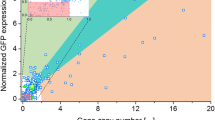
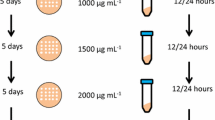
Abstract
Routine approaches for the efficient expression of heterogenous proteins in Pichia pastoris include using the strong methanol-regulated alcohol oxidase (AOX1) promoter and multiple inserts of expression cassettes. To screen the transformants harboring multiple integrations, antibiotic-resistant genes such as the Streptoalloteichus hindustanus bleomycin gene are constructed into expression vectors, given that higher numbers of insertions of antibiotic-resistant genes on the expression vector confer resistance to higher concentrations of the antibiotic for transformants. The antibiotic-resistant genes are normally driven by the strong constitutive translational elongation factor 1a promoter (PTEF1). However, antibiotic-resistant proteins are necessary only for the selection process. Their production during the heterogenous protein expression process may increase the burden in cells, especially for the high-copy strains which harbor multiple copies of the expression cassette of antibiotic-resistant genes. Besides, a high concentration of the expensive antibiotic is required for the selection of multiple inserts because of the effective expression of the antibiotic-resistant gene by the TEF1 promoter. To address these limitations, we replaced the TEF1 promoter with a weaker promoter (PDog2p300) derived from the potential promoter region of 2-deoxyglucose-6-phosphate phosphatase gene for driving the antibiotic-resistant gene expression. Importantly, the PDog2p300 has even lower activity under carbon sources (glycerol and methanol) used for the AOX1 promoter–based production of recombinant proteins compared with glucose that is usually used for the selection process. This strategy has proven to be successful in screening of transformants harboring more than 3 copies of the gene of interest by using plates containing 100 μg/ml of Zeocin. Meanwhile, levels of Zeocin resistance protein were undetectable by immunoblotting in these multiple-copy strains during expression of heterogenous proteins.
Key points
• P Dog2p300 was identified as a novel glucose-regulated promoter.
• The expression of antibiotic-resistant gene driven by PDog2p300 was suppressed during the recombinant protein expression, resulting in reducing the metabolic burden.
• The transformants harboring multiple integrations were cost-effectively selected by using the PDog2p300 for driving antibiotic-resistant genes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are included here and in the supplemental material.
References
Ahn J, Hong J, Park M, Lee H, Lee E, Kim C, Lee J, Choi ES, Jung JK, Lee H (2009) Phosphate-responsive promoter of a Pichia pastoris sodium phosphate symporter. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(11):3528–3534. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02913-08
Arruda A, Reis VC, Batista VD, Daher BS, Piva LC, De Marco JL, de Moraes LM, Torres FA (2016) A constitutive expression system for Pichia pastoris based on the PGK1 promoter. Biotechnol Lett 38(3):509–517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-2002-2
Aw R, Polizzi KM (2013) Can too many copies spoil the broth? Microb Cell Factories 12:128. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-12-128
Gurramkonda C, Polez S, Skoko N, Adnan A, Gabel T, Chugh D, Swaminathan S, Khanna N, Tisminetzky S, Rinas U (2010) Application of simple fed-batch technique to high-level secretory production of insulin precursor using Pichia pastoris with subsequent purification and conversion to human insulin. Microb Cell Factories 9:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-9-31
Inan M, Meagher MM (2001) Non-repressing carbon sources for alcohol oxidase (AOX1) promoter of Pichia pastoris. J Biosci Bioeng 92(6):585–589. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.92.585
Juturu V, Wu JC (2018) Heterologous protein expression in Pichia pastoris: latest research progress and applications. Chembiochem 19(1):7–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201700460
Karim AS, Curran KA, Alper HS (2013) Characterization of plasmid burden and copy number in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for optimization of metabolic engineering applications. FEMS Yeast Res 13(1):107–116. https://doi.org/10.1111/1567-1364.12016
Kitamoto N, Matsui J, Kawai Y, Kato A, Yoshino S, Ohmiya K, Tsukagoshi N (1998) Utilization of the TEF1-alpha gene (TEF1) promoter for expression of polygalacturonase genes, pgaA and pgaB, in Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50(1):85–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051260
Kretschmer M, Fraenkel DG (1991) Yeast 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase: sequence and mutant. Biochemistry 30(44):10663–10672. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00108a009
Liang S, Zou C, Lin Y, Zhang X, Ye Y (2013) Identification and characterization of P GCW14 : a novel, strong constitutive promoter of Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Lett 35(11):1865–1871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1265-8
Lucas JJ, Hernandez F, Gomez-Ramos P, Moran MA, Hen R, Avila J (2001) Decreased nuclear beta-catenin, tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration in GSK-3beta conditional transgenic mice. EMBO J 20(1-2):27–39. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.1.27
Menendez J, Valdes I, Cabrera N (2003) The ICL1 gene of Pichia pastoris, transcriptional regulation and use of its promoter. Yeast 20(13):1097–1108. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.1028
Norden K, Agemark M, Danielson JA, Alexandersson E, Kjellbom P, Johanson U (2011) Increasing gene dosage greatly enhances recombinant expression of aquaporins in Pichia pastoris. BMC Biotechnol 11:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-11-47
