Abstract
Purpose
There are reports that elemental diet (ED) ameliorates oral mucositis caused by antineoplastic chemotherapy. Although this effectiveness may be partly due to high nutrient absorption, the effects of chemotherapy on mucosal defense mechanisms remain unclear. We investigated the effects of oral supplementation with ED on mucin in 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)-induced intestinal mucositis.
Methods
5-FU was administered to rats orally once daily, and ED was supplied orally twice daily for 5 days. The severity of mucositis was assessed by length, dry tissue weight, and villus height of the intestinal tract. Using anti-mucin monoclonal antibody, we compared the immunoreactivity in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and mucin content by histological and biochemical examinations.
Results
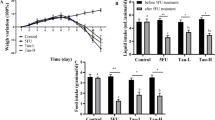
Oral supplementation with ED reduced histological damage and loss of length, dry tissue weight, and villus height induced by 5-FU administration. ED markedly altered PGM34 antibody immunoreactivity and mucin contents in the small intestine of rats with 5-FU-induced mucositis.
Conclusions
ED may possibly be more effective for the prevention of antineoplastic chemotherapy-induced mucositis through the activation of GI mucus cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ED:
-
Elemental diet
- 5-FU:
-
5-Fluorouracil
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
References
Sartori S, Trevisani L, Nielsen I, Tassinari D, Abbasciano V (1996) Misoprostol and omeprazole in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced acute gastroduodenal mucosal injury. A randomized, placebo-controlled pilot study. Cancer 78(7):1477–1482
Shirasaka T, Taguchi T (2006) Timeline from discovery of 5-FU to development of an oral anticancer agent S-1 and its drug concept. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 33(Suppl 1):4–18
Elting LS, Cooksley C, Chambers M, Cantor SB, Manzullo E, Rubenstein EB (2003) The burdens of cancer therapy. Clinical and economic outcomes of chemotherapy-induced mucositis. Cancer 98(7):1531–1539. doi:10.1002/cncr.11671
Slavin RE, Dias MA, Saral R (1978) Cytosine arabinoside induced gastrointestinal toxic alterations in sequential chemotherapeutic protocols: a clinical-pathologic study of 33 patients. Cancer 42(4):1747–1759
Saegusa Y, Ichikawa T, Iwai T, Goso Y, Ikezawa T, Nakano M, Shikama N, Saigenji K, Ishihara K (2008) Effects of acid antisecretory drugs on mucus barrier of the rat against 5-fluorouracil-induced gastrointestinal mucositis. Scand J Gastroenterol 43(5):531–537. doi:10.1080/00365520701811693
Yamamoto H, Ishihara K, Takeda Y, Koizumi W, Ichikawa T (2013) Changes in the mucus barrier during cisplatin-induced intestinal mucositis in rats. BioMed Res Int 2013:276186. doi:10.1155/2013/276186
Rubenstein EB, Peterson DE, Schubert M, Keefe D, McGuire D, Epstein J, Elting LS, Fox PC, Cooksley C, Sonis ST (2004) Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of cancer therapy-induced oral and gastrointestinal mucositis. Cancer 100(9 Suppl):2026–2046. doi:10.1002/cncr.20163
Sonis ST, Elting LS, Keefe D, Peterson DE, Schubert M, Hauer-Jensen M, Bekele BN, Raber-Durlacher J, Donnelly JP, Rubenstein EB (2004) Perspectives on cancer therapy-induced mucosal injury: pathogenesis, measurement, epidemiology, and consequences for patients. Cancer 100(9 Suppl):1995–2025. doi:10.1002/cncr.20162
Andrianifahanana M, Moniaux N, Batra SK (2006) Regulation of mucin expression: mechanistic aspects and implications for cancer and inflammatory diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1765(2):189–222
Azuumi Y, Ohara S, Ishihara K, Okabe H, Hotta K (1980) Correlation of quantitative changes of gastric mucosal glycoproteins with aspirin-induced gastric damage in rats. Gut 21(6):533–536
Ikezawa T, Ichikawa T, Adachi K, Sugano S, Ojima T, Nakamura Y, Watanabe Y, Ishihara K (2005) Analysis of mucin composition in gastric juices of chronic rheumatic patients with upper gastrointestinal damage. Biomed Res 26(4):147–151
Kojima Y, Ishihara K, Ohara S, Saigenji K, Hotta K (1992) Effects of the M1 muscarinic receptor antagonist pirenzepine on gastric mucus glycoprotein in rats with or without ethanol-induced gastric damage. Scand J Gastroenterol 27(9):764–768
Ishihara K, Kurihara M, Goso Y, Ota H, Katsuyama T, Hotta K (1996) Establishment of monoclonal antibodies against carbohydrate moiety of gastric mucins distributed in the different sites and layers of rat gastric mucosa. Glycoconj J 13(5):857–864
Tsubokawa D, Goso Y, Sawaguchi A, Kurihara M, Ichikawa T, Sato N, Suganuma T, Hotta K, Ishihara K (2007) A monoclonal antibody, PGM34, against 6-sulfated blood-group H type 2 antigen, on the carbohydrate moiety of mucin. The FEBS journal 274(7):1833–1848. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05731.x
Lochs H, Dejong C, Hammarqvist F, Hebuterne X, Leon-Sanz M, Schutz T, van Gemert W, van Gossum A, Valentini L, Lubke H, Bischoff S, Engelmann N, Thul P (2006) ESPEN guidelines on enteral nutrition: gastroenterology. Clin Nutr 25(2):260–274. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2006.01.007
