Abstract
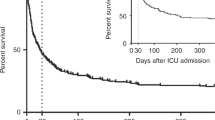
Despite significant advances in the treatment of complications requiring intensive care unit (ICU) admission, ICU mortality remains high for patients after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. We evaluated the role of thrombocytopenia and poor graft function in allogeneic stem cell recipients receiving ICU treatments along with established prognostic ICU markers in order to identify patients at risk for severe complications. At ICU admission, clinical and laboratory data of 108 allogeneic stem cell transplanted ICU patients were collected and retrospectively analyzed. Platelet counts (≤ 50,000/μl, p < 0.0005), hemoglobin levels (≤ 8.5 mg/dl, p = 0.019), and leukocyte count (≤ 1500/μl, p = 0.025) along with sepsis (p = 0.002) and acute myeloid leukemia (p < 0.0005) correlated significantly with survival. Multivariate analysis confirmed thrombocytopenia (hazard ratio (HR) 2.79 (1.58–4.92, 95% confidence interval (CI)) and anemia (HR 1.82, 1.06–3.11, 95% CI) as independent mortality risk factors. Predominant ICU diagnoses were acute respiratory failure (75%), acute kidney injury (47%), and septic shock (30%). Acute graft versus host disease was diagnosed in 42% of patients, and 47% required vasopressors. Low platelet (≤ 50,000/μl) and poor graft function are independent prognostic factors for impaired survival in critically ill stem cell transplanted patients. The underlying pathophysiology of poor graft function is not fully understood and currently under investigation. High-risk patients may be identified and ICU treatments stratified according to allogeneic stem cell patients’ individual risk profiles. In contrast to previous studies involving medical or surgical ICU patients, the fraction of thrombocytopenic patients was larger and low platelets were a better differentiating factor in multivariate analysis than any other parameter.


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
14 December 2018
The author name Philipp Wohlfarth was incorrectly spelled as Philipp Wohlfahrth in the original version of this article.
References
Champlin RE, Schmitz N, Horowitz MM, Chapuis B, Chopra R, Cornelissen JJ, Gale RP, Goldman JM, Loberiza FR Jr, Hertenstein B, Klein JP, Montserrat E, Zhang MJ, Ringden O, Tomany SC, Rowlings PA, Van Hoef ME, Gratwohl A (2000) Blood stem cells compared with bone marrow as a source of hematopoietic cells for allogeneic transplantation. IBMTR histocompatibility and stem cell sources working committee and the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Blood 95(12):3702–3709
Stasia A, Ghiso A, Galaverna F, Raiola AM, Gualandi F, Luchetti S, Pozzi S, Varaldo R, Lamparelli T, Bregante S, Van Lint MT, di Grazia C, Bacigalupo A (2014) CD34 selected cells for the treatment of poor graft function after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 20(9):1440–1443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.05.016
Torrecilla C, Cortes JL, Chamorro C, Rubio JJ, Galdos P, Dominguez de Villota E (1988) Prognostic assessment of the acute complications of bone marrow transplantation requiring intensive therapy. Intensive Care Med 14(4):393–398
Paz HL, Crilley P, Weinar M, Brodsky I (1993) Outcome of patients requiring medical ICU admission following bone marrow transplantation. Chest 104(2):527–531
Staudinger T, Stoiser B, Mullner M, Locker GJ, Laczika K, Knapp S, Burgmann H, Wilfing A, Kofler J, Thalhammer F, Frass M (2000) Outcome and prognostic factors in critically ill cancer patients admitted to the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 28(5):1322–1328
Azoulay E, Soares M, Darmon M, Benoit D, Pastores S, Afessa B (2011) Intensive care of the cancer patient: recent achievements and remaining challenges. Ann Intensive Care 1(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/2110-5820-1-5
Vogelzang NJ, Benowitz SI, Adams S, Aghajanian C, Chang SM, Dreyer ZE, Janne PA, Ko AH, Masters GA, Odenike O, Patel JD, Roth BJ, Samlowski WE, Seidman AD, Tap WD, Temel JS, Von Roenn JH, Kris MG (2012) Clinical cancer advances 2011: annual report on Progress against Cancer from the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 30(1):88–109. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.40.1919
