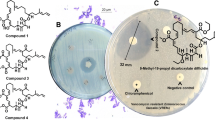
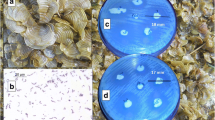
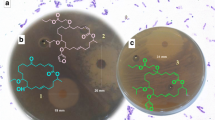
Abstract
Preliminary antibacterial metabolite production screening unveiled that B. amyloliquefaciens MTCC 12,713 associated with the intertidal red alga Kappaphycus alverezii exhibited potential inhibitory effects against drug-resistant pathogens methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Four homologous siderophore types of bacillibactins were isolated from a heterotrophic marine bacterium through bioactivity-guided purification. All detectable natural product gene clusters in B. amyloliquefaciens MTCC 12,713 were analyzed by sequencing the complete genome of the bacterium. The studied compounds displayed broad spectrum bactericidal activity against multidrug-resistant strains with a range of minimum inhibitory concentration values from 1.56 to 6.25 µg/mL, whereas standard antibiotic chloramphenicol was active at 6.25 to 12.5 µg/mL. Structure-bioactivity relationship assessment showed that higher electronic values were responsible for antibacterial properties against the nosocomial pathogens. The 2, 3-dihydroxybenzoate (dhb)-assisted biosynthetic pathway of catecholate-enclosed bacillibactins was proposed through the bacillibactin synthase multienzyme complex catalysis followed by dimerization of dhbACEBF operons with 16 genes (~ 12 kb bacterial genome). The present findings recognized an undescribed 4-methoxy-11′-pentanoyloxy-bacillibactin C as a source of potential antibacterial agent for use against drug-resistant pathogens for pharmaceutical applications.
Key points
• Bacillus amyloliquefaciens in association with Kappaphycus alverezii was isolated
• Four antibacterial bacillibactin analogs were identified from symbiotic bacterium
• 4-Methoxy-11′-pentanoyloxy-bacillibactin C showed potential antibacterial activity





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files. The whole genome sequence of the candidate bacterium was submitted in GenBank with an accession number of QKQQ00000000 (Biosample code: SAMN09389114; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/search/all/?term=QKQQ00000000).
References
Andryukov B, Mikhailov V, Besednova N (2019) The biotechnological potential of secondary metabolites from marine bacteria. J Mar Sci Eng 7(6):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7060176
Arasu MV, Duraipandiyan V, Ignacimuthu S (2013) Antibacterial and antifungal activities of polyketide metabolite from marine Streptomyces sp. AP-123 and its cytotoxic effect. Chemosphere 90(2):479–487. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.08.006.
Blin K, Shaw S, Steinke K, Villebro R, Ziemert N, Lee SY, Medema MH, Weber T (2019) antiSMASH 5.0: updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 47(W1):W81–W87. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz310.
Cassat JE, Skaar EP (2013) Iron in infection and immunity. Cell Host Microbe 13(5):509–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2013.04.010
Chakraborty K, Kizhakkekalam VK, Joy M, Chakraborty RD (2020) Moving away from traditional antibiotic treatment: can macrocyclic lactones from marine macroalga-associated heterotroph be the alternatives? Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(16):7117–7130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10658-0
Chakraborty K, Kizhakkekalam VK, Joy M, Dhara S (2021a) Difficidin class of polyketide antibiotics from marine macroalga-associated Bacillus as promising antibacterial agents. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105(16–17):6395–6408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11390-z
Chakraborty K, Kizhakkekalam VK, Joy M (2021b) Macrocyclic polyketides with siderophore mode of action from marine heterotrophic Shewanella algae: prospective anti-infective leads attenuate drug-resistant pathogens. J Appl Microbiol 130(5):1552–1570. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14875
Chen XH, Koumoutsi A, Scholz R, Eisenreich A, Schneider K, Heinemeyer I, Morgenstern B, Voss B, Hess WR, Reva O, Junge H, Voigt B, Jungblut PR, Vater J, Süssmuth R, Liesegang H, Strittmatter A, Gottschalk G, Borriss R (2007) Comparative analysis of the complete genome sequence of the plant growth-promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Nat Biotechnol 25(9):1007–1014. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1325
Chu BC, Garcia-Herrero A, Johanson TH, Krewulak KD, Lau CK, Peacock RS, Slavinskaya Z, Vogel HJ (2010) Siderophore uptake in bacteria and the battle for iron with the host; a bird’s eye view. Biometals 23(4):601–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9361-x
Helfrich EJ, Piel J (2016) Biosynthesis of polyketides by trans-AT polyketide synthases. Nat Prod Rep 33(2):231–316. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5np00125k
Hider RC, Kong X (2010) Chemistry and biology of siderophores. Nat Prod Rep 27(5):637–657. https://doi.org/10.1039/b906679a
Janda JM, Abbott SL (2014) The genus Shewanella: from the briny depths below to human pathogen. Crit Rev Microbiol 40(4):293–312. https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2012.726209
Jensen PR, Fenical W (1994) Strategies for the discovery of secondary metabolites from marine bacteria: ecological perspectives. Annu Rev Microbiol 48:559–584. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.mi.48.100194.003015
