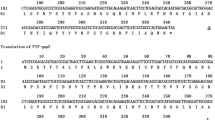
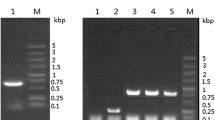
Abstract
Fungal immunomodulatory proteins (FIPs) are bioactive proteins with immunomodulatory properties. We previously reported the heterologous production in Escherichia coli of FIP-Lrh from Tiger milk mushroom (Lignosus rhinocerus) with potent cytotoxic effect on cancer cell lines. However, protein produced in E. coli lacks post-translational modifications and may be contaminated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) endotoxin. Therefore, in this study, yFIP-Lrh produced in Pichia pastoris was functionally compared with eFIP-Lrh produced in E. coli. Expression construct of FIP-Lrh cDNA in pPICZα was generated, transformed into P. pastoris X-33 and Mut+ transformants were verified by colony PCR. Induction with 0.5% or 1% methanol resulted in a secreted 13.6 kDa yFIP-Lrh which was subsequently purified and verified using LCMS/MS analysis. Size exclusion chromatography confirmed eFIP-Lrh as a homodimer whereas the larger size of yFIP-Lrh may indicate post-translational modification despite negative for glycoproteins staining. At lower concentration (4–8 μg/mL), yFIP-Lrh induced significantly higher Th1 (IFN-γ, TNF-α) and Th2 (IL-6, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13) cytokines production in mice splenocytes, whereas 16 μg/mL eFIP-Lrh induced significantly higher pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10), possibly due to higher residual LPS endotoxin (0.082 EU/mL) in eFIP-Lrh compared to negligible level in yFIP-Lrh (0.001 EU/mL). Furthermore, yFIP-Lrh showed higher cytotoxic effect on MCF-7 and HeLa cancer cells. Since both recombinant proteins of FIP-Lrh have the same peptide sequence, besides glycosylation, other post-translational modifications in yFIP-Lrh may account for its enhanced immunomodulatory and anti-proliferative activities. In conclusion, P. pastoris is preferred over E. coli for production of a functionally active yFIP-Lrh devoid of endotoxin contamination.
Key points
• FIP-Lrh can induced production of Th1 and Th2 cytokines by mouse splenocytes.
• Higher cytotoxic effect on cancer cells observed for yeast compared to E. coli produced FIP-Lrh.
• P. pastoris allows production of an endotoxin-free and functionally active recombinant FIP-Lrh.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Ahmad M, Hirz M, Pichler H, Schwab H (2017) Protein expression in Pichia pastoris: recent achievements and perspectives for heterologous protein production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:5301–5317
Bai JY, Li, YF, Liu Y, Lin ZP (2005) Isolation and sequence analysis of immunomodulatory protein gene from Ganoderma japonicum. UniProtKB, Q52PH4, Q52PH4_9APHY
Bastiaan-Net S, Chanput W, Hertz A, Zwittink RD, Mes JJ, Wichers HJ (2013) Biochemical and functional characterization of recombinant fungal immunomodulatory proteins (FIPs). Int Immunopharmacol 15(1):167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2012.11.003
Bin Z, Xiaoxia Y, Tongjie C (2007) Detection of airborne endotoxin and bacterial aerosol in fox farm. J Agro-Environ Sci 26:1585–1590
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantization of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chan CJ, Yong YS, Song AAL, Abdul RR, In LLA, Lim RLH (2019) Lactococcus lactis harboring Ara h 2.02 alleviates allergen specific Th2 associated responses in sensitized mice. J Appl Microbiol 128(3):862–874. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14524
Chang HH, Yeh CH, Sheu F (2009) A novel immunomodulatory protein from Poria cocos induces Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation within mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Agric Food Chem 57:6129–6139
Chanput W, Reitsma M, Kleinjans L, Mes JJ, Savelkoul HFJ, Wichers HJ (2012) Beta-glucans are involved in immune-modulation of THP-1 macrophages. Mol Nutr Food Res 56:822–833
Cregg JM, Vedvick TS, Raschke WC (1993) Recent advances in the expression of foreign genes in Pichia pastoris. Nat Biotechnol 11:905–910. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0893-905
Frederic GM, Olga S, Nicole C, Eulalia S, Anne O (2013) Concentration of airborne Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA and MSSA), total bacteria, and endotoxins in pig farms. Ann Occup Hyg 57:550–557
Gopal GJ, Kumar A (2013) Strategies for the production of recombinant protein in Escherichia coli. Protein J 32:419–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-013-9502-5
Hsieh KY, Hsu CI, Lin JY, Tsai CC, Lin RH (2003) Oral administration of an edible-mushroom-derived protein inhibits the development of food-allergic reactions in mice. Clin Exp Allergy 3:1595–1602
Hsu HC, Hsu CI, Lin RH, Kao CL, Lin JY (1997) Fip-vvo, a new fungal immunomodulatory protein isolated from Volvariella volvacea. Biochem J 323:557–565