Lindgaard SC, Nielsen J, Lindmark A, Sengelov H (2016) Prognosis of allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell recipients admitted to the intensive care unit: a retrospective, single-centre study. Acta Haematol 135(2):72–78. https://doi.org/10.1159/000440937
Legrand M, Max A, Peigne V, Mariotte E, Canet E, Debrumetz A, Lemiale V, Seguin A, Darmon M, Schlemmer B, Azoulay E (2012) Survival in neutropenic patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Crit Care Med 40(1):43–49. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31822b50c2
Zuber B, Tran TC, Aegerter P, Grimaldi D, Charpentier J, Guidet B, Mira JP, Pene F, Network CU-R (2012) Impact of case volume on survival of septic shock in patients with malignancies. Crit Care Med 40(1):55–62. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31822d74ba
Azoulay E, Alberti C, Bornstain C, Leleu G, Moreau D, Recher C, Chevret S, Le Gall JR, Brochard L, Schlemmer B (2001) Improved survival in cancer patients requiring mechanical ventilatory support: impact of noninvasive mechanical ventilatory support. Crit Care Med 29(3):519–525
Baughman RP, Lower EE, Flessa HC, Tollerud DJ (1993) Thrombocytopenia in the intensive care unit. Chest 104(4):1243–1247
Stephan F, Hollande J, Richard O, Cheffi A, Maier-Redelsperger M, Flahault A (1999) Thrombocytopenia in a surgical ICU. Chest 115(5):1363–1370
Vanderschueren S, De Weerdt A, Malbrain M, Vankersschaever D, Frans E, Wilmer A, Bobbaers H (2000) Thrombocytopenia and prognosis in intensive care. Crit Care Med 28(6):1871–1876
Boyacı N, Aygencel G, Turkoglu M, Yegin ZA, Acar K, Sucak GT (2014) The intensive care management process in patients with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and factors affecting their prognosis. Hematology 19(6):338–345. https://doi.org/10.1179/1607845413Y.0000000130
van Vliet M, van der Burgt MP, van der Velden WJ, van der Hoeven JG, de Haan AF, Donnelly JP, Pickkers P, Blijlevens NM (2014) Trends in the outcomes of Dutch haematological patients receiving intensive care support. Neth J Med 72(2):107–112
Afessa B, Tefferi A, Dunn WF, Litzow MR, Peters SG (2003) Intensive care unit support and acute physiology and chronic health evaluation III performance in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Crit Care Med 31(6):1715–1721. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ccm.0000065761.51367.2d
Neumann F, Lobitz O, Fenk R, Bruns I, Köstering M, Steiner S, Hennersdorf M, Kelm M, Strauer BE, Germing U, Hinke A, Haas R, Kobbe G (2008) The sepsis-related organ failure assessment (SOFA) score is predictive for survival of patients admitted to the intensive care unit following allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol 87(4):299–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-008-0440-9
Gilli K, Remberger M, Hjelmqvist H, Ringden O, Mattsson J (2010) Sequential organ failure assessment predicts the outcome of SCT recipients admitted to intensive care unit. Bone Marrow Transplant 45(4):682–688. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2009.220
Bayraktar UD, Shpall EJ, Liu P, Ciurea SO, Rondon G, de Lima M, Cardenas-Turanzas M, Price KJ, Champlin RE, Nates JL (2013) Hematopoietic cell transplantation-specific comorbidity index predicts inpatient mortality and survival in patients who received allogeneic transplantation admitted to the intensive care unit. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 31(33):4207–4214. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2013.50.5867
Benz R, Schanz U, Maggiorini M, Seebach JD, Stussi G (2014) Risk factors for ICU admission and ICU survival after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 49(1):62–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2013.141
Olsson R, Remberger M, Schaffer M, Berggren DM, Svahn BM, Mattsson J, Ringden O (2013) Graft failure in the modern era of allogeneic hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 48(4):537–543. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.239
