Abstract
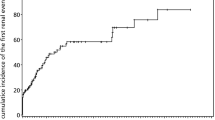
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare, life-threatening blood disease. With the advent of eculizumab treatment, renal function has substantially improved, although no data from real-world clinical practice are available. An observational, retrospective, multicenter study was conducted in Spain on clinical data obtained from outpatient visits of patients with PNH (Spanish PNH Registry) who had experienced acute (ARF) or chronic (CRF) renal failure. Of the 128 patients registered (April 2014), 60 were diagnosed with classic PNH. Twenty-seven (45.0%) patients with a mean age of 48.5 (±16.2) years had renal failure, ARF or CRF, and were included in this study. Near half of the patients (n = 13; 48.1%) presented with ARF alone, 33.3% (n = 9) had CRF with episodes of ARF, while 18.5% (n = 5) were diagnosed with CRF alone. For patients with diagnosis of PNH and renal failure (n = 27), the median time to the first ARF episode was 6.5 (CI 95%; 2.2, 14.9) years, whereas the median to the diagnosis of CRF was 14.5 (CI 95%; 3.8, 19.2) years after the diagnosis of PNH. Patients with ARF (n = 22) were treated with eculizumab and did not experience new episodes of ARF, except for one patient with sepsis. Of the patients with CRF, two received treatment without experiencing further episodes of ARF. Sixteen patients who completed treatment (11 with ARF and 5 with ARF + CRF) recovered from the episode of ARF or from CRF. Of the remaining patients treated with eculizumab, one patient improved from stages III to II, three patients stabilized without showing disease progression, and one patient progressed from stages III to IV. Treatment with eculizumab in PNH patients has beneficial effects on renal function, preventing ARF and progression to CRF.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brodsky RA (2009) How I treat paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 113:6522–6527
Hillmen P, Elebute M, Kelly R, Urbano-Ispizua A et al (2010) Long-term effect of the complement inhibitor eculizumab on kidney function in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am J Hematol 85:553–559
Hillmen P, Muus P, Röth A, Elebute MO et al (2013) Long-term safety and efficacy of sustained eculizumab treatment in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Br J Haematol 162:62–73
Takeda J, Miyata T, Kawagoe K, Iida Y (1993) Deficiency of the GPI anchor caused by a somatic mutation of the PIG-A gene in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Cell 73:703–711
Rother RP, Bell L, Hillmen P, Gladwin MT (2005) The clinical sequelae of intravascular hemolysis and extracellular plasma hemoglobin: a novel mechanism of human disease. JAMA 293:1653–1662
Kelly R, Richards S, Hillmen P, Hill A (2009) The pathophysiology of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and treatment with eculizumab. Ther Clin Risk Manag 5:911–921
Rachidi S, Musallam KM, Taher AT (2010) A closer look at paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Eur J Intern Med 21:260–267
Parker CJ (1991) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and glycosyl phosphatidylinositol anchored proteins that regulate complement. Clin Exp Immunol 86(Suppl. 1):36–42
Pu JJ, Brodsky RA (2011) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria from bench to bedside. Clin Transl Sci 4:219–224
Clark DA, Butler SA, Braren V, Hartmann RC et al (1981) The kidneys in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 57:83–89
Nath KA, Vercellotti GM, Grande JP, Miyoshi H et al (2001) Heme protein-induced chronic renal inflammation: suppressive effect of induced heme oxygenase-1. Kidney Int 59:106–117
Nishimura J, Kanakura Y, Ware RE, Shichishima T et al (2004) Clinical course and flow cytometric analysis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in the United States and Japan. Medicine 83:193–207
Hussain S, Qureshi A, Kazi J (2013) Renal involvement in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Nephron Clin Pract 123:28–35
Hillmen P, Hall C, Marsh JC, Elebute M et al (2004) Effect of eculizumab on hemolysis and transfusion requirements in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med 350:552–559
Hillmen P, Young NS, Schubert J, Brodsky RA et al (2006) The complement inhibitor eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med 355:1233–1243
Hillmen P, Muus P, Dührsen U, Risitano AM et al (2007) Effect of the complement inhibitor eculizumab on thromboembolism in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 110:4123–4128
Brodsky RA, Young NS, Antonioli E, Risitano AM et al (2008) Multicenter phase 3 study of the complement inhibitor eculizumab for the treatment of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 111:1840–1847
de Latour RP, Mary JY, Salanoubat C, Terriou L et al (2008) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: natural history of disease subcategories. Blood 112:3099–3106
Hill A, Rother RP, Wang X, Morris SM Jr et al (2010) Effect of eculizumab on haemolysis-associated nitric oxide depletion, dyspnoea, and measures of pulmonary hypertension in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Br J Haematol 149:414–425
Kelly RJ, Hill A, Arnold LM, Brooksbank GL et al (2011) Long-term treatment with eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: sustained efficacy and improved survival. Blood 117:6786–6792
Hill A, Sapsford RJ, Scally A, Kelly R et al (2012) Under-recognized complications in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria: raised pulmonary pressure and reduced right ventricular function. Br J Haematol 158:409–414
Hill A, Rother RP, Hillmen P (2005) Improvement in the symptoms of smooth muscle dystonia during eculizumab therapy in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Haematologica 90:ECR40
Reichel RR (2014) Acute kidney injury: quoi de neuf? Ochsner J 14:359–368
National Kidney Foundation (2002) K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 39(suppl 1):S1–S266
Ninomiya H, Obara N, Niiori-Onishi A, Yokoyama Y et al (2015) Improvement of renal function by long-term sustained eculizumab treatment in a patient with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Case Rep Hematol 2015:673195
Hill A, Richards SJ, Hillmen P (2007) Recent developments in the understanding and management of paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Br J Haematol 137:181–192
Muñoz-Linares C, Ojeda E, Forés R, Pastrana M et al (2014) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: a single Spanish center’s experience over the last 40 yr. Eur J Haematol 93:309–319
Schlaich MP, Schmitt D, Ott C, Schmidt BM, Schmieder RE (2008) Basal nitric oxide synthase activity is a major determinant of glomerular haemodynamics in humans. J Hypertens 26:110–116
Villegas A, González FA (2014) Renal manifestations in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). Grupo de Acción Médica ISSN 1889-7525. Deposito legal M-24749-2014. p 4–7
Hill A, Hillmen P, Richards SJ, Elebute D et al (2005) Sustained response and long-term safety of eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 106:2559–2565
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Prior to participation, written informed consent was obtained from all the patients included in the study or from their authorized representatives to retrospectively collect data from medical charts. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee in Human Experimentation of the Hospital Clínico San Carlos (Madrid, Spain) and procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the Helsinki Declaration, as revised in 2000.
Funding sources
This study was funded by Alexion Pharma Spain, SL (Barcelona, Spain).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villegas, A., Núñez, R., Gaya, A. et al. Presence of acute and chronic renal failure in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: results of a retrospective analysis from the Spanish PNH Registry. Ann Hematol 96, 1727–1733 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-017-3059-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-017-3059-x