Abstract
Background
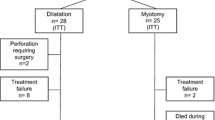
The most effective therapeutic strategy in newly diagnosed achalasia is yet to be established. Therefore we designed a study in which pneumatic dilatation was compared to laparoscopic cardiomyotomy to which was added a partial posterior fundoplication.
Patients and Results
A series of 51 patients (24 males, mean age 44 years) were randomly allocated to the therapeutic modalities (dilatation = 26, surgery = 25). All patients were followed for at least 12 months, and during that period the pneumatic dilatations strategy had significantly more treatment failures (P = 0.04). Only minor differences emerged between the study groups when symptoms, dysphagia scorings, and quality-of-life assessments were evaluated 12 months after initiation of therapy.
Conclusions
Laparoscopic myotomy was found to be superior to an endoscopic balloon dilatation strategy in the treatment of achalasia when studied during the first 12 months after treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Park W, Vaezi MF. Etiology and pathogenesis of achalasia: the current understanding. Am J Gastroenterol 2005;100:1404–1414
Ott DJ Motility disorders of the esophagus. In Gore RM, Levine MS, editors. Textbook of Gastrointestinal Radiology, 2nd ed. Philadelphia, WB Saunders Company, 2000;316–328
Castell DO. Esophageal disorders in the elderly. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 1990;19:235–254
Howard PJ, Maher L, Pryde A, et al. Five years prospective study of the incidence, clinical features, and diagnosis of achalasia in Edinburgh. GUT 1992;33:1011–1015
Hirano I, Tatum RP, Shi G, et al. Manometric heterogeneity in patients with idiopathic achalasia. Gastroenterology 2001;120:789–798
Ho K, Tay HH, Kang JY. A prospective study of the clinical features, manometric findings, incidence and prevalence of achalasia in Singapore. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1999;14:791–795
Mayberry JF, Atkinson M. Epidemiology and demographics of achalasia. Gastrointest Endosc Clin North Am 2001;11:235–248
Katz PO, Richter JE, Cowan R, et al. Apparent complete lower esophageal sphincter relaxation in achalasia. Gastroenterology 1986;90:978–983
Mearin F, Malegelada JR. Complete lower esophageal spincter relaxation observed in achalasia patients is functionally inadequate. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2000; 278:G376–G383
Van Herwaarden MA, Samsom M, Smout AJPM. Prolonged manometric recordings of oesophagus and lower oesophageal sphincter in achalasia patients. Gut 2001;49:813–821
Michael J, Fazel J, Montazeri G, et al. Randomized trial comparing Botulinus toxin injection to pneumatic dilatation for the treatment of achalasia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2001;15:1389–1396
Bansal R, Nostrand TT, Scheiman JM, et al. Intrasphincteric Botulinus toxin versus pneumatic dilation for treatment of primary achalasia. J Clin Gastroenterol 2003;36:209–214
Zaninotto G, Vergadoro V, Annese M, et al. Botulinus toxin injection versus laparoscopic myotomy for the treatment of esophageal achalasia: Surg Endosc 2004:18:691–695
Abir F, Modlin I, Kidd M, et al. Surgical treatment of achalasia: current status and controversies. Dig Surg 2004;21:165–176
Watson DI, Pike GK, BaigrieRJ, et al. Prospective double blind randomized trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with division and without division of short gastric vessels. Ann Surg 1997;22:642–652
Dimenäs E, Carlsson G, Glise H, et al. Relevance of norm values as part of the documentation of quality of life instruments for use in upper gastrointestinal disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 1996;31(Suppl 221):8–13
Dimenas E. Methodological aspects of evaluation of quality of life in upper gastrointestinal diseases. Scan J Gastroenterol 1993; 28(Suppl 199):18–21
Patrick DL, Deyo RA. Generic and disease-specific measures in assessing health status and quality of life. Med Care 1989; 27(Suppl): 217–232
Dupuy HJ. The Psychological General Well-Being (PGWB) index. In Wenger NK, Mattson ME, Furberg CF, editors, Assessment of Quality of Life in Clinical Trials of Cardiovascular Therapies. USA, LeJacq Publishing Inc, Malden, MA, 1984;170–183
Svedlund J, Sjödin I, Dotevall G. GSRS. A clinical rating scale for gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and peptic ulcer disease. Dig Dis Sci 1988;33
Svedlund J, Sullivan M, Sjodin I, et al. Quality of life in gastric cancer prior to gastrectomy. Qual Life Res 1996;5:255–264
Kostics S, Lönroth H, Lundell L. Leakage testing at the time of surgical oesophageal myotomy. Dig Surg 2004;21:223–226
Toupet A. Technique d’oesophago-gastroplastie avec phreno-gastropexie appliquee dans la cure radicale des hernies hiatales et comme complement de l’operation d’Heller dans les cardiospasmes. Mem Acad Chir 1963;89:394–399
Lundell L, Miettinen P, Myrvold H, et al. Continued (5-year) follow-up of a randomised clinical study comparing antireflux surgery and omeprazole in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 2001;192:172–181