Homan M, Baldassano RN, Mamula P (2005) Managing complicated Crohn’s disease in children and adolescents. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2(12):572–579. doi:10.1038/ncpgasthep0338
Johnson T, Macdonald S, Hill SM, Thomas A, Murphy MS (2006) Treatment of active Crohn’s disease in children using partial enteral nutrition with liquid formula: a randomised controlled trial. Gut 55(3):356–361. doi:10.1136/gut.2004.062554
Matsui T, Sakurai T, Yao T (2005) Nutritional therapy for Crohn’s disease in Japan. J Gastroenterol 40(Suppl 16):25–31
Yamamoto T, Nakahigashi M, Umegae S, Kitagawa T, Matsumoto K (2005) Impact of elemental diet on mucosal inflammation in patients with active Crohn’s disease: cytokine production and endoscopic and histological findings. Inflamm Bowel Dis 11(6):580–588
Andou A, Hisamatsu T, Okamoto S, Chinen H, Kamada N, Kobayashi T, Hashimoto M, Okutsu T, Shimbo K, Takeda T, Matsumoto H, Sato A, Ohtsu H, Suzuki M, Hibi T (2009) Dietary histidine ameliorates murine colitis by inhibition of proinflammatory cytokine production from macrophages. Gastroenterology 136(2):564.e562–574.e562. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.09.062
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker HH, Schwab U, Stein H (1984) Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol 133(4):1710–1715
Gerlach C, Golding M, Larue L, Alison MR, Gerdes J (1997) Ki-67 immunoexpression is a robust marker of proliferative cells in the rat. Lab Invest 77(6):697–698
Gerlach C, Sakkab DY, Scholzen T, Dassler R, Alison MR, Gerdes J (1997) Ki-67 expression during rat liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Hepatology 26(3):573–578. doi:10.1002/hep.510260307
Ichikawa T, Ito Y, Saegusa Y, Iwai T, Goso Y, Ikezawa T, Ishihara K (2009) Effects of combination treatment with famotidine and methylmethionine sulfonium chloride on the mucus barrier of rat gastric mucosa. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24(3):488–492. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05667.x
Saegusa Y, Ichikawa T, Iwai T, Goso Y, Okayasu I, Ikezawa T, Shikama N, Saigenji K, Ishihara K (2008) Changes in the mucus barrier of the rat during 5-fluorouracil-induced gastrointestinal mucositis. Scand J Gastroenterol 43(1):59–65
Ogata Y, Takeuchi M, Ishibashi N, Kibe S, Takahashi K, Uchida S, Murakami N, Yahara T, Shirouzu K (2012) Efficacy of Elental on prevention for chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis in colorectal cancer patients. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 39(4):583–587
Fukui T, Itoh Y, Orihara M, Yoshizawa K, Takeda H, Kawada S, Yoshioka T (2011) Elental prevented and reduced oral mucositis during chemotherapy in patients esophageal cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 38(13):2597–2601
Tobisawa Y, Imai Y, Fukuda M, Kawashima H (2010) Sulfation of colonic mucins by N-acetylglucosamine 6-O-sulfotransferase-2 and its protective function in experimental colitis in mice. J Biol Chem 285(9):6750–6760. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.067082
Sukhotnik I, Mogilner JG, Karry R, Shamian B, Lurie M, Kokhanovsky N, Ure BM, Coran AG (2009) Effect of oral glutamine on enterocyte turnover during methotrexate-induced mucositis in rats. Digestion 79(1):5–13. doi:10.1159/000191209
Jebb SA, Osborne RJ, Maughan TS, Mohideen N, Mack P, Mort D, Shelley MD, Elia M (1994) 5-Fluorouracil and folinic acid-induced mucositis: no effect of oral glutamine supplementation. Br J Cancer 70(4):732–735
Leitao RF, Ribeiro RA, Lira AM, Silva LR, Bellaguarda EA, Macedo FD, Sousa RB, Brito GA (2008) Glutamine and alanyl-glutamine accelerate the recovery from 5-fluorouracil-induced experimental oral mucositis in hamster. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 61(2):215–222. doi:10.1007/s00280-007-0463-2
Okuno SH, Woodhouse CO, Loprinzi CL, Sloan JA, LaVasseur BI, Clemens-Schutjer D, Swan D, Axvig C, Ebbert LP, Tirona MR, Michalak JC, Pierson N (1999) Phase III controlled evaluation of glutamine for decreasing stomatitis in patients receiving fluorouracil (5-FU)-based chemotherapy. Am J Clin Oncol 22(3):258–261
Fonnum F (1984) Glutamate: a neurotransmitter in mammalian brain. J Neurochem 42(1):1–11
Rothman S (1984) Synaptic release of excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter mediates anoxic neuronal death. J Neurosci 4(7):1884–1891
Acknowledgments
We express our sincere appreciation to S.Sugawara for technical assistance. This study was supported by a grant from the School of Allied Health Sciences, Kitasato University. Grant from Kitasato University (Kitasato University Research Grant for Young Researchers) supported this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawashima, R., Kawakami, F., Maekawa, T. et al. Elemental diet moderates 5-fluorouracil-induced gastrointestinal mucositis through mucus barrier alteration. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 76, 269–277 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2790-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2790-z