Abstract
Background
The aim in umbilicoplasty is to obtain a scar that is less visible, the appropriate navel shape and depth. In our study, we aimed to achieve a more natural and younger appearance of the navel which significantly affects the aesthetic result after abdominoplasty. Modification of diamond-shaped umbilicoplasty technique and clinical results were evaluated.
Patients and Methods
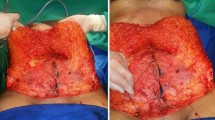
Fifty-three patients were included in the study. Modified diamond-shaped umbilicoplasty was performed in 21 patients, and diamond-shaped umbilicoplasty was performed in 32 patients. Demographic data, complications, revision surgery, and follow-up periods of the patients were reviewed retrospectively. Different from the standard technique, we deepithelialized the diamond-shaped skin over the abdomen flap and designed four triangular flaps. Then, the navel was inset over these four flaps.
Results
Forty-six (86.8%) of the patients were females and 7 (13.2%) were males, with a mean age of 39.49 ± 9.18 years, ranging from 22 to 57 years. Complications were occurred in 9 patients in total. There was no difference between groups in complication rates. The mean VAS value of the patients in the MDSU group was 9.48 ± 0.75, it was 8.28 ± 0.99 in the DSU group, and the difference was statistically significant (p:0.001). The mean age of the MDSU group was found to be significantly higher than the DSU group (p:0.008). The BMI of the MDSU group was found to be significantly higher between two groups (p:0.009).
Discussion
In our study, there was no difference between the complication rates of the two techniques. Therefore, MDSU is a reliable technique. High VAS score of the patients of MDSU was statistically significant. This shows that this modification provides good aesthetic results.
Conclusion
Modified diamond-shaped umbilicoplasty is easy to perform and provides better aesthetic results.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Visconti G, Visconti E, Bonomo L, Salgarello M (2015) Concepts in navel aesthetic: a comprehensive surface anatomy analysis. Aesthet Plast Surg 39(1):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-014-0434-z
Pallua N, Markowicz MP, Grosse F, Walter S (2010) Aesthetically pleasant umbilicoplasty. Ann Plast Surg 64(6):722–725. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e3181ba5770
Delpierre V, Coquerel-Beghin D, Aktouf A, Auquit-Auckbur I, Milliez PY (2012) Biometric and morphometric analyse of the umbilicus: about 70 cases. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 57(6):575–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anplas.2011.10.006
Hodgkinson DJ (1983) Umbilicoplasty: conversion of “outie” to “innie.” Aesthet Plast Surg 7(4):221–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01570663
Matarasso A, Matarasso DM, Matarasso EJ (2014) Abdominoplasty: classic principles and technique. Clin Plast Surg 41(4):655–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2014.07.005
Massiha H, Montegut W, Phillips R (1997) A method of reconstructing a natural-looking umbilicus in abdominoplasty. Ann Plast Surg 38(3):228–231. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000637-199703000-00007
Akbaş H, Güneren E, Eroǧlu L, Uysal OA (2003) Natural-looking umbilicus as an important part of abdominoplasty. Aesthet Plast Surg 27(2):139–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-003-0109-7
Juri J, Juri C, Raiden G (1979) Reconstruction of the umbilicus in abdominoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 63(4):580–582. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-197904000-00032. (PMID: 424470)
Lesavoy MA, Fan K, Guenther DA, Herrera F, William LJ (2012) The inverted-V chevron umbilicoplasty for breast reconstruction and abdominoplasty. Aesthet Surg J 32(1):110–116. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820X11430686
Dogan T (2010) Umbilicoplasty in abdominoplasty: a new approach. Ann Plast Surg 64(6):718–721. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e3181b02210
Kurt Yazar S, Serin M, Diyarbakırlıoğlu M, Şirvan SS, Irmak F, Yazar M (2019) Comparison of aesthetic outcome with round and three-armed star flap umbilicoplasty. J Plast Surg Hand Surg 53(4):227–231. https://doi.org/10.1080/2000656X.2019.1582424
Rozen SM, Redett R (2007) The two-dermal-flap umbilical transposition: a natural and aesthetic umbilicus after abdominoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 119(7):2255–2262. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000261037.69256.3e
Kajikawa A, Ueda K, Katsuragi Y, Kimura S, Hasegawa A (2012) How to reconstruct a natural and deep umbilicus: three methods of umbilicoplasty for five types of umbilical deformities. Ann Plast Surg 68(6):610–615. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e3182198c27
Hespe GE, Stepien DM, Sherif RD, Gilman RH (2021) Umbilicoplasty in abdominoplasty: modifications for improved aesthetic results. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum 3(3):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/asjof/ojab025
Visconti G, Salgarello M (2016) The divine proportion ace of spades umbilicoplasty a new method of navel positioning and plasty in abdominoplasty. Ann Plast Surg 76(3):265–269. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000000579
Dubou R, Ousterhout DK (1978) Placement of the umbilicus in an abdominoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 61(2):291–293. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-197802000-00030. (PMID: 622423)
Abhyankar SV, Rajguru AG, Patil PA (2006) Anatomical localization of the umbilicus: an Indian study. Plast Reconstr Surg 117(4):1153–1157. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000204793.70787.42
Rohrich RJ, Sorokin ES, Brown SA, Gibby DL (2003) Is the umbilicus truly midline? Clinical and medicolegal implications. Plast Reconstr Surg 112(1):259–263. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000066367.41067.C2
Lee SJ, Garg S, Lee HP (2014) Computer-aided analysis of the beautiful umbilicus. Aesthet Surg J 34(5):748–756. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820X14533565
Correia N, Jayyosi L, Chiriac S et al (2018) Morphometric analysis of the umbilicus according to age. Aesthet Surg J 38(6):627–634. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjx184
Funding
In the study, we do not have any financial or material support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was exempt from ethical board approval as there was a low and negligible risk to any participants. The identity of all participants was kept confidential.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Preoperative video of the patient (MP4 7430 kb) Video 1
Early postoperative video of the patient (MP4 8554 kb) Video 2
Short video of the surgical procedure (MP4 191544 kb) Video 3
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Çelik, V., Tuluy, Y. & Sır, E. Modified Diamond-Shaped Umbilicoplasty in Abdominoplasty. Aesth Plast Surg 47, 1911–1919 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03303-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03303-4