Abstract
Key message
Drastic changes in soil water content can activate the short-term high expression of key enzyme-encoding genes involved in secondary metabolite synthesis thereby increasing the content of secondary metabolites.
Abstract
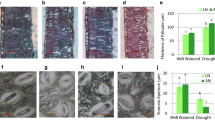
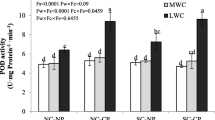
Bupleurum chinense DC. is a traditional medicinal herb that is famous for its abundant saikosaponins. In the current study, the effects of drought–re-watering–drought on the photosynthesis physiology and biosynthesis of saikosaponins were investigated in 1-year-old B. chinense. The results showed that alterations in soil moisture altered the photosynthesis physiological process of B. chinense. The dry weight and fresh weight of the roots, photosynthesis capacity, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, and SOD, POD and CAT activities were significantly reduced, and the contents of SP, soluble sugars, PRO and MDA increased. There were strong correlations between different physiological stress indices. All indices promoted and restricted each other, responded to soil moisture changes synergistically, maintained plant homeostasis and guaranteed normal biological activities. It was found that RW and RD_1 were the key stages of the water-control experiment affecting the expression of saikosaponin-related genes. At these two stages, the expression of multiple genes was affected by changes in soil moisture, with their expression levels reaching several-fold higher than those at the previous stage. We noticed that the expression of saikosaponin synthesis genes (which were rapidly upregulated at the RW and RD_1 stages) did not coincide with the rapid accumulation of saikosaponins (at the RD-2 stage), which were found to correspond to each other at the later stages of the water-control experiment. This finding indicates that there is a time lag between gene expression and the final product synthesis. Rapid changes in the external environment (RW to RD_1) have a short-term promoting effect on gene expression. This study reveals that short-term stress regulation may be an effective way to improve the quality of medicinal materials.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batlang U, Baisakh N, Ambavaram MM, Pereira A (2013) Phenotypic and physiological evaluation for drought and salinity stress responses in rice. Methods Mol Biol 956:209–225
Bhargava S, Sawant K, Tuberosa R (2013) Drought stress adaptation: metabolic adjustment and regulation of gene expression. Plant Breed 132:21–32
Blokhina O, Virolainen E, Fagerstedt KV (2003) Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: a review. Ann Bot 91(Spec No):179–194
Blum A (2017) Osmotic adjustment is a prime drought stress adaptive engine in support of plant production. Plant Cell Environ 40:4–10
Buschmann C (2007) Variability and application of the chlorophyll fluorescence emission ratio red/far-red of leaves. Photosynth Res 92:261–271
Centritto M, Brilli F, Fodale R, Loreto F (2011) Different sensitivity of isoprene emission, respiration and photosynthesis to high growth temperature coupled with drought stress in black poplar (Populus nigra) saplings. Tree Physiol 31:275–286
Chaves MM, Flexas J, Pinheiro C (2009) Photosynthesis under drought and salt stress: regulation mechanisms from whole plant to cell. Ann Bot 103:551–560
Cheng L, Han M, L-m Yang, Li Y, Sun Z, Zhang T (2018) Changes in the physiological characteristics and baicalin biosynthesis metabolism of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi under drought stress. Ind Crops Prod 122:473–482
Deak KI, Malamy J (2005) Osmotic regulation of root system architecture. Plant J 43:17–28
Deans RM, Brodribb TJ, Busch FA, Farquhar GD (2019) Plant water-use strategy mediates stomatal effects on the light induction of photosynthesis. New Phytol 222:382–395
Dubey VS, Bhalla R, Luthra R (2003) An overview of the non-mevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis in plants. J Biosci 28:637–646
Ge Y, He X, Wang J, Jiang B, Ye R, Lin X (2014) Physiological and biochemical responses of Phoebe bournei seedlings to water stress and recovery. Acta Physiol Plant 36:1241–1250