Hsu HY, Hua KF, Wu WC, Hsu J, Weng ST, Lin TL, Liu CY, Hseu RS, Huang CT (2008) Reishi immuno-modulation protein induces interleukin-2 expression via protein kinase-dependent signaling pathways within human T cells. J Cell Physiol 215:15–26
Kino K, Yamashita A, Yamaoka K, Watanabe J, Tanaka S, Ko K, Shimizu K, Tsunoo H (1989) Isolation and characterization of a new immunomodulatory protein Ling Zhi-8 (rLZ-8), from Ganoderma lucidium. J Biol Chem 264:472–478
Ko JL, Hsu CI, Lin RH, Kao CL, Lin JY (1995) A new fungal immunomodulatory protein, FIP-fve isolated from the edible mushroom, Flammulina velutipes and its complete amino acid sequence. Eur J Biochem 228(2):244–249
Kong X, Zhang J, Han X, Zhang P, Dai X, Liu J, Zhang X, Lee I, Liu S (2013) High-yield production in Escherichia coli of fungal immunomodulatory protein isolated from Flammulina velutipes and its bioactivity assay in vivo. Int J Mol Sci 14:2230–2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14022230
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lai CKM, Wong KH, Cheung PCK (2008) Antiproliferative effects of sclerotial polysaccharides from Polyporus rhinocerus Cooke (Aphyllophoromycetideae) on different kinds of leukemic cells. Int J Med Mushr 10:255–264
Lara AR (2011) Production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Rev Mex Ing Quim 10(2):209–223
Lee MN, Tan NH, Fung SY, Tan CS, Ng ST (2012) The antiproliferative activity of sclerotia of Lignosus rhinocerus (Tiger Milk Mushroom). Evid Based Complement Alternat Med:697603. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/697603
Lee YT, Lee SS, Sun HL, Lu KH, Ku MS, Sheu JN, Ko JL, Lue KH (2013) Effect of the fungal immunomodulatory protein FIP-fve on airway inflammation and cytokine production in mouse asthma model. Cytokine 61(1):237–244
Li Q, Wang X, Chen Y, Lin J, Zhou X (2010) Cytokines expression induced by Ganoderma sinensis fungal immunomodulatory proteins (FIP-gsi) in mouse spleen cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:1403–1413
Li QZ, Wang XF, Zhou XW (2011) Recent status and prospects of the fungal immunomodulatory protein family. Crit Rev Biotechnol 31(4):365–375. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2010.543967
Li H, Bu X, Li K, Wu D (2019a) Production of a novel Poria cocos immunomodulatory protein in Pichia pastoris: cloning, expression, purification and activities assays. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35(2):27
Li QZ, Zheng YZ, Zhou XW (2019b) Fungal immunomodulatory proteins: characteristic, potential antitumor activities and their molecular mechanisms. Drug Discov Today 24(1):307–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2018.09.014
Lin JW, Jia J, Shen YH, Zhong M, Chen LJ, Li HG, Ma H, Guo ZF, Qi MF, Liu LX, Li TL (2013) Functional expression of FIP-fve, a fungal immunomodulatory protein from the edible mushroom Flammulina velutipes in Pichia pastoris GS115. J Biotech 168(4):527–533
Mao PW, Li LD, Wang YL, Bai XH, Zhou XW (2019) Optimization of the fermentation parameters for the production of Ganoderma lucidum immunomodulatory protein by Pichia pastoris. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 50(4):357–364. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2019.1703194
Munson TE (1985) Guideline for validation of the LAL test as an end-product endotoxin test for human and biological drug products. Prog Clin Biol Res 189:211–220
Nilsson S, Merritt AS, Bellander T (2011) Endotoxins in urban air in Stockholm, Sweden. Atmos Environ 45(1):266–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.09.037
Oppliger A, Rusca S, Charriere N, Duc TV, Droz PO (2005) Assessment of bioaerosols and inhalable dust exposure in Swiss sawmills. Ann Occup Hyg 49:385–391
Ou CC, Hsiao YM, Wu WJ, Tasy GJ, Ko JL, Lin MY (2009a) FIP-fve stimulates interferon gamma production via modulation of calcium release and PKC-alpha activation. J Agric Food Chem 57(22):11008–11013. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf902725s
Ou CC, Hsiao YM, Wang WH, Ko JL, Lin MY (2009b) Stability of fungal immunomodulatory protein, FIP-gts and FIP-fve, in IFN-γ production. Food Agric Immunol 20:319–332. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540100903247688
Paaventhan P, Joseph JS, Seow SV, Vaday S, Robinson H, Chua KY, Kolatkar PR (2003) A 1.7 Å Structure of Fve, a member of the new fungal immunomodulatory protein family. J Mol Biol 332(2):461–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00923-9
Palomares LA, Estrada-Mondaca S, Ramírez OT (2004) Production of recombinant proteins: challenges and solutions. Methods Mol Biol 267:15–52. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-774-2:015
Peng YR, Li YB, Liu XD, Zhang JF, Duan JA (2008) Antitumor activity of C-21 steroidal glycosides from Cynanchum auriculatum Royle ex Wight. Phytomedicine 15(11):1016–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2008.02.021
European Pharmacopoeia (2017) Available from: https://www.edqm.eu/en/european-pharmacopoeia-9th-edition.