Ghobadi A, Fiala MA, Ramsingh G, Gao F, Abboud CN, Stockerl-Goldstein K, Uy GL, Grossman BJ, Westervelt P, DiPersio JF (2017) Fresh or cryopreserved CD34(+)-selected mobilized peripheral blood stem and progenitor cells for the treatment of poor graft function after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 23(7):1072–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.03.019
Klyuchnikov E, El-Cheikh J, Sputtek A, Lioznov M, Calmels B, Furst S, Chabannon C, Crocchiolo R, Lemarie C, Faucher C, Bacher U, Alchalby H, Stubig T, Wolschke C, Ayuk F, Reckhaus ML, Blaise D, Kroger N (2014) CD34(+)-selected stem cell boost without further conditioning for poor graft function after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients with hematological malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 20(3):382–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.11.034
Kim DH, Sohn SK, Baek JH, Kim JG, Lee NY, Won DI, Suh JS, Lee KB (2006) Clinical significance of platelet count at day +60 after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. J Korean Med Sci 21(1):46–51. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.1.46
Kim DH, Sohn SK, Jeon SB, Baek JH, Kim JG, Lee NY, Suh JS, Lee KB, Shin IH (2006) Prognostic significance of platelet recovery pattern after allogeneic HLA-identical sibling transplantation and its association with severe acute GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant 37(1):101–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705203
Dominietto A, Raiola Anna M, Van Lint Maria T, Lamparelli T, Gualandi F, Berisso G, Bregante S, Frassoni F, Casarino L, Verdiani S, Bacigalupo A (2001) Factors influencing haematological recovery after allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplants: graft-versus-host disease, donor type, cytomegalovirus infections and cell dose. Br J Haematol 112(1):219–227. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02468.x
Mokart D, Darmon M, Resche-Rigon M, Lemiale V, Pene F, Mayaux J, Rabbat A, Kouatchet A, Vincent F, Nyunga M, Bruneel F, Lebert C, Perez P, Renault A, Hamidfar R, Jourdain M, Meert AP, Benoit D, Chevret S, Azoulay E (2015) Prognosis of neutropenic patients admitted to the intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med 41(2):296–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-014-3615-y
Agarwal S, O'Donoghue S, Gowardman J, Kennedy G, Bandeshe H, Boots R (2012) Intensive care unit experience of haemopoietic stem cell transplant patients. Intern Med J 42(7):748–754. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1445-5994.2011.02533.x
Bayraktar UD, Milton DR, Shpall EJ, Rondon G, Price KJ, Champlin RE, Nates JL (2017) Prognostic index for critically ill allogeneic transplantation patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 23(6):991–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.03.003
Azoulay E, Thiery G, Chevret S, Moreau D, Darmon M, Bergeron A, Yang K, Meignin V, Ciroldi M, Le Gall JR, Tazi A, Schlemmer B (2004) The prognosis of acute respiratory failure in critically ill cancer patients. Medicine 83(6):360–370
Harris AC, Young R, Devine S, Hogan WJ, Ayuk F, Bunworasate U, Chanswangphuwana C, Efebera YA, Holler E, Litzow M, Ordemann R, Qayed M, Renteria AS, Reshef R, Wölfl M, Chen Y-B, Goldstein S, Jagasia M, Locatelli F, Mielke S, Porter D, Schechter T, Shekhovtsova Z, Ferrara JLM, Levine JE (2016) International, multicenter standardization of acute graft-versus-host disease clinical data collection: a report from the Mount Sinai acute GVHD international consortium. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 22(1):4–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2015.09.001
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA, Lerner KG, Thomas ED (1974) Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation 18(4):295–304
