Abstract
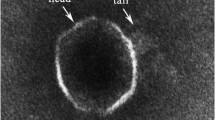
A novel Alteromonas phage JH01, with the host strain identified to be Alteromonas marina SW-47(T), was isolated from the Qingdao coast during the summer of 2017. Transmission electron microscopy analysis showed that phage JH01 can be categorized into the Siphoviridae family, with an icosahedral head of 62 ± 5 nm and a long contractile tail of 254 ± 10 nm. The bioinformatic analysis shows that this phage consists of a linear, double-stranded 46,500 bp DNA molecule with a GC content of 44.39%, and 58 ORFs with no tRNA genes. The ORFs are classified into four groups, including phage packaging, phage structure, DNA replication and regulation, and hypothetical protein. The phylogenetic tree, constructed using neighbor-joining analysis, shows that phage JH01 has altitudinal homology with some Vibrio and Pseudoalteromonas phage B8b. Comparative analysis reveals the high similarity between phage JH01 and phage B8b. Additionally, our study of phage JH01 provides useful information for further research on the interaction between Alteromonas phages and their hosts.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boetzer M, Pirovano W (2012) Toward almost closed genomes with GapFiller. Genome Biol 13(6):R56. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2012-13-6-r56
Duhaime MB, Wichels A, Waldmann J et al (2010) Ecogenomics and genome landscapes of marine Pseudoalteromonas phage H105/1. ISME J 5(1):107–121. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.94
Elena L, Karin H, Natalie S et al (2015) Life-style and genome structure of marine Pseudoalteromonas Siphovirus B8b isolated from the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 10(1):e0114829. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114829
Fuhrman JA (1999) Marine viruses and their biogeochemical and ecological effects. Nature 399(6736):541. https://doi.org/10.1038/21119
Gao Y, Liu Q, Wang M et al (2017) Characterization and genome sequence of marine Alteromonas gracilis phage PB15 Isolated from the Yellow Sea. China. Curr Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1251-9
Garcia-Heredia I, Rodriguez-Valera F, Martin-Cuadrado AB (2013) Novel group of podovirus infecting the marine bacterium Alteromonas macleodii. Bacteriophage 3(2):e24766. https://doi.org/10.4161/bact.24766
Gauthier G (1995) Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Alteromonas, Shewanella and Moritella using genes coding for small-subunit rRNA sequences and division of the genus Alteromonas into two genera: Alteromonas (emended) and Pseudoalteromonas, gen. nov., and proposal of twelve new species combinations. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45(4):755–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnt.2009.07.006
Gong Z, Wang M, Yang Q et al (2017) Isolation and complete genome sequence of a novel Pseudoalteromonas phage PH357 from the Yangtze River Estuary. Curr Microbiol 74(7):832–839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1244-8
Haq IU, Chaudhry WN, Qadri AI (2012) Isolation and partial characterization of a virulent bacteriophage IHQ1 specific for Aeromonas punctata from Stream Water. Microbial Ecol 63(4):954–963. https://doi.org/10.2307/41489237
Hyman P, Abedon ST (2010) Bacteriophage host range and bacterial resistance. Adv Appl Microbiol 70:217. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2164(10)70007-1
Kang I, Oh HM, Kang D et al (2013) Genome of a sar116 bacteriophage shows the prevalence of this phage type in the oceans. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(30):12343–12348. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1219930110
Kohji K, Takahashi NK, Hiroshi Y et al (1994) Involvement of RecE exonuclease and RecT annealing protein in DNA double-strand break repair by homologous recombination. Gene (Amsterdam) 138(1):17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(94)90778-1
Leitz T, Wagner T (1993) The marine bacterium Alteromonas espejiana induces metamorphosis of the hydroid Hydractinia echinata. Mar Biol (Berlin) 115(2):173–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00346332
Liu Q, Han Y, Wang D et al (2017) Complete genomic sequence of bacteriophage J2–1: a novel, Pseudoalteromonas phenolica phage isolated from the coastal water of Qingdao. China. Mar Genom. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2017.12.001
Liu Z, Wang M, Meng X et al (2016) Isolation and genome sequencing of a novel Pseudoalteromonas phage PH1. Curr Microbiology 74(2):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-016-1175-9
Lu LD, Sun Q, Fan XY et al (2010) Mycobacterial MazG is a novel NTP pyrophosphohydrolase involved in oxidative stress response. J Biol Chem 285(36):28076–28085. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m109.088872
López-Pérez Mario, Gonzaga A, Ivanova EP et al (2014) Genomes of Alteromonas australica, a world apart. BMC Genom 15(1):483. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-483
Matsuyama H, Minami H, Sakaki T et al (2015) Alteromonas gracilis sp. nov., a marine polysaccharide-producing bacterium. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 65(5):1498–1503. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.000127
Meng X, Wang M, You S et al (2017) Characterization and complete genome sequence of a novel siphoviridae bacteriophage BS5. Curr Microbiol 74(7):815–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1221-2
Middelboe M, Chan AM, Bertelsen ASK (2010) Isolation and life cycle characterization of lytic viruses infecting heterotrophic bacteria and cyanobacteria. Man Aquat Viral Ecol. https://doi.org/10.4319/mave.2010.978-0-9845591-0-7.118
Murray AG, Eldridge PM (1994) Marine viral ecology: incorporation of bacteriophage into the microbial planktonic food web paradigm. J Plankton Res 16(6):627–641. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/16.6.627
Nóbrega Maria S, Silva BS, Leomil L et al (2018) Description of Alteromonas abrolhosensis sp. nov. isolated from sea water of abrolhos bank, brazil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-1016-x
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor–joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evolut 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Short CM, Suttle CA (2005) Nearly identical bacteriophage structural gene sequences are widely distributed in both marine and freshwater environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(1):480–486. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.1.480-486.2005
Vandecandelaere I, Nercessian O, Segaert E et al (2008) Alteromonas genovensis sp. nov. isolated from a marine electroactive biofilm and emended description of Alteromonas macleodii Baumann et al. 1972 (approved lists 1980). Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 58(11):2589–2596. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65691-0
Weitz JS, Wilhelm SW (2012) Ocean viruses and their effects on microbial communities and biogeochemical cycles. F1000 Biol Rep 4(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3410/B4-17
Zhu M, Wang M, Jiang Y et al (2018) Isolation and complete genome sequence of a novel Marinobacter phage B23. Curr Microbiol 75(12):1619–1625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-018-1568-z
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the research vessel Dong Fang Hong 2, for providing the seawater samples. The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31500339, 41676178 and 41076088), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant Nos. 2017YFA0603200, 2018YFC1406704), Marine Scientific and Technological Innovation Project Financially Supported by Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao) (Grant Nos. 2018SDKJ0406-6, 2016ASKJ14), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central University of Ocean University of China (Grant Nos. 201812002, 201762017 and 201562018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Jiang, Y., Xiao, S. et al. Characterization and Genome Analysis of a Novel Alteromonas Phage JH01 Isolated from the Qingdao Coast of China. Curr Microbiol 76, 1256–1263 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01751-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01751-3