Abstract
Purpose
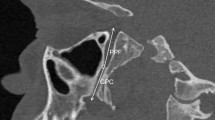
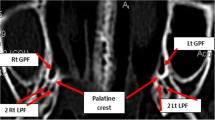
The pterygopalatine fossa is an important anatomical structure for several surgical and anaesthesiologic procedures; yet, very few data are available about its size. This study aims at providing a metrical assessment of pterygopalatine fossa through an innovative 3D segmentation procedure on head CT-scans.
Methods
CT-scans from 100 patients (50 males and 50 females) aged between 18 and 85 years were chosen for the study. Right and left pterygopalatine fossae were segmented through ITK-SNAP open source software. Height and volume were calculated on the acquired 3D models. In addition, anterior–posterior nasal spine distance, upper facial height (nasion–prosthion) and biorbital breadth (ectoconchion–ectoconchion) were measured as well. Statistically significant differences of height and volume according to sex and side were assessed through two-way ANOVA test: sexually dimorphic measurements were further assessed through one-way ANCOVA test using the three cranial measurements as covariates (p < 0.05).
Results
On average pterygopalatine fossa height was 24.1 ± 3.5 mm in males, and 22.8 ± 3.4 mm in females, whereas volume was 0.930 ± 0.181 cm3 in males and 0.817 ± 0.157 cm3 in females, with statistically significant differences according to sex (p < 0.05), but not to side (p > 0.05); interaction was negligible for both the measurements. ANCOVA test verified that sexual dimorphism of both measurements is independent from general cranial size (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
The present study highlighted the sexual dimorphism of pterygopalatine fossa: results may improve the knowledge of this anatomical structure difficult to explore, but crucial in several fields of clinics and surgery.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roberti F, Boari N, Mortini P, Caputy AJ (2007) The pterygopalatine fossa: an anatomic report. J Craniofac Surg 18:586–590
Tashi S, Purohit BS, Becker M, Mundada P (2016) The pterygopalatine fossa: imaging anatomy, communications, and pathology revisited. Insights Imaging 7:589–599
Allen GD (1984) Dental anaesthesia and analgesia (local and general). Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Cavallo LM, Messina A, Gardner P, Esposito F, Kassam AB, Cappabianca P, de Divitiis E, Tschabitscher M (2005) Extended endoscopic endonasal approach to the pterygopalatine fossa: anatomical study and clinical considerations. Neurosurg Focus 19:E5
Alvernia JE, Spomar DG, Olivero WC (2007) A computed tomography scan and anatomical cadaveric study of the pterygopalatine ganglion for use in Gamma Knife treatment of cluster headache. J Neurosurg 107:805–808
Sareen D, Agarwal AK, Kaul JM, Sethi A (2005) Study of sphenoid sinus anatomy in relation to endoscopic surgery. Int J Morphol 23:261–266
Stajcic Z, Todorovic LJ (1997) Blocks of the foramen rotundum and the oval foramen: a reappraisal of extra oral maxillary and mandibular nerve injections. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35:328–333
Stojcev Stajcic L, Gacic B, Popovic N, Stajcic Z (2010) Anatomical study of the pterygopalatine fossa pertinent to the maxillary nerve block at the foramen rotundum. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 39:493–496
Rusu MC, Didilescu AC, Jianu AM, Paduraru D (2013) 3D CBCT anatomy of the pterygopalatine fossa. Surg Radiol Anat 35:143–159
Erdogan N, Unur E, Baykara M (2003) CT anatomy of pterygopalatine fossa and its communications: a pictorial review. Comput Med Imaging Graph 27:481–487
Williams PL, Gray H, Bannister LH (1999) Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of medicine and surgery. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Codari M, Zago M, Guidugli GA, Pucciarelli V, Tartaglia GM, Ottaviani F, Righini S, Sforza C (2016) The nasal septum deviation index (NSDI) based on CBCT data. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 45:20150327
Yushkevich PA, Piven J, Hazlett HC, Smith RG, Ho S, Gee JC, Gerig G (2006) User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 31:1116–1128
Hwang SH, Seo JH, Joo YH, Kim BG, Cho JH, Kang JM (2011) An anatomic study using three-dimensional reconstruction for pterygopalatine fossa infiltration via the greater palatine canal. Clin Anat 24:576–582
Liu MC, Yin XR, Zhang YS, Yang W, Zhang HW, Duan HB, Liu JM, Cheng KL, Li YQ (2017) Computed tomography research: relative anatomy of Caldwell–Luc approach in pterygopalatine fossa surgery. J Craniofac Surg 28:1537–1540
Elhadi AM, Almefty KK, Mendes GA, Kalani MY, Kalani MY, Nakaji P, Dru A, Preul MC, Little AS (2014) Comparison of surgical freedom and area of exposure in three endoscopic transmaxillary approaches to the anterolateral cranial base. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base 75:346–353
Craiu C, Rusu MC, Hostiuc S, Sandulescu M, Derjac-Arama AI (2017) Anatomic variation in the pterygopalatine angle of the maxillary sinus and the maxillary bulla. Anat Sci Int 92:98–106
Pinheiro-Neto CD, Fernandez-Miranda JC, Rivera-Serrano CM, Paluzzi A, Snyderman CH, Gardner PA, Sennes LU (2012) Endoscopic anatomy of the palatovaginal canal (palatosphenoidal canal): a landmark for dissection of the vidian nerve during endonasal transpterygoid approaches. Laryngoscope 122:6–12
Sluder G (1913) Etiology, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of sphenopalatine ganglion neuralgia. JAMA 61:1201–1206
Bannon R, Parihar S, Skarparis Y, Varsou O, Cezayirli E (2018) 3D printing the pterygopalatine fossa: a negative space model of a complex structure. Surg Radiol Anat 40:185–191
Derinkuyu BE, Boyunaga O, Oztunali C, Alimli AG, Ucar M (2017) Pterygopalatine fossa: not a mystery! Can Assoc Radiol J 68:122–130
Wormald PJ, Athanasiadis T, Rees G, Robinson S (2005) An evaluation of effect of pterygopalatine fossa injection with local anesthetic and adrenalin in the control of nasal bleeding during endoscopic sinus surgery. Am J Rhinol 19:288–292
Nique TA, Bennett RC (1981) Inadvertent brainstem anaesthesia following extra oral trigeminal V2–V3 blocks. Oral Surg 51:468–470
Gallardo CAC, Galdames ICS, Lopez MGC, Matamala DAZ (2008) Relationship between pterygopalatine fossa volume and cephalic and upper facial indexes. Int J Morphol 26:393–396
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ms. Annalisa Gadler for data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DG: project development, data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing, manuscript editing. MC: project development, data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing, manuscript editing. SG: project development, data collection, manuscript editing. AC: data analysis, manuscript writing, manuscript editing. MMP: data analysis, manuscript editing. AGO: data collection, manuscript editing. GT: data collection, manuscript editing. CD: data analysis, manuscript editing. CS: project development, data analysis, manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gibelli, D., Cellina, M., Gibelli, S. et al. Anatomy of the pterygopalatine fossa: an innovative metrical assessment based on 3D segmentation on head CT-scan. Surg Radiol Anat 41, 523–528 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2153-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2153-7