Abstract
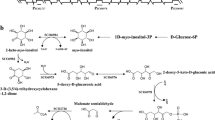
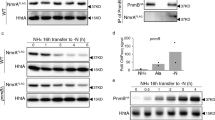
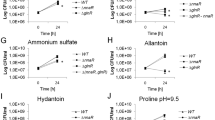
In Aspergillus nidulans, expression of sulfur metabolism genes is activated by the MetR transcription factor containing a basic region and leucine zipper domain (bZIP). Here we identified and characterized MetZ, a new transcriptional regulator in A. nidulans and other Eurotiales. It contains a bZIP domain similar to the corresponding region in MetR and this similarity suggests that MetZ could potentially complement the MetR deficiency. The metR and metZ genes are interrupted by unusually long introns. Transcription of metZ, unlike that of metR, is controlled by the sulfur metabolite repression system (SMR) dependent on the MetR protein. Overexpression of metZ from a MetR-independent promoter in a ΔmetR background activates transcription of genes encoding sulfate permease, homocysteine synthase and methionine permease, partially complementing the phenotype of the ΔmetR mutation. Thus, MetZ appears to be a second transcription factor involved in regulation of sulfur metabolism genes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- OE::metZ :
-
Overexpression of the metZ gene
- SMR:
-
Sulfur metabolite repression system
References
Altschul SF, Lipman DJ (1990) Protein database searches for multiple alignments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:5509–5513
Amich J, Schafferer L, Haas H, Krappmann S (2013) Regulation of sulphur assimilation is essential for virulence and affects iron homeostasis of the human-pathogenic mould Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003573
Barlow JJ, Mathias AP, Williamson R, Gammack DB (1963) A simple method for the quantitative isolation of undegraded high molecular weight ribonucleic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 13:61–66
Brody H, Griffith J, Cuticchia AJ, Arnold J, Timberlake WE (1991) Chromosome-specific recombinant DNA libraries from the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Nucleic Acids Res 19:3105–3109
Chomczyński P (1993) A reagent for the single-step simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA and proteins from cell and tissue samples. Biotechniques 15(532–534):536–537
Cove DJ (1966) The induction and repression of nitrate reductase in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Biochim Biophys Acta 113:51–56
Edgar R, Domrachev M, Lash AE (2002) Gene expression omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res 30:207–210
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP—phylogeny inference package (Version 3.2). Cladistics 5:164–166
Fu YH, Marzluf GA (1990) cys-3, the positive-acting sulfur regulatory gene of Neurospora crassa, encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem 265:11942–11947
Fu YH, Paietta JV, Mannix DG, Marzluf GA (1989) cys-3, the positive-acting sulfur regulatory gene of Neurospora crassa, encodes a protein with a putative leucine zipper DNA-binding element. Mol Cell Biol 9:1120–1127
Gems DH, Clutterbuck AJ (1993) Co-transformation with autonomously-replicating helper plasmids facilitates gene cloning from an Aspergillus nidulans gene library. Curr Genet 24:520–524
Glover JN, Harrison SC (1995) Crystal structure of the heterodimeric bZIP transcription factor c-Fos-c-Jun bound to DNA. Nature 373:257–261
Grigoryan G, Keating AE (2008) Structural specificity in coiled-coil interactions. Curr Opin Struct Biol 18:477–483
Hamer JE, Timberlake WE (1987) Functional organization of the Aspergillus nidulans trpC promoter. Mol Cell Biol 7:2352–2359
Harrison C, Katayama S, Dhut S, Chen D, Jones N, Bahler J, Toda T (2005) SCF(Pof1)-ubiquitin and its target Zip1 transcription factor mediate cadmium response in fission yeast. EMBO J 24:599–610
Kaiser P, Flick K, Wittenberg C, Reed SI (2000) Regulation of transcription by ubiquitination without proteolysis: Cdc34/SCF(Met30)-mediated inactivation of the transcription factor Met4. Cell 102:303–314
Kanaan MN, Fu YH, Marzluf GA (1992) The DNA-binding domain of the Cys-3 regulatory protein of Neurospora crassa is bipartite. Biochemistry 31:3197–3203
