Abstract
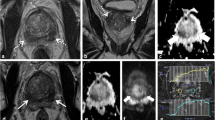
The purpose of the study was to relate morphometric features of prostate cancers in the anterior compartment of the prostate by dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI to subsequent histopathologic findings. We prospectively performed DCE-MRI before biopsy in patients with suspected prostate cancer and selected those showing both a suspicious lesion at MRI and positive biopsies in the anterior compartment of the gland. Tumor contours, margins, largest surface areas and volumes were assessed at MRI and histopathology, when available. Anterior compartment tumors were classified according to transition zone (TZ) boundaries with the peripheral zone (PZ) or with the anterior fibromuscular stroma (SFMA). Forty-three patients were included in this study [median PSA 12.7 ng/ml (3.6–72)]. Whole-mount radical prostatectomy specimens were available in 27 cases. Of the anterior cancers, 89% had ill-defined margins at T2-weighted MRI. Cancer location and contour established at MRI agreed well with histopathology in the 27 cases. Median largest surface area and volume were 1.38 cm² (0.35–5.82) and 1.01 cc (0.15–7.4) for MRI versus 1.86 cm² (0.2–14) and 2.84 cc (0.33–28.92) for histopathology with respective correlation coefficients (r²) of 0.73 and 0.69. The site of origin could be accurately determined for the 15 tumors of less than 3 cc. We found a good relationship between DCE-MRI and histopathology for localization, morphologic description and volume assessment of anterior prostate cancers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Namimoto T, Morishita S, Saitoh R, Kudoh J, Yamashita Y, Takahashi M (1998) The value of dynamic MR imaging for hypointensity lesions of the peripheral zone of the prostate. Comput Med Imaging Graph 22(3):239–245
Cruz M, Tsuda K, Narumi Y, Kuroiwa Y, Nose T, Kojima Y et al (2002) Characterization of low-intensity lesions in the peripheral zone of prostate on pre-biopsy endorectal coil MR imaging. Eur Radiol 12(2):357–365
Zakian KL, Eberhardt S, Hricak H, Shukla-Dave A, Kleinman S, Muruganandham M et al (2003) Transition zone prostate cancer: metabolic characteristics at 1H MR spectroscopic imaging-initial results. Radiology 229(1):241–247
van Dorsten FA, van der Graaf M, Engelbrecht MR, van Leenders GJ, Verhofstad A, Rijpkema M et al (2004) Combined quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging and (1)H MR spectroscopic imaging of human prostate cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging 20(2):279–287
Futterer JJ, Heijmink SW, Scheenen TW, Veltman J, Huisman HJ, Vos P et al (2006) Prostate cancer localization with dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 241(2):449–458
Sato C, Naganawa S, Nakamura T, Kumada H, Miura S, Takizawa O et al (2005) Differentiation of noncancerous tissue and cancer lesions by apparent diffusion coefficient values in transition and peripheral zones of the prostate. J Magn Reson Imaging 21(3):258–262
Villers A, Puech P, Mouton D, Leroy X, Ballereau C, Lemaitre L (2006) Dynamic contrast enhanced, pelvic phased array magnetic resonance imaging of localized prostate cancer for predicting tumor volume: correlation with radical prostatectomy findings. J Urol 176(6 Pt 1):2432–2437
McNeal JE, Redwine EA, Freiha FS, Stamey TA (1988) Zonal distribution of prostatic adenocarcinoma. Correlation with histologic pattern and direction of spread. Am J Surg Pathol 12(12):897–906
Turnbull LW, Buckley DL, Turnbull LS, Liney GP, Knowles AJ (1999) Differentiation of prostatic carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia: correlation between dynamic Gd-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging and histopathology. J Magn Reson Imaging 9(2):311–316
Muramoto S, Uematsu H, Kimura H, Ishimori Y, Sadato N, Oyama N et al (2002) Differentiation of prostate cancer from benign prostate hypertrophy using dual-echo dynamic contrast MR imaging. Eur J Radiol 44(1):52–58
Engelbrecht MR, Huisman HJ, Laheij RJ, Jager GJ, van Leenders GJ, Hulsbergen-Van De Kaa CA et al (2003) Discrimination of prostate cancer from normal peripheral zone and central gland tissue by using dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 229(1):248–254
Li H, Sugimura K, Kaji Y, Kitamura Y, Fujii M, Hara I et al (2006) Conventional MRI capabilities in the diagnosis of prostate cancer in the transition zone. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186(3):729–742
Akin O, Sala E, Moskowitz CS, Kuroiwa K, Ishill NM, Pucar D et al (2006) Transition zone prostate cancers: features, detection, localization, and staging at endorectal MR imaging. Radiology. 239(3):784–792
Puech P, Betrouni N, Viard R, Villers A, Leroy X, Lemaitre L.(2007) Prostate cancer computer-assisted diagnosis software using dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE; 2007; p. 5567–5570.