Kizhakkekalam VK, Chakraborty K (2019) Pharmacological properties of marine macroalgae-associated heterotrophic bacteria. Arch Microbiol 201(4):505–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1592-1
Kizhakkekalam VK, Chakraborty K, Joy M (2020) Oxygenated elansolid-type of polyketide spanned macrolides from a marine heterotrophic Bacillus as prospective antimicrobial agents against multidrug-resistant pathogens. Int J Antimicrob Agents 55(3):105892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105892
Li J, Liu S, Jiang Z, Sun C (2017) Catechol amide iron chelators produced by a mangrove-derived Bacillus subtilis. Tetrahedron 73(35):5245–5252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2017.07.007
Li JW, Vederas JC (2009) Drug discovery and natural products: end of an era or an endless frontier? Science 325(5937):161–165. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1168243
May JJ, Wendrich TM, Marahiel MA (2001) The dhb operon of Bacillus subtilis encodes the biosynthetic template for the catecholic siderophore 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate-glycine-threonine trimeric ester bacillibactin. J Biol Chem 276(10):7209–7217. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M009140200
Mondol MA, Shahidullah Tareq F, Kim JH, Lee MA, Lee HS, Lee JS, Lee YJ, Shin HJ (2013) New antimicrobial compounds from a marine-derived Bacillus sp. J Antibiot (tokyo) 66(2):89–95. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2012.102
Newman DJ, Cragg GM (2016) Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J Nat Prod 79(3):629–661. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b01055
Piel J (2010) Biosynthesis of polyketides by trans-AT polyketide synthases. Nat Prod Rep 27(7):996–1047. https://doi.org/10.1039/b816430b
Rütschlin S, Gunesch S, Böttcher T (2017) One enzyme, three metabolites: Shewanella algae controls siderophore production via the cellular substrate pool. Cell Chem Biol 24(5):598–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.03.017
Saha M, Sarkar S, Sarkar B, Sharma BK, Bhattacharjee S, Tribedi P (2016) Microbial siderophores and their potential applications: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(5):3984–3999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4294-0
Soldatou S, Eldjarn GH, Huerta-Uribe A, Rogers S, Duncan KR (2019) Linking biosynthetic and chemical space to accelerate microbial secondary metabolite discovery. FEMS Microbiol Lett 366(13):fnz142. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnz142.
Stein T (2005) Bacillus subtilis antibiotics: structures, syntheses and specific functions. Mol Microbiol 56(4):845–857. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04587.x
Temirov IuV, Esikova TZ, Kashparov IA, Balashova TA, Vinokurov LM, Alakhov IuB (2003) Katekhol'nyĭ siderofor, produtsiruemyĭ termorezistentnym shtammom Bacillus licheniformis VK21 [Catechol siderophore, produced by thermoresistent strain of Bacillus licheniformis VK21]. Bioorg Khim 29(6):597–604. Russian. doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/b:rubi.0000008894.80972.2e.
Thilakan B, Chakraborty K, Chakraborty RD (2016) Antimicrobial properties of cultivable bacteria associated with seaweeds in the Gulf of Mannar on the southeast coast of India. Can J Microbiol 62(8):668–681. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2015-0769
Wang T, Liang Y, Wu M, Chen Z, Lin J, Yang L (2015) Natural products from Bacillus subtilis with antimicrobial properties. Chinese J Chem Eng 23(4):744–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2014.05.020
World Health Organization. (2017) World health organization and WHO advisory group on integrated surveillance of antimicrobial resistance (AGISAR). Critically important antimicrobials for human medicine: ranking of antimicrobial agents for risk management of antimicrobial resistance due to non-human use, 5th rev. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/255027:48 p. ISBN 9789241512220.
Zhou M, Liu F, Yang X, Jin J, Dong X, Zeng KW, Liu D, Zhang Y, Ma M, Yang D (2018) Bacillibactin and bacillomycin analogues with cytotoxicities against human cancer cell lines from marine Bacillus sp. PKU-MA00093 and PKU-MA00092. Mar Drugs 16(1):22. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010022.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (ICAR-CMFRI), India under the project titled as “Development of Bioactive Pharmacophores from Marine Organisms” (grant number MBT/HLT/SUB23). The authors thank the Director, ICAR-CMFRI, and Head, Marine Biotechnology Division of ICAR-CMFRI for guidance and support. The authors are thankful to the Dean, Faculty of Marine Sciences, Lakeside Campus, Cochin University of Science and Technology for providing with necessary support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. KC conceived and designed research, acquired funds, and conducted the experiments. KC and VKK analyzed data. KC, VKK, MJ, and RDC drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, K., Kizhakkekalam, V.K., Joy, M. et al. Bacillibactin class of siderophore antibiotics from a marine symbiotic Bacillus as promising antibacterial agents. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106, 329–340 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11632-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11632-0