Jagasia MH, Greinix HT, Arora M, Williams KM, Wolff D, Cowen EW, Palmer J, Weisdorf D, Treister NS, Cheng G-S, Kerr H, Stratton P, Duarte RF, McDonald GB, Inamoto Y, Vigorito A, Arai S, Datiles MB, Jacobsohn D, Heller T, Kitko CL, Mitchell SA, Martin PJ, Shulman H, Wu RS, Cutler CS, Vogelsang GB, Lee SJ, Pavletic SZ, Flowers MED (2015) National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. the 2014 diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 21(3):389–401.e381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.12.001
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ, Martin P, Chien J, Przepiorka D, Couriel D, Cowen EW, Dinndorf P, Farrell A, Hartzman R, Henslee-Downey J, Jacobsohn D, McDonald G, Mittleman B, Rizzo JD, Robinson M, Schubert M, Schultz K, Shulman H, Turner M, Vogelsang G, Flowers ME (2005) National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 11(12):945–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2005.09.004
Larocca A, Piaggio G, Podesta M, Pitto A, Bruno B, Di Grazia C, Gualandi F, Occhini D, Raiola AM, Dominietto A, Bregante S, Lamparelli T, Tedone E, Oneto R, Frassoni F, Van Lint MT, Pogliani E, Bacigalupo A (2006) Boost of CD34+−selected peripheral blood cells without further conditioning in patients with poor graft function following allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 91(7):935–940
Le Gall JR, Lemeshow S, Saulnier F (1993) A new simplified acute physiology score (SAPS II) based on a European/north American multicenter study. JAMA 270(24):2957–2963
Schellongowski P, Benesch M, Lang T, Traunmuller F, Zauner C, Laczika K, Locker GJ, Frass M, Staudinger T (2004) Comparison of three severity scores for critically ill cancer patients. Intensive Care Med 30(3):430–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-2043-1
Knaus WA, Zimmerman JE, Wagner DP, Draper EA, Lawrence DE (1981) APACHE-acute physiology and chronic health evaluation: a physiologically based classification system. Crit Care Med 9(8):591–597
Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonca A, Bruining H, Reinhart CK, Suter PM, Thijs LG (1996) The SOFA (Sepsis-Related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the working group on Sepsis-related problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med 22(7):707–710
Lameire NH, Bagga A, Cruz D, De Maeseneer J, Endre Z, Kellum JA, Liu KD, Mehta RL, Pannu N, Van Biesen W, Vanholder R (2013) Acute kidney injury: an increasing global concern. Lancet 382(9887):170–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60647-9
Scala R, Heunks L (2018) Highlights in acute respiratory failure. Eur Respir Rev 27(147)
Pène F, Aubron C, Azoulay E, Blot F, Thiéry G, Raynard B, Schlemmer B, Nitenberg G, Buzyn A, Arnaud P, Socié G, Mira J-P (2006) Outcome of critically ill allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation recipients: a reappraisal of indications for organ failure supports. J Clin Oncol 24(4):643–649. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.03.9073
Claushuis TA, van Vught LA, Scicluna BP, Wiewel MA, Klein Klouwenberg PM, Hoogendijk AJ, Ong DS, Cremer OL, Horn J, Franitza M, Toliat MR, Nurnberg P, Zwinderman AH, Bonten MJ, Schultz MJ, van der Poll T, Molecular D, Risk Stratification of Sepsis C (2016) Thrombocytopenia is associated with a dysregulated host response in critically ill sepsis patients. Blood 127(24):3062–3072. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-11-680744
Depuydt P, Kerre T, Noens L, Nollet J, Offner F, Decruyenaere J, Benoit D (2011) Outcome in critically ill patients with allogeneic BM or peripheral haematopoietic SCT: a single-Centre experience. Bone Marrow Transplant 46(9):1186–1191. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2010.255
Platon L, Amigues L, Ceballos P, Fegueux N, Daubin D, Besnard N, Larcher R, Landreau L, Agostini C, Machado S, Jonquet O, Klouche K (2016) A reappraisal of ICU and long-term outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients and reassessment of prognosis factors: results of a 5-year cohort study (2009-2013). Bone Marrow Transplant 51(2):256–261. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.269
Christou G, Kekre N, Petrcich W, Tokessy M, Neurath D, Giulivi A, Saidenberg E, McDiarmid S, Atkins H, Bence-Bruckler I, Bredeson C, Huebsch L, Sabloff M, Sheppard D, Tay J, Tinmouth A, Allan DS (2015) Impact of platelet transfusion on toxicity and mortality after hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation. Transfusion 55(2):253–258. https://doi.org/10.1111/trf.12817