Kuwano T, Shirataki C, Itoh Y (2008) Comparison between polyethylene glycol- and polyethylenimine-mediated transformation of Aspergillus nidulans. Curr Genet 54:95–103
Lee TA, Jorgensen P, Bognar AL, Peyraud C, Thomas D, Tyers M (2010) Dissection of combinatorial control by the Met4 transcriptional complex. Mol Biol Cell 21:456–469
Li Q, Marzluf GA (1996) Determination of the Neurospora crassa CYS 3 sulfur regulatory protein consensus DNA-binding site: amino-acid substitutions in the CYS3 bZIP domain that alter DNA-binding specificity. Curr Genet 30:298–304
Lukaszkiewicz Z, Paszewski A (1976) Hyper-repressible operator-type mutant in sulphate permease gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Nature 259:337–338
Marcel V, Dichtel-Danjoy ML, Sagne C, Hafsi H, Ma D, Ortiz-Cuaran S, Olivier M, Hall J, Mollereau B, Hainaut P, Bourdon JC (2011) Biological functions of p53 isoforms through evolution: lessons from animal and cellular models. Cell Death Differ 18:1815–1824
Martinelli SD (1994) Media. Prog Ind Microbiol 29:829–832
Marzluf GA (1997) Molecular genetics of sulfur assimilation in filamentous fungi and yeast. Annu Rev Microbiol 51:73–96
Marzluf GA, Metzenberg RL (1968) Positive control by the cys-3 locus in regulation of sulfur metabolism in Neurospora. J Mol Biol 33:423–437
Menant A, Baudouin-Cornu P, Peyraud C, Tyers M, Thomas D (2006) Determinants of the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the Met4 transcription factor. J Biol Chem 281:11744–11754
Natorff R, Piotrowska M, Paszewski A (1998) The Aspergillus nidulans sulphur regulatory gene sconB encodes a protein with WD40 repeats and an F-box. Mol Gen Genet 257:255–263
Natorff R, Sienko M, Brzywczy J, Paszewski A (2003) The Aspergillus nidulans metR gene encodes a bZIP protein which activates transcription of sulphur metabolism genes. Mol Microbiol 49:1081–1094
Paszewski A, Brzywczy J, Natorff R (1994) Sulphur metabolism. Prog Ind Microbiol 29:299–319
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Piotrowska M, Natorff R, Paszewski A (2000) sconC, a gene involved in the regulation of sulphur metabolism in Aspergillus nidulans, belongs to the SKP1 gene family. Mol Gen Genet 264:276–282
Priebe S, Linde J, Albrecht D, Guthke R, Brakhage AA (2011) FungiFun: a web-based application for functional categorization of fungal genes and proteins. Fungal Genet Biol 48:353–358
Pu WT, Struhl K (1993) Dimerization of leucine zippers analyzed by random selection. Nucleic Acids Res 21:4348–4355
Rouillon A, Barbey R, Patton EE, Tyers M, Thomas D (2000) Feedback-regulated degradation of the transcriptional activator Met4 is triggered by the SCF(Met30)complex. EMBO J 19:282–294
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sieńko M, Natorff R, Skoneczny M, Kruszewska J, Paszewski A, Brzywczy J (2014) Regulatory mutations affecting sulfur metabolism induce environmental stress response in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet Biol 65:37–47
Tao Y, Marzluf GA (1998) Synthesis and differential turnover of the CYS3 regulatory protein of Neurospora crassa are subject to sulfur control. J Bacteriol 180:478–482
Thomas D, Surdin-Kerjan Y (1997) Metabolism of sulfur amino acids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:503–532
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M, Rozen SG (2012) Primer3–new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 40:e115
Waring RB, May GS, Morris NR (1989) Characterization of an inducible expression system in Aspergillus nidulans using alcA and tubulin-coding genes. Gene 79:119–130
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the State Committee for Scientific Research/National Center of Science (NCN), grant number 2762/B/P01/2009/37 to A. P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. Ebbole.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piłsyk, S., Natorff, R., Sieńko, M. et al. The Aspergillus nidulans metZ gene encodes a transcription factor involved in regulation of sulfur metabolism in this fungus and other Eurotiales . Curr Genet 61, 115–125 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-014-0459-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-014-0459-5