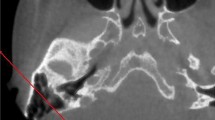
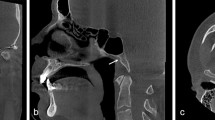
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this retrospective study was to assess the prevalence and morphometric features of the mastoid foramen (MF) and mastoid emissary canal (MEC) using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT), as well as their relationship with age, sex, and side.
Methods
CBCT scans of 500 patients aged 8–87 years were examined retrospectively. The presence and number of MF, mean diameter of the MEC and MF, MF location, and the distance between MF and asterion were all examined. The collected data were subjected to appropriate statistical analysis. P values < 0.05 were accepted as statistically significant at a 95% confidence interval.
Results
The study included 472 patients. MF was present in 82% and absent bilaterally in 18% of the 472 patients. The prevalence of MF was 67.8% on the right side and 65.7% on the left. The mean diameter of the MF was 3.39 ± 1.48 mm and the number of the MF ranged from zero to four. The mean diameter of the MEC was 2.05 ± 1.06 mm and the distance between MF and asterion was 22,46 ± 5,18 mm. 52.4% of the MF was observed on the occipito-mastoid suture.
Conclusion
To prevent surgical complications, particularly those that concern the temporal and mastoid areas, radiologists should report the results of the preoperative examination of the morphometry of the MF and MEC. CBCT imaging is a reliable diagnostic method that can be used to evaluate the MEC and MF before surgical procedures.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available upon request from the corresponding author.
References
Ahmad R, Ali I, Naikoo GM, Choo NA, Jan F (2011) Giant mastoid emissary vein: source of profuse bleeding during mastoid surgery. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 63:102–103
Bayrak S, Kurşun-Çakmak EŞ, Atakan C, Orhan K (2018) Anatomic study on sphenoidal emissary foramen by using cone-beam computed tomography. J Craniofac Surg 29:e477–e480
Berge JK, Bergman RA (2001) Variations in size and symmetry of foramina of the human skull. Clin Anat 14(6):406–413
Calligas JP, Todd NW (2014) Hemorrhage from large mastoid emissary vein: pedicled, rotated, indented, periosteal-galeal flap. Laryngoscope 124(2):551–553
Chauhan NS, Sharma YP, Bhagra T, Sud B (2011) Persistence of multiple emissary veins of posterior fossa with unusual origin of left petrosquamosal sinus from mastoid emissary. Surg Radiol Anat 33:827–831
Dahmani-Causse M, Marx M, Deguine O, Fraysse B, Lepage B, Escudé B (2011) Morphologic examination of the temporal bone by cone beam computed tomography: comparison with multislice helical computed tomography. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 128(5):230–235
Dalchow CV, Weber AL, Bien S, Yanagihara N, Werner JA (2006) Value of digital volume tomography in patients with conductive hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263(2):92–99
Dalchow CV, Weber AL, Yanagihara N, Bien S, Werner JA (2006) Digital volume tomography: radiologic examinations of the temporal bone. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186(2):416–423
Demirpolat G, Bulbul E, Yanik B (2016) The prevalence and morphometric features of mastoid emissary vein on multidetector computed tomography. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 75(4):448–453
Gulmez Cakmak P, Ufuk F, Yagci AB, Sagtas E, Arslan M (2019) Emissary veins prevalence and evaluation of the relationship between dural venous sinus anatomic variations with posterior fossa emissary veins: MR study. Radiol Med 124(7):620–627
Hadeishi H, Yasui N, Suzuki A (1995) Mastoid canal and migrated bone wax in the sigmoid sinus: technical report. Neurosurgery 36:1220–1223
Hadimani GA, Bagoji IB (2013) Study of mastoid canals and grooves in North Karnataka human skulls. J Clin Diagn Res 7(8):1537–1539
Hampl M, Kachlik D, Kikalova K, Riemer R, Halaj M, Novak V, Stejskal P, Vaverka M, Hrabalek L, Krahulik D, Nanka O (2018) Mastoid foramen, mastoid emissary vein and clinical implications in neurosurgery. Acta Neurochir 160(7):1473–1482
Hauser G, De Stefano GF (1989) Epigenetic variants of the human skull. E. Schweizerbartsche Verlagsbuchhhandlung, Stuttgart
Hoshi M, Yoshida K, Ogawa K, Kawase T (2000) Hypoglossal neurinoma–two case reports. Neurol Med Chir 40:489–493
Keskil S, Gözil R, Calgüner E (2003) Common surgical pitfalls in the skull. Surg Neurol 59:228–231
Kim LK, Ahn CS, Fernandes AE (2014) Mastoid emissary vein: anatomy and clinical relevance in plastic & reconstructive surgery. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 67:775–780
Koesling S, Kunkel P, Schul T (2005) Vascular anomalies, sutures and small canals of the temporal bone on axial CT. Eur J Radiol 54:335–343
