Abstract
Purpose
To assess normal distribution of fluid in the tendon sheaths of the ankle.
Methods
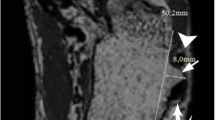
21 healthy volunteers were evaluated. Bilateral ankle MRI was performed on a 3T unit with PD-weighted images with fat saturation. The images were interpreted by two radiologists separately, and the short-axis dimension of fluid amount was measured. Bland–Altman plots and correlation plots were used to assess consistency between readers.
Results
There were 13 men and 8 women. The mean age was 24.7 years. Fluid in the retromalleolar part of the peroneus longus was seen in three ankles of three volunteers and in the inframalleolar part in three ankles of three volunteers. Fluid in the retromalleolar part of the peroneus brevis was seen in four ankles of three volunteers and in the inframalleolar part in three ankles of two volunteers. Fluid in the retromalleolar part of the tibialis posterior was seen in 37 ankles of 20 volunteers and in the inframalleolar part in 38 ankles of 21 volunteers Fluid in the retromalleolar part of the flexor digitorum was seen in 14 ankles of eight volunteers and in the inframalleolar part in 11 ankles of eight volunteers Fluid in the retromalleolar part of the flexor hallucis longus was seen in 23 ankles of 16 volunteers and in the inframalleolar part in 17 ankles of 11 volunteers.
Conclusion
Fluid is common in the retro- and inframalleolar parts of the medial tendons. Fluid is virtually absent in the peroneal tendons and anterior tendon sheaths in normal volunteers.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bencardino J, Rosenberg ZS, Delfaut E (1999) MR imaging of sports injuries of the foot and ankle. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 7:131–149
Cheung Y, Rosenberg Z, Magee T, Chinitz L (1992) Normal anatomy and pathologic conditions of ankle tendons: current imaging techniques. Radiographics 12:429–444
Nazarian LN, Rawool NM, Martin CE, Schweitzer ME (1995) Synovial fluid in the hindfoot and ankle: detection of amount and distribution with US. Radiology 197:275–278
O’Neill J, Pedowitz D, Kerbel Y, Codding J, Zoga A, Raikin S (2016) Peroneal tendon abnormalities on routine magnetic resonance imaging of the foot and ankle. Foot Ankle Int 37(7):743–747
Saxena A, Luhafiya A, Ewen B et al (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging and incidental findings of lateral ankle pathologic features with asymptomatic ankles. J Foot Ankle Surg 50(4):413–4156
Schmidt WA, Schmidt H, Schicke B, Gromma-Ihle E (2004) Standard reference values for musculoskeletal ultrasonography. Ann Rheum Diss 63:988–994
Schweitzer ME, van Leersum M, Ehrlich SS, Wapner K (1994) Fluid in normal and abnormal ankle joints: amount and distribution as seen on MR images. AJR Am J Roentgenol 162:111–114
Teitz CC, Garret WE, Miniaci A, Lee MH, Mann RA (1997) Tendon problems in athletic individuals. J Bone Jt Surg Ann 79:138–152
Trevino S, Baumhauer JF (1992) Tendon injuries of the foot and ankle. Clin Sports Med 11:727–739
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IW: data collection, analysis, writing. MS writing and final editing. LL: writing, editing. NB: data analysis. JM: analysis and final editing. SP: data collection and analysis. MM: data collection, analysis, writing and final editing
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial/personal conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Willekens, I., Shahabpour, M., Lenchik, L. et al. Fluid distribution in ankle tendon sheaths in healthy volunteers: MRI findings. Surg Radiol Anat 41, 1445–1449 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-019-02355-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-019-02355-z