Abstract
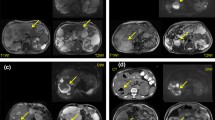
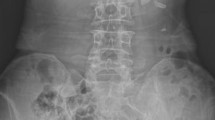
The course of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is frequently complicated by infection of a cyst within a polycystic kidney, which is a diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma damaging the clinical course of patients. The aim of this study was to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of percutaneous drainage in management of infected cysts in ADPKD patients. Between May 2003 and December 2006, percutaneous drainage was performed in 16 infected renal cysts of four kidneys in three patients (two females, one male), with a mean age of 57.3 years. Cyst dimensions, total amount of drained cyst fluid, catheterization duration, isolated microorganisms, and follow-up duration were recorded. Technical, clinical success rates were 100%; the complication rate was 0%. Diameters of cysts ranged between 3 and 8 cm. Average volume of drained fluid and average duration of catheterization for one cyst were 226 ml and 9.8 days. No recurrence was encountered but one patient (no. 3), who had pyocystis in the right kidney and was treated with catheterization, referred with left flank pain due to pyocystis in her left kidney 3 months later. Follow-up durations were 35, 47, and 11 months for patients 1, 2, and 3, respectively. For patient 3, follow-up duration for the second procedure was 7 months. We conclude that percutaneous drainage with antibiotic therapy should be the initial method in management of infected cysts in ADPKD patients, with high success and low complication rates.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Romao EA, Moyses Neto M, Teixeira SR, Muglia VF, Vieira-Neto OM, Dantas M (2006) Renal and extrarenal manifestations of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Braz J Med Biol Res 39:533–538
Gibson P, Watson ML (1998) Cyst infection in polycystic kidney disease: a clinical challenge. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:2455–2457
Gabow PA (1993) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 329:3323–3342
Elzinga LW, Golper TA, Rashad AL, Carr ME, Bennett WM (1988) Ciprofloxacin activity in cyst fluid from polycystic kidneys. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 32:844–847
Rothermel FJ, Miller FJ Jr, Sanford E, Drago J, Rohner TJ (1977) Clinical and radiographic findings of focally infected polycystic kidneys. Urology 9:580–585
Wetzel O, Hormi M, Le Normand L, et al. (1993) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: urologic complications and results of kidney transplantation: 217 patients. Prog Urol 3:252–262
Chapman AB, Thickman D, Gabow PA (1990) Percutaneous cyst puncture in the treatment of cyst infection in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis 16:252–255
Palou J, Monreal F, Caparros J, Marti J, Calero F, Ballarin J (1998) Percutaneous drainage by multiple and bilateral puncture of infected renal cysts in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:1606–1608
Kaim AH, Burger C, Ganter CC, et al. (2001) PET-CT-guided percutaneous puncture of an infected cyst in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: case report. Radiology 221:818–821
Erkoc R, Sayarlioglu H, Ceylan K, Dogan E, Kara PS (2006) Gas-forming infection in a renal cyst of a patient with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:555–556
Van Zijl PS, Chai TC (2004) Gas-forming infection from Clostridium perfringens in a renal cyst of a patient with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Urology 63:1178–1179
Schwab SJ, Bander SJ, Klahr S (1987) Renal infection in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Am J Med 82:714–718
Sklar AH, Caruana RJ, Lammers JE, Strauser GD (1987) Renal infections in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis 10:81–88
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akinci, D., Turkbey, B., Yilmaz, R. et al. Percutaneous Treatment of Pyocystis in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 31, 926–930 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-007-9273-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-007-9273-5