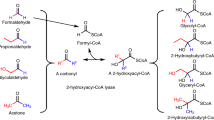
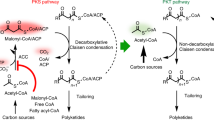
Abstract
Because of their function of catalyzing the rearrangement of the carbon chains, thiolases have attracted increasing attentions over the past decades. The 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase (KAT) is a member of the thiolase, which is capable of catalyzing the Claisen condensation reaction between the two acyl-CoAs, thereby achieving carbon chain elongation. In this way, diverse value-added compounds might be synthesized starting from simple small CoA thioesters. However, most KATs are hampered by low stability and poor substrate specificity, which has hindered the development of large-scale biosynthesis. In this review, the common characteristics in the three-dimensional structure of KATs from different sources are summarized. Moreover, structure-guided rational engineering is discussed as a strategy for enhancing the performance of KATs. Finally, we reviewed the metabolic engineering applications of KATs for producing various energy-storage molecules, such as n-butanol, fatty acids, dicarboxylic acids, and polyhydroxyalkanoates.
Key points
• Summarize the structural characteristics and catalyzation mechanisms of KATs.
• Review on the rational engineering to enhance the performance of KATs.
• Discuss the applications of KATs for producing energy-storage molecules.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agler MT, Spirito CM, Usack JG, Werner JJ, Angenent LT (2012) Chain elongation with reactor microbiomes: upgrading dilute ethanol to medium-chain carboxylates. Energy Environ Sci 5:8189–8192. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ee22101b
Agnew DE, Stevermer AK, Youngquist JT, Pfleger BF (2012) Engineering Escherichia coli for production of C12-C14 polyhydroxyalkanoate from glucose. Metab Eng 14:705–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2012.08.003
Anbazhagan P, Harijan RK, Kiema TR, Janardan N, Murthy M, Michels PA, Juffer AH, Wierenga RK (2014) Phylogenetic relationships and classification of thiolases and thiolase-like proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium smegmatis. Tuberculosis 94:405–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tube.2014.03.003
Andrew CM, Charles SB, John BB (2018) Structure of Aspergillus fumigatus cytosolic thiolase: trapped tetrahedral reaction intermediates and activation by monovalent cations. ACS Catal 8:1973–1989. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.7b02873
Angenent LT, Richter H, Buckel W, Spirito CM, Steinbusch KJ, Plugge CM, Strik DP, Grootscholten TI, Buisman CJ, Hamelers HV (2016) Chain elongation with reactor microbiomes: open-culture biotechnology to produce biochemicals. Environ Sci Technol 50:2796–2810. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04847
Antonenkov VD, Van Veldhoven PP, Waelkens E, Mannaerts GP (1999) Comparison of the stability and substrate specificity of purified peroxisomal 3-oxoacyl-CoA thiolases A and B from rat liver. Bba-Mol Cell Biol L 1437:136–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1388-1981(99)00003-7
Bastian V, Sylvain E, Eric G, François R, Olivier M, Tobias JE, Seigo S, Tristan W (2018) Archaeal acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase/HMG-CoA synthase complex channels the intermediate via a fused CoA-binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:3380–3385. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1718649115
Bhaskar S, Steer DL, Anand R, Panjikar S (2020) Structural basis for differentiation between two classes of thiolase: degradative vs biosynthetic thiolase. J Struct Biol X 4:100018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjsbx.2019.100018
Blaisse MR, Dong H, Fu B, Chang MCY (2017) Discovery and engineering of pathways for production of α-branched organic acids. J Am Chem Soc 139:14526–14532. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b07400
Blaisse MR, Fu B, Chang MCY (2018) Structural and biochemical studies of substrate selectivity in Ascaris suum thiolases. Biochemistry 57:3155–3166. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.7b01123
Bolon DN, Mayo SL (2001) Enzyme-like proteins by computational design. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:14274–14279. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.251555398