Nevo S, Fuller AK, Zahurak ML, Hartley E, Borinsky ME, Vogelsang GB (2007) Profound thrombocytopenia and survival of hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients without clinically significant bleeding, using prophylactic platelet transfusion triggers of 10 x 10(9) or 20 x 10(9) per L. Transfusion 47(9):1700–1709. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1537-2995.2007.01345.x
Clark SR, Ma AC, Tavener SA, McDonald B, Goodarzi Z, Kelly MM, Patel KD, Chakrabarti S, McAvoy E, Sinclair GD, Keys EM, Allen-Vercoe E, DeVinney R, Doig CJ, Green FHY, Kubes P (2007) Platelet TLR4 activates neutrophil extracellular traps to ensnare bacteria in septic blood. Nat Med 13:463–469. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1565 https://www.nature.com/articles/nm1565#supplementary-information
Hara T, Shimizu K, Ogawa F, Yanaba K, Iwata Y, Muroi E, Takenaka M, Komura K, Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M, Sato S (2010) Platelets control leukocyte recruitment in a murine model of cutaneous Arthus reaction. Am J Pathol 176(1):259–269. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2010.081117
Xiang B, Zhang G, Guo L, Li X-A, Morris AJ, Daugherty A, Whiteheart SW, Smyth SS, Li Z (2013) Platelets protect from septic shock by inhibiting macrophage-dependent inflammation via the cyclooxygenase 1 signalling pathway. Nat Commun 4:2657. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3657 https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms3657#supplementary-information
Zhang X, Fu H, Xu L, Liu D, Wang J, Liu K, Huang X (2011) Prolonged thrombocytopenia following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and its association with a reduction in ploidy and an Immaturation of megakaryocytes. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 17(2):274–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.09.007
Song Y, Shi M-M, Zhang Y-Y, Mo X-D, Wang Y, Zhang X-H, Xu L-P, Huang X-J, Kong Y (2017) Abnormalities of the bone marrow immune microenvironment in patients with prolonged isolated thrombocytopenia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 23(6):906–912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.02.021
Kong Y, Chang Y-J, Wang Y-Z, Chen Y-H, Han W, Wang Y, Sun Y-Q, Yan C-H, Wang F-R, Liu Y-R, Xu L-P, Liu D-H, Huang X-J (2013) Association of an Impaired Bone Marrow Microenvironment with secondary poor graft function after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 19(10):1465–1473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.07.014
Acknowledgements
We thank Sabine Fiebig-Kuhnert for the logistical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TL, WL, and ATT designed the study. EB, WL, and ATT performed the statistical analysis. CS and WL performed the data collection. PW, MM, and FA participated in the data acquisition and analysis. ATT and TL wrote the manuscript. WL, DWB, and CS contributed to the writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was conducted in accordance with Good Clinical Practice Guidelines and the amended 1964 Declaration of Helsinki. The Institutional Ethical Review Board of the University Duisburg-Essen approved the protocol (board protocol no. 15–6446-BO).
Conflict of interest
ATT has received lecture fees from Jazz Pharmaceuticals and travel subsidies from Neovii Biotech outside the submitted work. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised due to a spelling error of the author name Philipp Wohlfarth.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplement Table S1
Causes of death (DOCX 16.6kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turki, A.T., Lamm, W., Schmitt, C. et al. Platelet number and graft function predict intensive care survival in allogeneic stem cell transplantation patients. Ann Hematol 98, 491–500 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3538-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3538-8