grade glioma. J Nucl Med 48:519–527
Roessler K, Gatterbauer B, Becherer A, Paul M, Kletter K, Prayer D, Hoeftberger R, Hainfellner J, Asenbaum S, Knosp E (2007) Surgical target selection in cerebral glioma surgery: linking methionine (MET) PET image fusion and neuronavigation. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 50:273–280
Stöber B, Tanase U, Herz M, Seidl C, Schwaiger M, Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R (2006) Differentiation of tumour and inflammation: characterisation of [methyl-3H]methionine (MET) and O-(2-[18F] fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine (FET) uptake in human tumour and inflammatory cells. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 33:932–939
Stockhammer F, Plotkin M, Amthauer H, van Landeghem FK, Woiciechowsky C (2008) Correlation of F-18-fluoro-ethyl-tyrosin uptake with vascular and cell density in non-contrast-enhancing gliomas. J Neuro Oncol 88:205–210
Hara T, Kondo T, Hara T, Kosaka N (2003) Use of 18F-choline and 11C-choline as contrast agents in positron emission tomography imaging-guided stereotactic biopsy sampling of gliomas. J Neurosurg 99:474–479
Chen W, Silverman DH, Delaloye S, Czernin J, Kamdar N, Pope W, Satyamurthy N, Schiepers C, Cloughesy T (2006) 18F-FDOPA PET imaging of brain tumors: comparison study with 18F-FDG PET and evaluation of diagnostic accuracy. J Nucl Med 47:904–911
Beuthien-Baumann B, Bredow J, Burchert W, Füchtner F, Bergmann R, Alheit HD, Reiss G, Hliscs R, Steinmeier R, Franke WG, Johannsen B, Kotzerke J (2003) 3-O-methyl-6-[18F]fluoro-L-DOPA and its evaluation in brain tumour imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30:1004–1008
Langen KJ, Jarosch M, Hamacher K, Mühlensiepen H, Weber F, Floeth F, Pauleit D, Herzog H, Coenen HH (2004) Imaging of gliomas with cis-4-[18F]fluoro-L-proline. Nucl Med Biol 31:67–75
Jacobs AH, Thomas A, Kracht LW, Li H, Dittmar C, Garlip G, Galldiks N, Klein JC, Sobesky J, Hilker R, Vollmar S, Herholz K, Wienhard K, Heiss WD (2005) 18F-fluoro-L-thymidine and 11C-methylmethionine as markers of increased transport and proliferation in brain tumors. J Nucl Med 46:1948–1958
Valk PE, Mathis CA, Prados MD, Gilbert JC, Budinger TF (1992) Hypoxia in human gliomas: demonstration by PET with fluorine-18-fluoromisonidazole. J Nucl Med 33:2133–2137
Hemm S, Rigau V, Chevalier J, Picot MC, Bauchet L, El Fertit H, Rodriguez MA, Cif L, Vayssière N, Zanca M, Baldet P, Segnarbieux F, Coubes P (2005) Stereotactic coregistration of 201Tl SPECT and MRI applied to brain tumor biopsies. J Nucl Med 46:1151–1157
del Valle M, Torres MD, Gómez Rio M, Rodríguez Fernández A, Sabatel Hernandez G, Ortega Lozano S, Ramos Font C, Bellon Guardia M, López Ramírez E, Llamas Elvira JM (2004) Value of thallium 201-SPECT in typing brain space-occupying lesions. Rev Esp Med Nucl 23:330–337
Källén K, Heiling M, Andersson AM, Brun A, Holtås S, Ryding E, Rosén I (1997) Evaluation of malignancy in ring enhancing brain lesions on CT by thallium-201 SPECT. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63:569–574
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plotkin, M., Blechschmidt, C., Auf, G. et al. Comparison of F-18 FET-PET with F-18 FDG-PET for biopsy planning of non-contrast-enhancing gliomas. Eur Radiol 20, 2496–2502 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1819-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1819-2