Bowen CH, Bonin J, Kogler A, Barba-Ostria C, Zhang F (2016) Engineering Escherichia coli for conversion of glucose to medium-chain ω-hydroxy fatty acids and α,ω-dicarboxylic acids. ACS Synth Biol 5:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.5b00201
Brian MB, Yekaterina T, Michael AH, Bruce T, Kristala LJP (2018) Rational design of thiolase substrate specificity for metabolic engineering applications. Biotechnol Bioeng 115:2167–2182. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26737
Burg V, Vincent GHE (2002) Selection of mutations for increased protein stability. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:333–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-1669(02)00325-7
Cathleen Z, Donald H (2018) Directed evolution of protein catalysts. Annu Rev Biochem 81:131–157. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-012034
Chae T, Ahn J, Ko Y, Kim J, Lee J, Lee E, Lee S (2020) Metabolic engineering for the production of dicarboxylic acids and diamines. Metab Eng 58:2–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.03.005
Chen Q, Wang Q, Wei G, Liang Q, Qi Q (2011) Production in Escherichia coli of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) with differing monomer compositions from unrelated carbon sources. Appl Environ Microb 77:4886–4893. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00091-11
Chen J, Li W, Zhang Z, Tan T, Li Z (2018) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates using acetate as a main carbon source. Microb Cell Factories 17:102. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-0949-0
Cheon Y, Kim J-S, Park J-B, Heo P, Lim JH, Jung GY, Seo J-H, Park JH, Koo HM, Cho KM, Park J-B, Ha S-J, Kweon D-H (2014) A biosynthetic pathway for hexanoic acid production in Kluyveromyces marxianus. J Biotechnol 182-183:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.04.010
Cheong S, Clomburg JM, Gonzalez R (2016) Energy- and carbon-efficient synthesis of functionalized small molecules in bacteria using non-decarboxylative Claisen condensation reactions. Nat Biotechnol 34:556–561. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3505
Choi SY, Cho IJ, Lee Y, Kim Y-J, Kim K-J, Lee SY (2020) Microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates and nonnatural polyesters. Adv Mater:1907138. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201907138
Chubukov V, Mukhopadhyay A, Petzold CJ, Keasling JD, Martín HG (2016) Synthetic and systems biology for microbial production of commodity chemicals. NPJ Syst Biol Appl 2:16009. https://doi.org/10.1038/npjsba.2016.9
Cintolesi A, Clomburg JM, Gonzalez R (2014) In silico assessment of the metabolic capabilities of an engineered functional reversal of the β-oxidation cycle for the synthesis of longer-chain (C>/=4) products. Metab Eng 23:100–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2014.02.011
Clomburg JM, Vick JE, Blankschien MD, Rodríguez-Moya M, Gonzalez R (2012) A synthetic biology approach to engineer a functional reversal of the β-oxidation cycle. ACS Synth Biol 1:541–554. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb3000782
Clomburg JM, Blankschien MD, Vick JE, Chou A, Kim S, Gonzalez R (2015) Integrated engineering of β-oxidation reversal and ω-oxidation pathways for the synthesis of medium chain ω-functionalized carboxylic acids. Metab Eng 28:202–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.01.007
Clomburg JM, Contreras SC, Chou A, Siegel JB, Gonzalez R (2018) Combination of type II fatty acid biosynthesis enzymes and thiolases supports a functional β-oxidation reversal. Metab Eng 45:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.11.003
Dai L, Yang Y, Kim HR, Zhou Y (2010) Improving computational protein design by using structure-derived sequence profile. Proteins 78:2338–2348. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.22746
Dekishima Y, Lan EI, Shen CR, Km C, Liao JC (2011) Extending carbon chain length of 1-butanol pathway for 1-hexanol synthesis from glucose by engineered Escherichia coli. J Am Chem Soc 133:11399–11401. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja203814d
Dellomonaco C, Clomburg JM, Miller EN, Gonzalez R (2011) Engineered reversal of the β-oxidation cycle for the synthesis of fuels and chemicals. Nature 476:355–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10333
Eko Roy M, Carina H, Verena S, Irina B (2018) Engineering microbial fatty acid metabolism for biofuels and biochemicals. Curr Opin Biotech 50:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2017.10.002