Pushparajah V, Fatima A, Chong CH, Gambule TZ, Chan CJ, Ng ST, Tan CS, n.d.Fung SY, Lee SS, Tan NH, Lim RLH (2016) Characterisation of a new fungal immunomodulatory protein from Tiger Milk Mushroom, Lignosus rhinocerotis. Sci Rep 6:30010.
Qu ZW, Zhou SY, Guan SX, Gao R, Duan ZW, Zhang X, Sun WY, Fan WL, Chen SS, Chen LJ, Lin JW, Ruan YY (2018) Recombinant expression and bioactivity comparison of four typical fungal immunomodulatory proteins from three main Ganoderma species. BMC Biotechnol 18(1):80. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-018-0488-0
Ramana KV, Fadl AA, Tammali R, Reddy AB, Chopra AK, Srivastava SK (2006) Aldose reductase mediates the lipopolysaccharide-induced release of inflammatory mediators in RAW264.7 murine macrophages. J Biol Chem 281(44):33019–33029. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M603819200
Rosano GL, Ceccarelli EA (2014) Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: advances and challenges. Front Microbiol 5:1–172. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00172
Roth Z, Yehezkel G, Khalaila I (2012) Identification and quantification of protein glycosylation. Int J Carbohydrate Chem 2012:640923–640910. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/640923
Tanaka S, Ko K, Kino K, Tsuchiya K, Yamashita A, Murasugi A, Sakuma S, Tsunoo H (1989) Complete amino acid sequence of an immunomodulatory protein, ling zhi-8 (rLZ-8), an immunomodulator from a fungus, Ganoderma lucidium, having similarity to immunoglobulin variable regions. J Biol Chem 264(28):16372–16377
Tong MH, Chien PJ, Chang HH, Tsai MJ, Sheu F (2008) High processing tolerances of immunomodulatory proteins in enoki and reishi mushrooms. J Agric Food Chem 56:3160–3166
Uribe-Echeverry PT, Lopez-Gartner GA (2017) Fungal immunomodulatory proteins in the context of biomedicine. Front Biosci 9:286–306. https://doi.org/10.2741/e803
Wang SY, Hsu ML, Hsu HC, Tzeng CH, Lee SS, Shiao MS, Ho CK (1997) The anti-tumor effect of Ganoderma lucidum is mediated by cytokines released from activated macrophages and T lymphocytes. Int J Cancer 70(6):699–705. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19970317)70:6<699::aid-ijc12>3.0.co;2-5
Wang PH, Hsu CI, Tang SC, Huang YL, Lin JY, Ko JL (2004) Fungal immunomodulatory protein from Flammulina velutipes induces interferon-γ production through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem 52(9):2721–2725
Wang Y, Gao YN, Bai R, Chen HY, Wu YY, Shang JJ, Bao DP (2019) Identification of a novel anticancer protein, FIP-bbo, from Botryobasidium botryosum and protein structure analysis using molecular dynamic simulation. Sci Rep 9:5818. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42104-1
Wen N, Liu H, Fu Y, Wang C (2017) Optimization and influence mechanism of sampling and analysis of airborne endotoxin based on Limulus Amebocyte lysate assay. Aerosol Air Qual Res 17:1000–1010
Wu CM, Wu TY, Kao SS, Ko JL, Jinn TR (2008) Expression and purification of a recombinant Fip-fve protein from Flammulina velutipes in baculovirus-infected insect cells. J Appl Microbiol 104(5):1354–1362
Xue Q, Ding YX, Shang CH, Jiang C, Zhao MW (2008) Functional expression of rLZ-8, a fungal immunomodulatory protein from Ganoderma lucidium in Pichia pastoris. J Gen Appl Microbiol 54:393–398
Yeh CM, Yeh CK, Hsu XY, Luo QM, Lin MY (2008) Extracellular expression of a functional recombinant Ganoderma lucidium immunomodulatory protein by Bacillus subtilis and Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(4):1039–1049. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01547-07
Yen H, Fauzi AR, Din LB, McKelvey-Martin VJ, Meng CK, Inayat-Hussain SH, Rajab NF (2014) Involvement of Seladin-1 in goniothalamin-induced apoptosis in urinary bladder cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:295
Funding
This work was supported by UCSI Research Excellence & Innovative Grant (REIG-FAS-2020/005) from the Centre of Excellence for Research, Value Innovation and Entrepreneurship (CERVIE), UCSI University, Kuala Lumpur Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RLHL conceived and designed the research. UCE and CJC conducted the experiments. RLHL, CJC, and UCE analyzed the data. UCE and RLHL wrote the manuscript. RLHL and CSYL contributed to the materials and reagents. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The mouse experiment was performed according to the protocol for animal experiment from Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Animal Ethics Committee (UKMAEC) and was approved by the Ethics Committee of UKMAEC (UCSI/2018/RENEE LIM/25-JULY/934-AUG-2018-SEPT-2020).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ejike, U.C., Chan, C.J., Lim, C.S.Y. et al. Functional evaluation of a recombinant fungal immunomodulatory protein from L. rhinocerus produced in P. pastoris and E. coli host expression systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 2799–2813 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11225-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11225-x