Abstract
Purpose
Resistance to treatment with inhibitors of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is partially mediated by activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). We conducted a phase I study to determine the recommended phase II dose (RP2D) and dose-limiting toxicities (DLT) of temsirolimus (mTOR inhibitor) combined with erlotinib (EGFR inhibitor) in patients with refractory solid tumors.
Methods
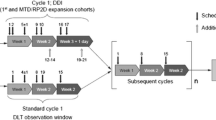
Standard “3 + 3” design was used for dose escalation. An expansion cohort at RP2D included only patients with squamous histology or mutations relevant to PI3K or EGFR pathway activation. Patients started daily erlotinib 7 days prior to starting temsirolimus on cycle 1. Intravenous temsirolimus was then administered weekly. Starting dose levels were 15 mg for temsirolimus and 100 mg for erlotinib.
Results
Forty-four patients received treatment on this study (28 in dose escalation and 16 in the expansion cohort). The RP2D was temsirolimus 25 mg IV weekly and erlotinib 100 mg orally daily. Two patients experienced DLTs (G3 dehydration and G4 renal failure). The most common drug-related adverse events (all grades) were rash, mucositis/stomatitis, diarrhea, nausea and fatigue. No complete or partial responses were observed. The median duration on this study was 69 days (range 3–770) for escalation and 88 days (range 25–243) for expansion cohorts. Among 11 response-evaluable patients in the expansion cohort, 9 (82%) had stable disease and 2 (18%) had progressive disease.
Conclusion
The combination of temsirolimus and erlotinib at the RP2D was well tolerated, and the regimen resulted in prolonged disease stabilization in selected patients (NCT00770263).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Franke TF, Kaplan DR, Cantley LC (1997) PI3K: downstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell 88(4):435–437
Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J, Figlin R, Kapoor A, Staroslawska E, Sosman J, McDermott D, Bodrogi I, Kovacevic Z, Lesovoy V, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Barbarash O, Gokmen E, O’Toole T, Lustgarten S, Moore L, Motzer RJ, Global AT (2007) Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356(22):2271–2281. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa066838
Baselga J, Campone M, Piccart M, BurrisRugo HAHS, Sahmoud T, Noguchi S, Gnant M, Pritchard KI, Lebrun F, Beck JT, Ito Y, Yardley D, Deleu I, Perez A, Bachelot T, Vittori L, Xu Z, Mukhopadhyay P, Lebwohl D, Hortobagyi GN (2012) Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 366(6):520–529. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1109653
Yao JC, Pavel M, Lombard-Bohas C, Van Cutsem E, Voi M, Brandt U, He W, Chen D, Capdevila J, de Vries EGE, Tomassetti P, Hobday T, Pommier R, Oberg K (2016) Everolimus for the treatment of advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: overall survival and circulating biomarkers from the randomized, phase III RADIANT-3 study. J Clin Oncol 34(32):3906–3913. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.68.0702
Yang JC, Wu YL, Schuler M, Sebastian M, Popat S, Yamamoto N, Zhou C, Hu CP, O’Byrne K, Feng J, Lu S, Huang Y, Geater SL, Lee KY, Tsai CM, Gorbunova V, Hirsh V, Bennouna J, Orlov S, Mok T, Boyer M, Su WC, Lee KH, Kato T, Massey D, Shahidi M, Zazulina V, Sequist LV (2015) Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol 16(2):141–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71173-8
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R, Pallares C, Sanchez JM, Porta R, Cobo M, Garrido P, Longo F, Moran T, Insa A, De Marinis F, Corre R, Bover I, Illiano A, Dansin E, de Castro J, Milella M, Reguart N, Altavilla G, Jimenez U, Provencio M, Moreno MA, Terrasa J, Munoz-Langa J, Valdivia J, Isla D, Domine M, Molinier O, Mazieres J, Baize N, Garcia-Campelo R, Robinet G, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Lopez-Vivanco G, Gebbia V, Ferrera-Delgado L, Bombaron P, Bernabe R, Bearz A, Artal A, Cortesi E, Rolfo C, Sanchez-Ronco M, Drozdowskyj A, Queralt C, de Aguirre I, Ramirez JL, Sanchez JJ, Molina MA, Taron M, Paz-Ares L, Spanish Lung Cancer Group in collaboration with Groupe Francais de P-C, Associazione Italiana Oncologia T (2012) Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 13(3):239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X
Wu YL, Cheng Y, Zhou X, Lee KH, Nakagawa K, Niho S, Tsuji F, Linke R, Rosell R, Corral J, Migliorino MR, Pluzanski A, Sbar EI, Wang T, White JL, Nadanaciva S, Sandin R, Mok TS (2017) Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18(11):1454–1466. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30608-3
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, Ohe Y, Yang JJ, Chewaskulyong B, Jiang H, Duffield EL, Watkins CL, Armour AA, Fukuoka M (2009) Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361(10):947–957. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0810699