Eric JNH, Jörn P (2016) Biosynthesis of polyketides by trans-AT polyketide synthases. Nat Prod Rep 33:231–316. https://doi.org/10.1039/b816430b
Fage CD, Meinke JL, Keatinge-Clay AT (2015) Coenzyme A-free activity, crystal structure, and rational engineering of a promiscuous β-ketoacyl thiolase from Ralstonia eutropha. J Mol Catal B Enzym 121:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2015.08.007
Felnagle EA, Chaubey A, Noey EL, Houk KN, Liao JC (2012) Engineering synthetic recursive pathways to generate non-natural small molecules. Nat Chem Biol 8(6):518–526. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.959
Fluchter S, Follonier S, Schiel-Bengelsdorf B, Bengelsdorf FR, Zinn M, Durre P (2019) Anaerobic production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and its precursor 3-hydroxybutyrate from synthesis gas by autotrophic Clostridia. Biomacromolecules 20:3271–3282. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.9b00342
Freund GS, O’Brien TE, Vinson L, Carlin DA, Yao A, Mak WS, Tagkopoulos I, Facciotti MT, Tantillo DJ, Siegel JB (2017) Elucidating substrate promiscuity within the fabi enzyme family. ACS Chem Biol 12:2465–2473. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.7b00400
Gobin M, Loulergue P, Audic J-L, Lemiègre L (2015) Synthesis and characterisation of bio-based polyester materials from vegetable oil and short to long chain dicarboxylic acids. Ind Crop Prod 70:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.03.041
Guo J, Zhou H (2016) Protein allostery and conformational dynamics. Chem Rev 116:6503–6515. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00590
Haapalainen AM, Merilainen G, Wierenga RK (2006) The thiolase superfamily: condensing enzymes with diverse reaction specificities. Trends Biochem Sci 31:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2005.11.011
Harijan RK (2017) Coenzyme-A dependent catalysis: an overview of thiolase superfamily enzymes and drug discovery. Res Chron Dis 1(2):017–019
Harijan RK, Kiema T-R, Syed SM, Qadir I, Mazet M, Bringaud F, Michels PAM, Wierenga RK (2017) Crystallographic substrate binding studies of Leishmania mexicana SCP2-thiolase (type-2): unique features of oxyanion hole-1. Protein Eng Des Sel 30:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/gzw080
Haushalter RW, Phelan RM, Hoh KM, Su C, Wang G, Baidoo EEK, Keasling JD (2017) Production of odd-carbon dicarboxylic acids in Escherichia coli using an engineered biotin-fatty acid biosynthetic pathway. J Am Chem Soc 139:4615–4618. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b11895
Insomphun C, Kobayashi S, Fujiki T, Numata K (2016) Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates containing hydroxyl group from glycolate in Escherichia coli. AMB Express 6:3–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-016-0200-5
Ithayaraja M, Janardan N, Wierenga RK, Savithri HS, Murthy MR (2016) Crystal structure of a thiolase from Escherichia coli at 1.8 Å resolution. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 72:534–544. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X16008451
Iyer PV, Ananthanarayan L (2008) Enzyme stability and stabilization-aqueous and non-aqueous environment. Process Biochem 43:1019–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2008.06.004
Jacob EV, James MC, Matthew DB, Alexander C, Ramon G (2014) Escherichia coli enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (FabI) supports efficient operation of a functional reversal of the β-oxidation cycle. Appl Environ Microb 81:1406–1416. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03521-14
Janardan N, Harijan RK, Kiema T-R, Wierenga RK, Murthy MRN (2015) Structural characterization of a mitochondrial 3-ketoacyl-CoA (T1)-like thiolase from Mycobacterium smegmatis. Acta Crystallogr Sect D Biol Crystallogr 71:2479–2493. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004715019331
Jung H-R, Lee J-H, Park YL, Moon Y-M, Shashi KB, Choi T-R, Ranjit G, Yang S-Y, Song H-S, Ko BJ, Yang Y-H, Park JY (2019) Increased tolerance to furfural by introduction of polyhydroxybutyrate synthetic genes to Escherichia coli. J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:776–784. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1901.01070
Kallscheuer N, Gätgens J, Lübcke M, Pietruszka J, Bott M, Polen T (2017a) Improved production of adipate with Escherichia coli by reversal of β-oxidation. Appl Microbiol Biot 101:2371–2382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8033-3