Preziosi P, Orlacchio A, Di Giambattista G, Di Renzi P, Bortolotti L, Fabiano A et al (2003) Enhancement patterns of prostate cancer in dynamic MRI. Eur Radiol. 13(5):925–930
Stamey TA, Donaldson AN, Yemoto CE, McNeal JE, Sozen S, Gill H (1998) Histological and clinical findings in 896 consecutive prostates treated only with radical retropubic prostatectomy: epidemiologic significance of annual changes. J Urol 160(6 Pt 2):2412–2417
Stamey TA, Yemoto CM, McNeal JE, Sigal BM, Johnstone IM (2000) Prostate cancer is highly predictable: a prognostic equation based on all morphological variables in radical prostatectomy specimens. J Urol 163(4):1155–1160
Stamey TA, McNeal JE, Freiha FS, Redwine E (1988) Morphometric and clinical studies on 68 consecutive radical prostatectomies. J Urol 139(6):1235–1241
Augustin H, Erbersdobler A, Graefen M, Jaekel T, Haese A, Huland H et al (2003) Differences in biopsy features between prostate cancers located in the transition and peripheral zone. BJU Int 91(6):477–481
McNeal JE, Haillot O (2001) Patterns of spread of adenocarcinoma in the prostate as related to cancer volume. Prostate 49(1):48–57
Futterer JJ, Engelbrecht MR, Jager GJ, Hartman RP, King BF, Hulsbergen-Van de Kaa CA et al (2007) Prostate cancer: comparison of local staging accuracy of pelvic phased-array coil alone versus integrated endorectal-pelvic phased-array coils: Local staging accuracy of prostate cancer using endorectal coil MR imaging. Eur Radiol 17(4):1055–1065 Epub 2006 Oct 6
Haider MA, van der Kwast TH, Tanguay J, Evans AJ, Hashmi AT, Lockwood G et al (2007) Combined T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted MRI for localization of prostate cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189(2):323–328
Husband JE, Padhani AR, MacVicar AD, Revell P (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging of prostate cancer: comparison of image quality using endorectal and pelvic phased array coils. Clin Radiol 53(9):673–681
Sosna J, Pedrosa I, Dewolf WC, Mahallati H, Lenkinski RE, Rofsky NM (2004) MR imaging of the prostate at 3 Tesla: comparison of an external phased-array coil to imaging with an endorectal coil at 1.5 Tesla. Acad Radiol 11(8):857–862
Heijmink SW, Futterer JJ, Hambrock T, Takahashi S, Scheenen TW, Huisman HJ et al (2007) Prostate cancer: Body-array versus endorectal coil MR imaging at 3 T — Comparison of image quality, localization, and staging performance. Radiology 244(1):184–195 Epub 2007 May 10
Kirkham AP, Emberton M, Hoh IM, Illing RO, Freeman AA, Allen C (2008) MR imaging of prostate after treatment with high-intensity focused ultrasound. Radiology 246(3):833–844 Epub 2008 Jan 25
Villers A, Puech P, Leroy X, Biserte J, Fantoni JC, Lemaitre L (2007) Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for preoperative identification of localised prostate cancer. Eur Urol [Suppl] 6:525–532
Tiguert R, Kabbani W, Sakr W, Gheiler EL, Pontes JE (1999) Origin and racial distribution of glandular tissue in the anterior compartment of the prostate: an autopsy study. Prostate 39(4):310–315
McNeal JE (1997) Prostate cancer volume. Am J Surg Pathol 21(11):1392–1393
Kabalin JN, McNeal JE, Price HM, Freiha FS, Stamey TA (1989) Unsuspected adenocarcinoma of the prostate in patients undergoing cystoprostatectomy for other causes: incidence, histology and morphometric observations. J Urol 141(5):1091–1094 discussion 3–4
Kirkham AP, Emberton M, Allen C (2006) How good is MRI at detecting and characterising cancer within the prostate? Eur Urol 50(6):1163–1175
Quint LE, Van Erp JS, Bland PH, Mandell SH, Del Buono EA, Grossman HB et al (1991) Carcinoma of the prostate: MR images obtained with body coils do not accurately reflect tumor volume. AJR Am J Roentgenol 156(3):511–516
Nakashima J, Tanimoto A, Imai Y, Mukai M, Horiguchi Y, Nakagawa K et al (2004) Endorectal MRI for prediction of tumor site, tumor size, and local extension of prostate cancer. Urology 64(1):101–105
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from ARTP (Association de Recherche sur les Tumeurs de la Prostate).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lemaitre, L., Puech, P., Poncelet, E. et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of anterior prostate cancer: morphometric assessment and correlation with radical prostatectomy findings. Eur Radiol 19, 470–480 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-1153-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-1153-0