Ohi H, Miura M, Hiramatsu R, Ohmura T (1994) The positive and negative cis-acting elements for methanol regulation in the Pichia pastoris AOX2 gene. Mol Gen Genet 243(5):489–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284196
Portela RM, Vogl T, Kniely C, Fischer JE, Oliveira R, Glieder A (2017) Synthetic core promoters as universal parts for fine-tuning expression in different yeast species. ACS Synth Biol 6(3):471–484. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.6b00178
Prattipati M, Ramakrishnan K, Sankaranarayanan M (2020) Pichia pastoris protein disulfide isomerase (PDI1) promoter for heterologous protein production and its sequence characterization. Enzym Microb Technol 140:109633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2020.109633
Qin X, Qian J, Yao G, Zhuang Y, Zhang S, Chu J (2011) GAP promoter library for fine-tuning of gene expression in Pichia pastoris. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(11):3600–3608. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02843-10
Sallada ND, Harkins LE, Berger BW (2019) Effect of gene copy number and chaperone coexpression on recombinant hydrophobin HFBI biosurfactant production in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Bioeng 116(8):2029–2040. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26982
Shen Q, Wu M, Wang HB, Naranmandura H, Chen SQ (2012) The effect of gene copy number and co-expression of chaperone on production of albumin fusion proteins in Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96(3):763–772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4337-0
Shen Q, Yu Z, Lv PJ, Li Q, Zou SP, Xiong N, Liu ZQ, Xue YP, Zheng YG (2020) Engineering a Pichia pastoris nitrilase whole cell catalyst through the increased nitrilase gene copy number and co-expressing of ER oxidoreductin 1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(6):2489–2500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10422-4
Stadlmayr G, Mecklenbrauker A, Rothmuller M, Maurer M, Sauer M, Mattanovich D, Gasser B (2010) Identification and characterisation of novel Pichia pastoris promoters for heterologous protein production. J Biotechnol 150(4):519–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.09.957
Theron CW, Berrios J, Delvigne F, Fickers P (2018) Integrating metabolic modeling and population heterogeneity analysis into optimizing recombinant protein production by Komagataella (Pichia) pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(1):63–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8612-y
Tschopp JF, Brust PF, Cregg JM, Stillman CA, Gingeras TR (1987) Expression of the lacZ gene from two methanol-regulated promoters in Pichia pastoris. Nucleic Acids Res 15(9):3859–3876. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/15.9.3859
Tsujimoto Y, Izawa S, Inoue Y (2000) Cooperative regulation of DOG2, encoding 2-deoxyglucose-6-phosphate phosphatase, by Snf1 kinase and the high-osmolarity glycerol-mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in stress responses of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol 182(18):5121–5126. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.182.18.5121-5126.2000
Vogl T, Glieder A (2013) Regulation of Pichia pastoris promoters and its consequences for protein production. New Biotechnol 30(4):385–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2012.11.010
Weninger A, Hatzl AM, Schmid C, Vogl T, Glieder A (2016) Combinatorial optimization of CRISPR/Cas9 expression enables precision genome engineering in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. J Biotechnol 235:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.03.027
Wu S, Letchworth GJ (2004) High efficiency transformation by electroporation of Pichia pastoris pretreated with lithium acetate and dithiothreitol. BioTechniques 36(1):152–154. https://doi.org/10.2144/04361DD02
Wu M, Liu W, Yang G, Yu D, Lin D, Sun H, Chen S (2014) Engineering of a Pichia pastoris expression system for high-level secretion of HSA/GH fusion protein. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172(5):2400–2411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0688-y
Xu N, Zhu J, Zhu Q, Xing Y, Cai M, Jiang T, Zhou M, Zhang Y (2018) Identification and characterization of novel promoters for recombinant protein production in yeast Pichia pastoris. Yeast 35(5):379–385. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.3301
Zahrl RJ, Pena DA, Mattanovich D, Gasser B (2017) Systems biotechnology for protein production in Pichia pastoris. FEMS Yeast Res 17(7). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/fox068
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2019YFA0905300) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31971342 and 31700095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZQL, YGZ, YPX, SPZ, NX, and QS initiated and supervised the project. ZY, XTZ, and SJZ carried out all the experiments and data analyses. QS and ZQL are responsible for the preparation and revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study does not contain any studies involving human participants and/or animals
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 85 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Q., Yu, Z., Zhou, XT. et al. Identification of a novel promoter for driving antibiotic-resistant genes to reduce the metabolic burden during protein expression and effectively select multiple integrations in Pichia Pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 3211–3223 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11195-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11195-0