Kallscheuer N, Polen T, Bott M, Marienhagen J (2017b) Reversal of β-oxidative pathways for the microbial production of chemicals and polymer building blocks. Metab Eng 42:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.05.004
Kiema T-R, Harijan RK, Strozyk M, Fukao T, Alexson SEH, Wierenga RK (2014) The crystal structure of human mitochondrial 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase (T1): insight into the reaction mechanism of its thiolase and thioesterase activities. Acta Crystallogr Sect D Biol Crystallogr 70:3212–3225. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004714023827
Kim S, Gonzalez R (2018) Selective production of decanoic acid from iterative reversal of β-oxidation pathway. Biotechnol Bioeng 115:1311–1320. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26540
Kim J, Kim K-J (2016) Crystal structure and biochemical characterization of a 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase from Ralstoniaeutropha H16. Int J Biol Macromol 82:425–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.10.054
Kim E-J, Son HF, Kim S, Ahn J-W, Kim K-J (2014) Crystal structure and biochemical characterization of beta-keto thiolase B from polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16. Biochem Bioph Res Co 444:365–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.055
Kim S, Cho K, Shin Y, Um H, Choi K, Chang J, Cho Y, Park Y (2015a) Microorganism producing L-methionine precursor and method of producing L-methionine and organic acid from the L-methionine precursor. U.S. Patent
Kim S, Clomburg JM, Gonzalez R (2015b) Synthesis of medium-chain length (C6-C10) fuels and chemicals via β-oxidation reversal in Escherichia coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42:465–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1589-6
Kim S, Jang Y, Ha S, Ahn J, Kim E, Lim J, Cho C, Ryu Y, Lee S, Lee S, Kim K (2015c) Redox-switch regulatory mechanism of thiolase from Clostridium acetobutylicum. Nat Commun 6:8410. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9410
Kim S, Cheong S, Gonzalez R (2016) Engineering Escherichia coli for the synthesis of short-and medium-chain α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids. Metab Eng 36:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.03.005
Kim SG, Jang S, Lim JH, Jeon BS, Kim J, Kim KH, Sang B-I, Jung GY (2018) Optimization of hexanoic acid production in recombinant Escherichia coli by precise flux rebalancing. Bioresour Technol 247:1253–1257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.014
King NP, Bale JB, Sheffler W, McNamara DE, Gonen S, Gonen T, Yeates TO, Baker D (2014) Accurate design of co-assembling multi-component protein nanomaterials. Nature 510:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13404
Koga N, Tatsumi-Koga R, Liu G, Xiao R, Acton TB, Montelione GT, Baker D (2012) Principles for designing ideal protein structures. Nature 491:222–227. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11600
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Li Z, Qiao K, Che X, Stephanopoulos G (2017) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the synthesis of the quadripolymer poly(glycolate-co-lactate-co-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) from glucose. Metab Eng 44:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.09.003
Li M, Chen X, Che X, Zhang H, Wu L, Du H, Chen G (2018) Engineering Pseudomonas entomophila for synthesis of copolymers with defined fractions of 3-hydroxybutyrate and medium-chain-length 3-hydroxyalkanoates. Metab Eng 52:253–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.12.007
Li G, Huang D, Sui X, Li S, Huang B, Zhang X, Wu H, Deng Y (2020) Advances in microbial production of medium-chain dicarboxylic acids for nylon materials. React Chem Eng 5:221–238. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9re00338j
Lian J, Zhao H (2015) Reversal of the β-oxidation cycle in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for production of fuels and chemicals. ACS Synth Biol 4:332–341. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb500243c
Machado HB, Dekishima Y, Luo H, Lan EI, Liao JC (2012) A selection platform for carbon chain elongation using the CoA-dependent pathway to produce linear higher alcohols. Metab Eng 14:504–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2012.07.002