Hayano-Kanashiro C, Calderon-Vazquez C, Ibarra-Laclette E, Herrera-Estrella L, Simpson J (2009) Analysis of gene expression and physiological responses in three Mexican maize landraces under drought stress and recovery irrigation. PLoS One 4:e7531
Haznagy-Radnai E, Czigle S, Zupko I, Falkay G, Mathe I (2006) Comparison of antioxidant activity in enzyme-independent system of six Stachys species. Fitoterapia 77:521–524
He F, Sheng M, Tang M (2017) Effects of Rhizophagus irregularis on photosynthesis and antioxidative enzymatic system in Robinia pseudoacacia L. under drought stress. Front Plant Sci 8:183
Huang HQ, Zhang X, Lin M, Shen YH, Yan SK, Zhang WD (2008) Characterization and identification of saikosaponins in crude extracts from three Bupleurum species using LC-ESI-MS. J Sep Sci 31:3190–3201
Jin R, Wang Y, Liu R, Gou J, Chan Z (2015) Physiological and metabolic changes of purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) in response to drought, heat, and combined stresses. Front Plant Sci 6:1123
Khabibullaev PK, Zakhidov EA, Zakhidova MA, Kasymdzhanov MA, Nematov ShK, Abdukarimov AA, Nabiev SM, Saakova NA, Stamp P, Fracheboud I (2003) Evaluation of the effects of drought on cotton plants using characteristics of chlorophyll fluorescence. Dokl Biol Sci 392:442–444
Lange BM, Rujan T, Martin W, Croteau R (2000) Isoprenoid biosynthesis: the evolution of two ancient and distinct pathways across genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:13172–13177
Lee MH, Jeong JH, Seo JW, Shin CG, Kim YS, In JG, Yang DC, Yi JS, Choi YE (2004) Enhanced triterpene and phytosterol biosynthesis in Panax ginseng overexpressing squalene synthase gene. Plant Cell Physiol 45:976–984
Lin WY, Chen LR, Lin TY (2008) Rapid authentication of Bupleurum species using an array of immobilized sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes. Planta Med 74:464–469
Lin TY, Chiou CY, Chiou SJ (2013) Putative genes involved in saikosaponin biosynthesis in Bupleurum species. Int J Mol Sci 14:12806–12826
Liu C, Liu Y, Guo K, Fan D, Li G, Zheng Y, Yu L, Yang R (2011a) Effect of drought on pigments, osmotic adjustment and antioxidant enzymes in six woody plant species in karst habitats of southwestern China. Environ Exp Bot 71:174–183
Liu H, Wang X, Wang D, Zou Z, Liang Z (2011b) Effect of drought stress on growth and accumulation of active constituents in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Ind Crops Prod 33:84–88
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Lu S, Peng X, Guo Z, Zhang G, Wang Z, Wang C, Pang C, Fan Z, Wang J (2007) In vitro selection of salinity tolerant variants from triploid bermudagrass (Cynodon transvaalensis × C. dactylon) and their physiological responses to salt and drought stress. Plant Cell Rep 26:1413–1420
Massacci A, Nabiev SM, Pietrosanti L, Nematov SK, Chernikova TN, Thor K, Leipner J (2008) Response of the photosynthetic apparatus of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) to the onset of drought stress under field conditions studied by gas-exchange analysis and chlorophyll fluorescence imaging. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:189–195
Maxwell K, Johnson GN (2000) Chlorophyll fluorescence—a practical guide. J Exp Bot 51:659–668
Meng LS (2018) Compound synthesis or growth and development of roots/stomata regulate plant drought tolerance or water use efficiency/water uptake efficiency. J Agric Food Chem 66:3595–3604
Mitra S, Irshad M, Debnath B, Lu X, Li M, Dash CK, Rizwan HM, Qiu Z, Qiu D (2018) Effect of vineyard soil variability on chlorophyll fluorescence, yield and quality of table grape as influenced by soil moisture, grown under double cropping system in protected condition. PeerJ 6:e5592
Mittler R, Zilinskas BA (1994) Regulation of pea cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase and other antioxidant enzymes during the progression of drought stress and following recovery from drought. Plant J 5:397–405
Mitton JB, Grant MC, Yoshino AM (1998) Variation in allozymes and stomatal size in pinyon (Pinus edulis, Pinaceae), associated with soil moisture. Am J Bot 85:1262–1265
Mizutani M, Ohta D (2010) Diversification of P450 genes during land plant evolution. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:291–315
Monti A, Brugnoli E, Scartazza A, Amaducci MT (2006) The effect of transient and continuous drought on yield, photosynthesis and carbon isotope discrimination in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). J Exp Bot 57:1253–1262
