Abstract
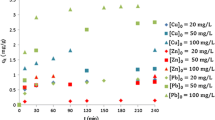
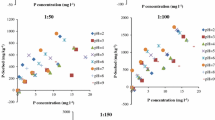
Various soil zones such as Bw, C1, and C3 are developed on spilite. Montmorillonite, vermiculite and chlorite is moderately occurred in the C1 and C3 soil zones, in contrast montmorillonite and vermiculite are absent in Bw soils whereas illite and sesquioxide are relatively increased. The high cation exchange capacity (CEC) of montmorillonite and vermiculte and moderate CEC of chlorite and illite resulted in the high adsorption of heavy metals. The adsorption of the heavy metals on spilite soil zones was studied at different concentrations and pH levels. Heavy metals like lead, cadmium, and copper were selected for adsorption studies considering their contribution as toxic metals in the environment. The initial solute concentrations ranged from 7.0 × 10−3 to 1.0 × 102 mg/L. The sorption behavior of Cd2+, Pb2+, and Cu2+ on soil zones of spilite was investigated using the batch equilibrium technique at 25°C. The characteristics of the adsorption process were investigated using Scatchard plot analysis (q/C vs. q) by the batch equilibrium technique at 25°C. In the adsorption of heavy metals, deviation from linearity in the plot of q/C versus q was observed, indicating the presence of multi-model interaction and non-Langmuirean behavior. When the Scatchard plot showed a deviation from linearity, greater emphasis was placed on the analysis of the adsorption data in terms of the Freundlich model, in order to construct the adsorption isotherms of the metal(s) at particular concentration(s) in solutions. The adsorption behavior of these metal ions on spilite soil zones is expressed by the Freundlich isotherms. Adsorption constants and correlation coefficients for the Cd, Pb, and Cu on spilite soil zones were calculated from Freundlich plots.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayar A, Pekacar AI, Mercimek B (2003) Determination of binding constants of labile ligands in metal-ligand complexes containing carboxylic groups bound polymer by using breakthrough technique. Colloids Surf A 212:51–55
Benincasa E, Brigatti MF, Malferrari D, Medici L, Poppi L (2002) Sorption of Cd–cysteine complexes by kaolinite. Appl Clay Sci 21:191–201
Bojemueller E, Nennemann A, Lagaly G (2001) Enhanced pesticide adsorption by thermally modified bentonites. Appl Clay Sci 18:277–284
Brindley GW (1980) Quantitative X-ray analysis of clays. In Brindley GW, Brown G (eds) Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals, their X-ray Identification, vol 5. Mineralogical Society Monograph, London, pp 411–438
Eren M, Kadir S (1999) Colour origin of upper cretaceous pelagic red sediments within the Eastern Pontides, northern Turkey. Inter J Earth Sci 88:593–595
Ghosh D, Bhattacharyya KG (2002) Adsorption of methylene blue on kaolinite. Appl Clay Sci 20:295–300
Gürel A (1991) Veränderung im Stoffbestand der Verwitterungsdecke als Folge natürlicher Bodenbildungsprozesse und antropogener atmosphärischer Deposition. Berichte Forschungszentrums Waldökosysteme. Universität Göttingen, Reich A, Bd. pp. 82
Lawrence MAM, Kukkadapu RK, Boyd SA (1998) Adsorption of phenol and chlorinated phenols from aqueous solution by tetramethylammonium- and tetramethylphosphonium-exchanged montmorillonite. Appl Clay Sci 13:13–20
Maliou E, Malamis M, Sakellarides PO (1992) Lead and cadmium removal by ion-exchange, Wat Sci Technol 25:133–138
Matschullat J, Schneider J, Heitkamp U, Lessmann D, Siewers U, Rostai A, Malessa V, Andreae H (1990) Verbundforschung Fallstudie Harz. Berichte Forschungszentrums Waldökosysteme, Reich B, Bd. 19
Matschullat J, Heinrichs H, Schneider J, Ulrich B (1994) Gefahr für Ökosysteme und Wasserqualität. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 478S
Mazidji CN, Koopman B, Bitton G (1992) Chelating resin versus ion-exchange resin for heavy metal removal in toxicity fractionation. Wat Sci Technol 26:189–196
Meiwes KJ, König N, Khanna PK, Prenzel J, Ulrich B (1984) Chemische Untersuchungsverfahren für Mineralboden, Auflagehumus und Wurzeln zur Charakterisierung und Bewertung der Versauerung in Waldböden. Berichte der Forschungszentrum Waldökosysteme. Band 7, Universität Göttingen
Moore DM, Reynolds RC (1989) X-ray diffraction and the identification and analysis of clay minerals. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 332
Öztekin N, Alemdar A, Güngör N, Erim FB (2002) Adsorption of polyethyleneimine from aqueous solutions. Mater Lett 55:73–76
Patchineelam SR (1975) Untersuchungen über die Hauptbindungsarten und die Mobilisierbarkeit von Schwermetallen in fluviatilen Sedimenten. Dissertation Universität Heidelberg, pp 136
Rodriguez-Sarmiento DC, Pinzon-Bello JA (2001) Adsorption of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate on organophilic bentonites. Appl Clay Sci 18:173–181
Scatchard G (1949) The attraction of proteins for small molecules and ions. Ann New York Acad Sci 51:660–672
Schoeder D, Dümmler H (1962) Tonminerale in Böden Schleswig-Holsteins Zeitschrift Pflanzenernährung Düngung. Bodenkunde Weinheim 101:129–140
Suraj G, Iyer CSP, Lalithambika M (1998) Adsorption of cadmium and copper by modified. Appl Clay Sci 13:293–306
Tarrah J (1989) Verwitterungsbilanzen von Böden auf der Basis modaler Mineralbestände, Berichte des Forschungszentrums Waldökosysteme, Reiche A., Bd., pp 52:229
Uçan M, Ayar A (2002) Sorption equilibria of chlorinated anilines in aqueous solution on resin-bound cobalt ion. Colloids Surf A 207:41–47
Acknowledgments
I am greatly indebted to anonymous reviewers for their critical reviews and suggestions, which resulted improvement of the manuscript. I am also extremely grateful to Prof. Dr. J. Schwarzbauer and Prof. Dr. G. Dörhöfer for their editorial comments and suggestions. I thank Dr. A. Ayar from the Niğde University, Assoc. Prof. Dr. S. Kadir from the Eskişehir Osmangazi University and Dr. E. Çiftçi from the Niğde University for their help in preparing the manuscript. In addition, I thank Prof. Dr. R. Mayer and Mrs. B. Köhne from the Kassel University for their help during this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gürel, A. Adsorption characteristics of heavy metals in soil zones developed on spilite. Environ Geol 51, 333–340 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0329-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0329-7