Csendes A, Velasco N, Braghetto J, et al. A prospective randomised study comparing forceful dilatation and esophagomyotomy in patients with achalasia of the esophagus. Gastroenterology 1981;80:789–795
Csendes A, Braghetto J, Henriquez A, et al. Late results of a prospective randomised study comparing forceful dilatation and esophagomyotomy in patients with achalasia of the esophagus. GUT 1989;30:299–304
St Peter SD, Swain JM. Achalasia. A comprehensive review. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 2003;13:227–240
Gideon RH, Castell DO, Yarze J. Prospective randomized comparison of pneumatic dilatation technique in patients with idiopathic achalasia. Dig Dis Sci 1999;9:1853–1857
Bishehsari JMF, Montazeri G, Yaghoobi M, et al. Pneumatic balloon dilatation in achalasia: a prospective comparison of safety and efficacy with different balloon diameters. Aliment. Pharamacol Ther 2004;20:431–436
Khan AA, Shah SWH, Alam A, et al. Sixteen years follow up of achalasia: a prospective study of graded dilatation using Rigiflex balloon. Dis Esophagus 2005;18:41–45
West RL, Hirsch DP, Bartelsman JFWM, et al. Long-term results of pneumatic dilation in achalasia followed for more than 5 years. Am J Gastroenterol 2002;97:1346–1351
Andreollo NA, Earlam JH. Hellers myotomy for achalasia: is an added antireflux procedure necessary? Br J Surg 1987;774:765–769
Csendes A, Braghetto I, Burdiles P, et al. Very late results of esophagomyotomy for patients with achalasia. Ann Surg 2006;243:196–203
Bonavina L, Nosadini A, Bardini R, et al. Primary treatment of esophageal achalasia. Long-term results of myotomy and Dor fundoplication. Arch Surg 1992;127:222–226
Patti MG, Molena D, Fisichella PM, et al. Laparoscopic Heller myotomy and Dor fundoplication for achalasia. Arch Surg 2001;136:870–877
Vantrappen G, Hellemans J, Deloof W, et al. Treatment of achalasia with pneumatic dilatation. GUT 1971;12:268–275
Perrone JM, Frisella M, Desai KM, et al. Results of laparoscopic Heller-Toupet operation for achalasia. Surg Endosc 2004;18:1565–1571
Ramacciato G, Dángelo FA, Aurello P, et al. Laparoscopic Heller myotomy with or without partial fundoplication: a matter of debate. World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:1558–1561
Dempsey DT, Delano M, Bradley K, et al. Laparoscopic esophagomyotomy for achalasia. Does anterior hemifundoplication affect clinical outcome? Ann Surg 2004;239:779–787
Richards WO, Torquati A, Holzman MD, et al. Heller myotomy versus Heller myotomy with Dor fundoplication for achalasia. A prospective randomized double blind clinical trial Ann Surg 2004;240:405–415
Lundell L, Abrahamsson H, Ruth M, et al. Long-term results of a prospective randomized comparison of total fundic wrap (Nissen-Rossetti) or semifundoplication (Toupet) for gastrooesophageal reflux. Br J Surg 1996;83:830–835
Rydberg L, Ruth M, Lundell L. Mechanism of action of antireflux procedures. Br J Surg 1999;86:405–410
Velanovich V, Vallance SR, Gusz JR, et al. Quality of life scale for gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 1996;183:217–224
Blomqvist A, Dalenbäck J, Hagedorn C, et al. Impact of complete gastric fundus mobilization on outcome after laparoscopic total fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 2000;4:493–500
Decker G, Borie F, Bouamrirene D. Gastrointestinal quality of life before and after laparoscopic Heller myotomy with partial posterior fundoplication. Ann Surg 2002;236:750–758
Ben-Meyer A, Urbach DR, Kajanchee YS, et al. Quality of life before and after laparoscopic Heller myotomy for achalasia. Am J Surg 2001;181:471–474
Raptopoulos Y, Landreneau RJ, Hayetian F, et al. Factors affecting quality of life after minimally invasive Heller myotomy for achalasia. J Gastrointest Surg 2004;8:233–239
Urbach DR, Tomlinson GA, Harnish JL, et al. A measure of disease-specific health related quality of life for achalasia. Am J. Gastroenterol 2005;100:1668–1676
Dimenäs E, Glise H, Hallerbäck B, et al. Well-being and gastrointestinal symptoms among patients referred to endoscopy owing to suspected duodenal ulcer. Scand J Gastroenterol 1995;30:1046–1052
Kamolz T, Pointner R, Velanovich V. The impact of gastroesophageal reflux disease on quality of life. Surg Endosc 2003;17:1193–1199
Blomqvist A, Lönroth H, Dalenbäck J, et al. Quality of life assessment after laparoscopic and open fundoplications. Results of a prospective, clinical study. Scand J Gastroenterol 1996;31:1052–1058
Havelund T, Lind T, Wiklund I, et al. Quality of life patients with heartburn but without esophagitis: effects of treatment with omeprazole. Am J Gastroenterol 1999;94:1782–1789
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostic, S., Kjellin, A., Ruth, M. et al. Pneumatic Dilatation or Laparoscopic Cardiomyotomy in the Management of Newly Diagnosed Idiopathic Achalasia. World J. Surg. 31, 470–478 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-006-0600-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-006-0600-9