Nagegowda DA (2010) Plant volatile terpenoid metabolism: biosynthetic genes, transcriptional regulation and subcellular compartmentation. FEBS Lett 584:2965–2973
Nilsen ET, Freeman J, Grene R, Tokuhisa J (2014) A rootstock provides water conservation for a grafted commercial tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) line in response to mild-drought conditions: a focus on vegetative growth and photosynthetic parameters. PLoS One 9:e115380
Nolan RH, Tarin T, Santini NS, McAdam SAM, Ruman R, Eamus D (2017) Differences in osmotic adjustment, foliar abscisic acid dynamics, and stomatal regulation between an isohydric and anisohydric woody angiosperm during drought. Plant Cell Environ 40:3122–3134
Oukarroum A, Schansker G, Strasser RJ (2009) Drought stress effects on photosystem I content and photosystem II thermotolerance analyzed using Chl a fluorescence kinetics in barley varieties differing in their drought tolerance. Physiol Plant 137:188–199
Ramachandra Reddy A, Chaitanya KV, Vivekanandan M (2004) Drought-induced responses of photosynthesis and antioxidant metabolism in higher plants. J Plant Physiol 161:1189–1202
Rogerio AP, Sa-Nunes A, Faccioli LH (2010) The activity of medicinal plants and secondary metabolites on eosinophilic inflammation. Pharmacol Res 62:298–307
Seki H, Tamura K, Muranaka T (2015) P450s and UGTs: key players in the structural diversity of triterpenoid saponins. Plant Cell Physiol 56:1463–1471
Selmar D, Kleinwächter M (2013) Influencing the product quality by deliberately applying drought stress during the cultivation of medicinal plants. Ind Crops Prod 42:558–566
Shalata A, Mittova V, Volokita M, Guy M, Tal M (2001) Response of the cultivated tomato and its wild salt-tolerant relative Lycopersicon pennellii to salt-dependent oxidative stress: the root antioxidative system. Physiol Plant 112:487–494
Singh B, Sharma RA (2015) Plant terpenes: defense responses, phylogenetic analysis, regulation and clinical applications. 3 Biotech 5:129–151
Sui C, Zhang J, Wei J, Chen S, Li Y, Xu J, Jin Y, Xie C, Gao Z, Chen H, Yang C, Zhang Z, Xu Y (2011) Transcriptome analysis of Bupleurum chinense focusing on genes involved in the biosynthesis of saikosaponins. BMC Genom 12:539
Tan LL, Cai X, Hu ZH, Ni XL (2008) Localization and dynamic change of saikosaponin in root of Bupleurum chinense. J Integr Plant Biol 50:951–957
Wang X, Feng Q, Xiao Y, Li P (2015) Radix Bupleuri ameliorates depression by increasing nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:9205–9217
Wu S, Hu C, Tan Q, Nie Z, Sun X (2014) Effects of molybdenum on water utilization, antioxidative defense system and osmotic-adjustment ability in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum) under drought stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 83:365–374
Yadav RK, Sangwan RS, Sabir F, Srivastava AK, Sangwan NS (2014) Effect of prolonged water stress on specialized secondary metabolites, peltate glandular trichomes, and pathway gene expression in Artemisia annua L. Plant Physiol Biochem 74:70–83
Yang C (2016) Adaptive plant physiology in extreme environments. J Plant Physiol 194:1
Yang ZY, Chao Z, Huo KK, Xie H, Tian ZP, Pan SL (2007) ITS sequence analysis used for molecular identification of the Bupleurum species from northwestern China. Phytomedicine 14:416–423
Zhu Z, Liang Z, Han R (2009a) Saikosaponin accumulation and antioxidative protection in drought-stressed Bupleurum chinense DC. plants. Environ Exp Bot 66:326–333
Zhu Z, Liang Z, Han R, Je Dong (2009b) Growth and saikosaponin production of the medicinal herb Bupleurum chinense DC. under different levels of nitrogen and phosphorus. Ind Crops Prod 29:96–101
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by China Agriculture Research System (Grant number CARS-21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Leena Tripathi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Zhao, Y., Zhang, Q. et al. Effects of drought–re-watering–drought on the photosynthesis physiology and secondary metabolite production of Bupleurum chinense DC.. Plant Cell Rep 38, 1181–1197 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02436-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02436-8