Abstract
Introduction
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of percutaneous thermal ablation of liver tumours in a juxta-cardiac (JC) location.
Materials and Methods
From January 2010 to December 2014, out of 274 cases of hepatic ablation, 33 consecutive patients who received thermal ablation (radiofrequency or microwave) to left hepatic lobe tumours were included in this study. Patients were divided into two groups: JC or non-juxta-cardiac (NJC) (tumour margin ≤ 10 mm or > 10 mm from the cardiac border, respectively). Imaging follow-up was performed at 6-week and 3-monthly intervals. Technical success, 30-day complications and local tumour control/recurrence were recorded. Statistical analysis was performed with t test and Fisher’s test. Univariate and multivariate survival analyses were performed using Cox regression.
Results
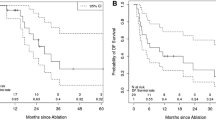
Patients comprised of 23 men and 10 women (mean age 67.0 years). Mean tumour size was 2.2 ± 0.9 cm (28 hepatocellular carcinoma and 5 metastases). Mean follow-up time was 21.2 months (range 2–72 months). There were no differences between the JC and NJC groups in the rates of complete ablation (86.7 vs 83.3% P = 1.0), tumour recurrence (20.0 vs 22.2%, P = 0.95) or complication rates (6.7 vs 11.1% P = 1.0). Metastatic lesions were associated with a higher rate of recurrent disease (hazard ratio 3.86, 95% CI 1.0–14.8%, P = 0.05).
Discussion
Percutaneous thermal ablation of JC tumours has similar rates of local tumour control and safety profile when compared to tumours in a NJC location. Tumours in a JC location should not be considered a contraindication for thermal ablation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tombesi P, Di Vece F, Sartori S. Resection vs thermal ablation of small hepatocellular carcinoma; what’s the 1st choice? World J Radiol. 2013;5(1):1–4.
Alexander ES, Wolf FJ, Machan JT, Charpentier KP, Beland MD, Lannuccilli JD, et al. Microwave ablation of focal hepatic malignancies regardless of size: a 9-year retrospective study of 64 patients. Eur J Radiol. 2015;84(6):1083–90.
Gazelle GS, Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Livraghi T. Tumor ablation with radio-frequency energy. Radiology. 2000;217(3):633–46.
Tateishi R, Shinna S, Teratani T, Obi S, Sato S, Koike Y, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma—an analysis of 1000 cases. Cancer. 2005;103(6):1201–9.
Choi D, Lim HK, Kim MJ, Kim SH, Lee WJ, Kim SH, et al. Therapeutic efficacy and safety of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the gastrointestinal tract. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183(5):1417–24.
Teratani T, Yoshida H, Shiina S, Obi S, Sato S, Tateishi R, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in so-called high-risk locations. Hepatology. 2006;43(5):1101–8.
Chopra S, Dodd GD 3rd, Chanin MP, Chintapalli KN. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors adjacent to the gallbladder: feasibility and safety. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;180(3):697–701.
Snoeren N, Nijkamp MW, Berendsen T, Govaert KM, van Kessel CS, Borel Rinkes IH, et al. Multipolar radiofrequency ablation for colorectal liver metastases close to major hepatic vessels. Surgeon. 2015;13(2):77–82.
Meloni MF, Goldberg SN, Moser V, Piazza G, Livraghi T. Colonic perforation and abscess following radiofrequency ablation treatment of hepatoma. Eur J Ultrasound. 2002;15(1–2):73–6.
Mulier S, Mulier P, Ni Y, Miao Y, Dupas B, Marchal G, De Wever I, et al. Complications of radiofrequency coagulation of liver tumours. Br J Surg. 2002;89(10):1206–22.
Carberry GA, Smolock AR, Cristescu M, Wells SA, Ziemlewicz TJ, Lubner MG, et al. Safety and Efficacy of percutaneous microwave hepatic ablation near the heart. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017;28(4):490–7.
Carberry GA, Nocerino E, Mason PJ, Schwahn DJ, Hetzel S, Turnquist AM, et al. Pulmonary microwave ablation near the heart: antenna positioning can mitigate cardiac complications in a porcine model. Radiology. 2017;282(3):892–902.
Morrison PR, vanSonnenberg E, Shankar S, Godleski J, Silverman SG, Tuncali K, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of thoracic lesions: part 1, experiments in the normal porcine thorax. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;184(2):375–80.
Lu DS, Raman SS, Vodopich DJ, Wang M, Sayre J, Lassman C. Effect of vessel size on creation of hepatic radiofrequency lesions in pigs: assessment of the ‘heat sink’ effect. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;1787:47–51.
Iguchi T, Hiraki T, Gobara H, Mimura H, Fujiwara H, Tajiri N, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung tumours close to the heart or aorta: evaluation of safety and effectiveness. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007;18(6):733–40.
Omary RA, Bettmann MA, Cardella JF, Bakal CW, Schwartzberg MS, Sacks D, et al. Quality improvement guidelines for the report and archiving of interventional radiology procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002;13:879–81.
Livraghi T, Solbiati L, Meloni MF, Gazelle GS, Halpern EF, Goldberg SN. Treatment of focal liver tumors with percutaneous radio-frequency ablation: complications encountered in a multicenter study. Radiology. 2003;226(2):441–51.
Kim SK, Rhim H, Kim YS, Koh BH, Cho OK, Seo HS, et al. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors: pitfalls and challenges. Abdom Imaging. 2005;30(6):727–33.
Ding J, Jing X, Liu J, Wang Y, Wang F, Wang Y, et al. Complications of thermal ablation of hepatic tumours: comparison of radiofrequency and microwave ablative techniques. Clin Radiol. 2013;68(6):608–15.
Song I, Rhim H, Lim HK, Kim YS, Choi D. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the diaphragm and gastrointestinal tracts with the use of artificial ascites: safety and technical efficacy in 134 patients. Eur Radiol. 2009;19(11):2630–40.
Hakime A, Tselikas L, Otmezguine Y, Deschamps F, de Baere T. Artificial ascites for pain relief during microwave ablation of subcapsular liver tumours. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2015;38(6):1557–62.
Pua U. Transmitted water pump vibration precluding intraprocedureal electrocardiographic monitoring in juxtacardiac microwave ablation of liver tumour. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012;23(6):847–8.
Dachman AH, McGhee JA, Beam TE, Burris JA, Powell DA. US-guided percutaneous laser ablation of liver tissues in a chronic pig model. Radiology. 1990;176(1):129–33.
Rossi S, DiStasi M, Buscarini E, Quaretti P, Garbagnati F, Squassante L, et al. Percutaneous RF interstitial thermal ablation in the treatment of hepatic cancer. AJR. 1996;167(3):759–68.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Ms. Sun Bing Fan for helping with the statistical analysis of the results within this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Video 1
Sagittal oblique ultrasound cine clip taken during immediately after the ablation procedure of the same patient, demonstrating the extent of the gas cloud extending to the cardiac margin interface (MOV 1720 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwan, J., Appuhamy, C., Lim, G.H.T. et al. Safety and Efficacy of Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Juxta-Cardiac Hepatic Tumours. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 41, 920–927 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-018-1938-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-018-1938-8