Louis RG Jr, Loukas M, Wartmann CT, Tubbs RS, Apaydin N, Gupta AA, Spentzouris G, Ysique JR (2009) Clinical anatomy of the mastoid and occipital emissary veins in a large series. Surg Radiol Anat 31(2):139–144
Martinez F, Laxague A, Vida L, Prinzo H, Sgarbi N, Soria VR, Bianchi C (2005) Anatomía topográfica del asterion [Topographic anatomy of the asterion]. Neurocirugia (Astur) 16(5):441–446
Matsushima K, Kawashima M, Matsushima T, Hiraishi T, Noguchi T, Kuraoka A (2014) Posterior condylar canals and posterior condylar emissary veins—a microsurgical and CT anatomical study. Neurosurg Rev 37:115–126
Mortazavi MM, Tubbs RS, Riech S, Verma K, Shoja MM, Zurada A, Benninger B, Loukas M, Cohen Gadol AA (2012) Anatomy and pathology of the cranial emissary veins: a review with surgical implications. Neurosurgery 70:1312–1318
Muche A (2021) Morphometry of Asterion and its proximity to dural venous sinuses in Northwest Ethiopian Adult Skulls. J Craniofac Surg 32(3):1171–1173
Murlimanju BV, Chettiar GK, Prameela MD, Tonse M, Kumar N, Saralaya VV, Prabhu LV (2014) Mastoid emissary foramina: an anatomical morphological study with discussion on their evolutionary and clinical implications. Anat Cell Biol 47(3):202–206
Okudera T, Huang YP, Ohta T, Yokota A, Nakamura Y, Maehara F, Utsunomiya H, Uemura K, Fukasawa H (1994) Development of posterior fossa dural sinuses, emissary veins and jugular bulb: morphological and radiologic study. Am J Neuroradiol 15:1871–1883
Ozen O, Sahin C (2020) Evaluation of the mastoid emissary canals with computerized tomography in patients with chronic otitis media. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base 81(1):82–87
Pekçevik Y, Pekçevik R (2014) Why should we report posterior fossa emissary veins? Diagn Interv Radiol 20:78–81
Pekcevik Y, Sahin H, Pekcevik R (2014) Prevalence of clinically important posterior fossa emissary veins on CT angiography. J Neurosci Rural Pract 5:135–138
Pekçevik R, Öztürk A, Pekçevik Y, Toka O, Güçlü Aslan G, Çukurova İ (2021) Mastoid emissary vein canal incidence and its relationship with jugular bulb and sigmoid sulcus anatomical variations. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol 59(4):244–252
Pereira GA, Lopes PT, Santos AM, Pozzobon A (2013) Study of landmarks in dried skulls in a Brazil population. J Morphol Sci 30:94–97
Reis CV, Deshmukh V, Zabramski JM, Crusius M, Desmukh P, Spetzler RF, Preul MC (2007) Anatomy of the mastoid emissary vein and venous system of the posterior neck region: neurosurgical implications. Neurosurgery 61(5 Suppl 2):193–200
Robson CD, Mulliken JB, Robertson RL, Proctor MR, Steinberger D, Barnes PD, McFarren A, Muller U, Zurakowski D (2000) Prominent basal emissary foramina in syndromic craniosynostosis: correlation with phenotypic and molecular diagnoses. Am J Neuroradiol 21:1707–1717
Roser F, Ebner FH, Ememann U et al (2016) Improved CT imaging for mastoid emissary vein visualization prior to posterior fossa approaches. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg 77:511–514
San Millan Ruíz D, Gailloud P et al (2002) The craniocervical venous system in relation to cerebral venous drainage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1500–1508
Syed AZ, Sin C, Rios R, Mupparapu M (2016) Incidental occurrence of an unusually large mastoid foramen on cone-beam computed tomography and review of the literature. Imaging Sci Dent 46:39–45
Takahashi S, Sakuma I, Omachi K et al (2005) Craniocervical junction venous anatomy around the suboccipital cavernous sinus: evaluation by MR imaging. Eur Radiol 15:1694–1700
Tanoue S, Kiyosue H, Sagara Y et al (2010) Venous structures at the craniocervical junction: anatomical variations evaluated by multidetector row CT. Br J Radiol 83:831–840
Tsutsumi S, Ono H, Yasumoto Y (2017) The mastoid emissary vein: an anatomic study with magnetic resonance imaging. Surg Radiol Anat 39:351–356
Wang C, Lockwood J, Iwanaga J, Dumont AS, Bui CJ, Tubbs RS (2021) Comprehensive review of the mastoid foramen. Neurosurg Rev 44(3):1255–1258
Wysocki J, Reymond J, Skarzyński H, Wróbel B (2006) The size of selected human skull foramina in relation to skull capacity. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 65:301–308
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZZY: study design and conception, data collection and management, data analysis, manuscript writing, and editing. ÖO: study design and conception, data collection, manuscript editing. KO: supervision, study design and conception, and manuscript editing. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Statement is included in the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yurdabakan, Z.Z., Okumuş, Ö. & Orhan, K. The morphometric analysis of mastoid foramen and mastoid emissary canal on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). Surg Radiol Anat 45, 303–314 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-023-03089-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-023-03089-9