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, Dechaphunkul A, Imamura F, Nogami N, Kurata T, Okamoto I, Zhou C, Cho BC, Cheng Y, Cho EK, Voon PJ, Planchard D, Su WC, Gray JE, Lee SM, Hodge R, Marotti M, Rukazenkov Y, Ramalingam SS, Investigators F (2018) Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 378(2):113–125. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1713137
Wheeler DL, Dunn EF, Harari PM (2010) Understanding resistance to EGFR inhibitors-impact on future treatment strategies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 7(9):493–507. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2010.97
She QB, Solit D, Basso A, Moasser MM (2003) Resistance to gefitinib in PTEN-null HER-overexpressing tumor cells can be overcome through restoration of PTEN function or pharmacologic modulation of constitutive phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase/Akt pathway signaling. Clin Cancer Res 9(12):4340–4346
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, Lindeman N, Gale CM, Zhao X, Christensen J, Kosaka T, Holmes AJ, Rogers AM, Cappuzzo F, Mok T, Lee C, Johnson BE, Cantley LC, Janne PA (2007) MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 316(5827):1039–1043. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1141478
Chakravarti A, Loeffler JS, Dyson NJ (2002) Insulin-like growth factor receptor I mediates resistance to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy in primary human glioblastoma cells through continued activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling. Cancer Res 62(1):200–207
Buck E, Eyzaguirre A, Brown E, Petti F, McCormack S, Haley JD, Iwata KK, Gibson NW, Griffin G (2006) Rapamycin synergizes with the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib in non-small-cell lung, pancreatic, colon, and breast tumors. Mol Cancer Ther 5(11):2676–2684. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0166
Rodrik-Outmezguine VS, Chandarlapaty S, Pagano NC, Poulikakos PI, Scaltriti M, Moskatel E, Baselga J, Guichard S, Rosen N (2011) mTOR kinase inhibition causes feedback-dependent biphasic regulation of AKT signaling. Cancer Discov 1(3):248–259. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0085
Um SH, Frigerio F, Watanabe M, Picard F, Joaquin M, Sticker M, Fumagalli S, Allegrini PR, Kozma SC, Auwerx J, Thomas G (2004) Absence of S6K1 protects against age- and diet-induced obesity while enhancing insulin sensitivity. Nature 431(7005):200–205. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02866
Wei F, Liu Y, Bellail AC, Olson JJ, Sun SY, Lu G, Ding L, Yuan C, Wang G, Hao C (2012) K-Ras mutation-mediated IGF-1-induced feedback ERK activation contributes to the rapalog resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Cancer Lett 322(1):58–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2012.02.005
Chaturvedi D, Gao X, Cohen MS, Taunton J, Patel TB (2009) Rapamycin induces transactivation of the EGFR and increases cell survival. Oncogene 28(9):1187–1196. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.490
Wei F, Zhang Y, Geng L, Zhang P, Wang G, Liu Y (2015) mTOR inhibition induces EGFR feedback activation in association with its resistance to human pancreatic cancer. Int J Mol Sci 16(2):3267–3282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16023267
Bianco R, Garofalo S, Rosa R, Damiano V, Gelardi T, Daniele G, Marciano R, Ciardiello F, Tortora G (2008) Inhibition of mTOR pathway by everolimus cooperates with EGFR inhibitors in human tumours sensitive and resistant to anti-EGFR drugs. Br J Cancer 98(5):923–930. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6604269
Dong S, Zhang XC, Cheng H, Zhu JQ, Chen ZH, Zhang YF, Xie Z, Wu YL (2012) Everolimus synergizes with gefitinib in non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines resistant to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 70(5):707–716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-012-1946-3
Herberger B, Berger W, Puhalla H, Schmid K, Novak S, Brandstetter A, Pirker C, Gruenberger T, Filipits M (2009) Simultaneous blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway by epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors and rapamycin results in reduced cell growth and survival in biliary tract cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 8(6):1547–1556. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0003
Dragowska WH, Weppler SA, Qadir MA, Wong LY, Franssen Y, Baker JH, Kapanen AI, Kierkels GJ, Masin D, Minchinton AI, Gelmon KA, Bally MB (2011) The combination of gefitinib and RAD001 inhibits growth of HER2 overexpressing breast cancer cells and tumors irrespective of trastuzumab sensitivity. BMC Cancer 11:420. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-11-420
El Guerrab A, Bamdad M, Bignon YJ, Penault-Llorca F, Aubel C (2020) Co-targeting EGFR and mTOR with gefitinib and everolimus in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Sci Rep 10(1):6367. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63310-2
La Monica S, Galetti M, Alfieri RR, Cavazzoni A, Ardizzoni A, Tiseo M, Capelletti M, Goldoni M, Tagliaferri S, Mutti A, Fumarola C, Bonelli M, Generali D, Petronini PG (2009) Everolimus restores gefitinib sensitivity in resistant non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Biochem Pharmacol 78(5):460–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.04.033