Maja K, Martin G (2018) Engineering strategies for rational polyketide synthase design. Nat Prod Rep 35:1070–1081. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NP00030A
Mann MS, Lütke-Eversloh T (2013) Thiolase engineering for enhanced butanol production in Clostridium acetobutylicum. Biotechnol Bioeng 110:887–897. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24758
Martin CH, Dhamankar H, Tseng H-C, Sheppard MJ, Reisch CR, Prather KLJ (2013) A platform pathway for production of 3-hydroxyacids provides a biosynthetic route to 3-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone. Nat Commun 4:1414. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2418
Masami N, Hiroko A, Keiichiro K, Yomi W, Takeo N, Mitsuhiro U, Sakamoto T, Inui H, Yoshihisa N, Miyatake K (2015) Alteration of wax ester content and composition in Euglena gracilis with gene silencing of 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase isozymes. Lipids 50:483–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-015-4010-3
Matthew W, Nansook H, Matthew S, Ashley MB, Colin JJ (2019) Protein engineering: the potential of remote mutations. Biochem Soc Trans 47:701–711. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20180614
McMahon MD, Prather KLJ (2014) Functional screening and in vitro analysis reveal thioesterases with enhanced substrate specificity profiles that improve short-chain fatty acid production in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microb 80:1042–1050. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03303-13
Meriläinen G, Schmitz W, Wierenga RK, Kursula P (2008) The sulfur atoms of the substrate CoA and the catalytic cysteine are required for a productive mode of substrate binding in bacterial biosynthetic thiolase, a thioester-dependent enzyme. FEBS J 275:6136–6148. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06737.x
Meriläinen G, Poikela V, Kursula P, Wierenga RK (2009) The thiolase reaction mechanism: the importance of Asn316 and His348 for stabilizing the enolate intermediate of the Claisen condensation. Biochemistry 48:11011–11025. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi901069h
Mifune J, Nakamura S, Fukui T (2010) Engineering of pha operon on Cupriavidus necator chromosome for efficient biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from vegetable oil. Polym Degrad Stabil 95:1305–1312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.02.026
Mitra R, Xu T, Xiang H, Han J (2020) Current developments on polyhydroxyalkanoates synthesis by using halophiles as a promising cell factory. Microb Cell Factories 19(1):86. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01342-z
Modis Y, Wierenga RK (2000) Crystallographic analysis of the reaction pathway of Zoogloea ramigera biosynthetic thiolase. J Mol Biol 297:1171–1182. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.3638
Mordukhova EA, Lee H-S, Pan J-G (2008) Improved thermostability and acetic acid tolerance of Escherichia coli via directed evolution of homoserine o-succinyltransferase. Appl Environ Microb 74:7660–7668. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00654-08
Pavelka A, Chovancova E, Damborsky J (2009) HotSpot Wizard: a web server for identification of hot spots in protein engineering. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W376–W383. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp410
Petri K, Herkko S, Toshiyuki F, Naomi K, Rik KW (2005) High resolution crystal structures of human cytosolic thiolase (CT): a comparison of the active sites of human CT, bacterial thiolase, and bacterial KAS I. J Mol Biol 347:189–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.01.018
Pye VE, Christensen CE, Dyer JH, Arent S, Henriksen A (2010) Peroxisomal plant 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase structure and activity are regulated by a sensitive redox switch. J Biol Chem 285:24078–24088. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.106013
Raynaud C, Meynial-Salles I, Soucaille P (2018) Reviving the Weizmann process for commercial n-butanol production. Nat Commun 9:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05661-z
RazaZulfiqar A, Sharjeel A, Ibrahim MB (2018) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: characteristics, production, recent developments and applications. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 126:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.10.001