Massarelli E, Lin H, Ginsberg LE, Tran HT, Lee JJ, Canales JR, Williams MD, Blumenschein GR Jr, Lu C, Heymach JV, Kies MS, Papadimitrakopoulou V (2015) Phase II trial of everolimus and erlotinib in patients with platinum-resistant recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol 26(7):1476–1480. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv194
Bryce AH, Rao R, Sarkaria J, Reid JM, Qi Y, Qin R, James CD, Jenkins RB, Boni J, Erlichman C, Haluska P (2012) Phase I study of temsirolimus in combination with EKB-569 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 30(5):1934–1941. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9742-1
Price KA, Azzoli CG, Krug LM, Pietanza MC, Rizvi NA, Pao W, Kris MG, Riely GJ, Heelan RT, Arcila ME, Miller VA (2010) Phase II trial of gefitinib and everolimus in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 5(10):1623–1629. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181ec1531
Moran T, Palmero R, Provencio M, Insa A, Majem M, Reguart N, Bosch-Barrera J, Isla D, Costa EC, Lee C, Puig M, Kraemer S, Schnell D, Rosell R (2017) A phase Ib trial of continuous once-daily oral afatinib plus sirolimus in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer and/or disease progression following prior erlotinib or gefitinib. Lung Cancer 108:154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.03.009
Hollebecque A, Bahleda R, Faivre L, Adam J, Poinsignon V, Paci A, Gomez-Roca C, Thery JC, Le Deley MC, Varga A, Gazzah A, Ileana E, Gharib M, Angevin E, Malekzadeh K, Massard C, Soria JC, Spano JP (2017) Phase I study of temsirolimus in combination with cetuximab in patients with advanced solid tumours. Eur J Cancer 81:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2017.05.021
Rathkopf DE, Larson SM, Anand A, Morris MJ, Slovin SF, Shaffer DR, Heller G, Carver B, Rosen N, Scher HI (2015) Everolimus combined with gefitinib in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: phase 1/2 results and signaling pathway implications. Cancer 121(21):3853–3861. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29578
Gadgeel SM, Lew DL, Synold TW, LoRusso P, Chung V, Christensen SD, Smith DC, Kingsbury L, Hoering A, Kurzrock R (2013) Phase I study evaluating the combination of lapatinib (a Her2/Neu and EGFR inhibitor) and everolimus (an mTOR inhibitor) in patients with advanced cancers: South West Oncology Group (SWOG) Study S0528. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72(5):1089–1096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2297-4
Bauman JE, Arias-Pulido H, Lee SJ, Fekrazad MH, Ozawa H, Fertig E, Howard J, Bishop J, Wang H, Olson GT, Spafford MJ, Jones DV, Chung CH (2013) A phase II study of temsirolimus and erlotinib in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic, platinum-refractory head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 49(5):461–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.12.016
TORISEL® Dosage and Administration (2020) https://www.pfizermedicalinformation.com/en-us/torisel/dosage-admin. Accessed 8 July 2020
Tarceva Prescribing Information (2020) https://www.gene.com/download/pdf/tarceva_prescribing.pdf. Accessed 8 July 2020
Wen PY, Chang SM, Lamborn KR, Kuhn JG, Norden AD, Cloughesy TF, Robins HI, Lieberman FS, Gilbert MR, Mehta MP, Drappatz J, Groves MD, Santagata S, Ligon AH, Yung WK, Wright JJ, Dancey J, Aldape KD, Prados MD, Ligon KL (2014) Phase I/II study of erlotinib and temsirolimus for patients with recurrent malignant gliomas: North American Brain Tumor Consortium trial 04–02. Neuro Oncol 16(4):567–578. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/not247
Azzariti A, Porcelli L, Gatti G, Nicolin A, Paradiso A (2008) Synergic antiproliferative and antiangiogenic effects of EGFR and mTor inhibitors on pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 75(5):1035–1044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2007.11.018
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Rugo HS, Seneviratne L, Beck JT, Glaspy JA, Peguero JA, Pluard TJ, Dhillon N, Hwang LC, Nangia C, Mayer IA, Meiller TF, Chambers MS, Sweetman RW, Sabo JR, Litton JK (2017) Prevention of everolimus-related stomatitis in women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer using dexamethasone mouthwash (SWISH): a single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 18(5):654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30109-2
Funding
This study was supported by Pfizer and partially supported by Washington University UL1 TR000448 and KL2 TR000450.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Drs. Morgensztern, Van Tine, and Govindan have potential conflict of interest. Other authors do not have any relevant COI to report.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, H., Williams, K., Trikalinos, N.A. et al. A phase I trial of temsirolimus and erlotinib in patients with refractory solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 87, 337–347 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04183-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04183-0