Richard JH, Charles OR (2002) The Claisen condensation in biology. Nat Prod Rep 19:581–596. https://doi.org/10.1039/b110221b
Shen CR, Lan EI, Dekishima Y, Baez A, Km C, Liao JC (2011) Driving forces enable high-titer anaerobic 1-butanol synthesis in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microb 77:2905–2915. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03034-10
Srirangan K, Liu X, Tran TT, Charles TC, Moo-Young M, Chou CP (2016) Engineering of Escherichia coli for direct and modulated biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) copolymer using unrelated carbon sources. Sci Rep 6:36470. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36470
Stephen S, Nicholas SK, Pamela P-Y (2017) Microbial synthesis of medium-chain chemicals from renewables. Nat Biotechnol 35:1158–1166. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4022
Sudesh K, Abe H, Doi Y (2000) Synthesis, structure and properties of polyhydroxyalkanoates: biological polyesters. Prog Polym Sci 25:1503–1555. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6700(00)00035-6
Thompson S, Mayerl F, Peoples OP, Masamune S, Sinskey AJ, Walsh CT (1989) Mechanistic studies on β-ketoacyl thiolase from Zoogloea ramigera: identification of the active-site nucleophile as Cys89, its mutation to Ser89, and kinetic and thermodynamic characterization of wild-type and mutant enzymes. Biochemistry 28:5735–5742. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00440a006
Torres-Salas P, Bernal V, Lopez-Gallego F, Martinez-Crespo J, Sanchez-Murcia PA, Barrera V, Morales-Jimenez R, Garcia-Sanchez A, Manas-Fernandez A, Seoane JM, Sagrera Polo M, Miranda JD, Calvo J, Huertas S, Torres JL, Alcalde-Bascones A, Gonzalez-Barrera S, Gago F, Morreale A, Gonzalez-Barroso MDM (2018) Engineering Erg10 thiolase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a synthetic toolkit for the production of branched-chain alcohols. Biochemistry 57(8):1338–1348. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.7b01186
Wang X, Zhang W (2017) Protein catenation enhances both the stability and activity of folded structural domains. Angew Chem Int Edit 56:13985–13989. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201705194
Wei L, Wang Q, Xu N, Cheng J, Zhou W, Han G, Jiang H, Liu J, Ma Y (2019) Combining protein and metabolic engineering strategies for high-level production of o-acetylhomoserine in Escherichia coli. ACS Synth Biol 8:1153–1167. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.9b00042
Wu J, Zhang X, Xia X, Dong M (2017) A systematic optimization of medium chain fatty acid biosynthesis via the reverse beta-oxidation cycle in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 41:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.03.012
Xu L, Du Y (2018) Rational and semi-rational engineering of cytochrome P450s for biotechnological applications. Synth Syst Biotechnol 3:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2018.10.001
Xu D, Wang B, Meroueh SO (2016) Structure-based computational approaches for small-molecule modulation of protein-protein interactions. Methods Mol Biol 77:1278. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2425-7_5
Xu Y, Zhu Y, Li X, Sun B (2020) Dynamic balancing of intestinal short-chain fatty acids: the crucial role of bacterial metabolism. Trends Food Sci Technol 100:118–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.02.026
Yan M, Xu X, Zhang N, Jing G, Zang D (2017) cDNA cloning and expression analysis of the chalcone synthases (CHS) in Osmanthus fragrans. J Mol Biol 7:41–48. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajmb.2017.71004
Yu J, Xia X, Zhong J, Qian Z (2014) Direct biosynthesis of adipic acid from a synthetic pathway in recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 111:2580–2586. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25293
Yu J, Qian Z, Zhong J (2018) Advances in bio-based production of dicarboxylic acids longer than C4. Eng Life Sci 18(9):668–681. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201800023
Yu L, Yan X, Zhang X, Chen X, Wu Q, Jiang X, Chen G (2020) Biosynthesis of functional polyhydroxyalkanoates by engineered Halomonas bluephagenesis. Metab Eng 59:119–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2020.02.005
Zhao M, Huang D, Zhang X, Koffas MA, Zhou J, Deng Y (2018a) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for producing adipic acid through the reverse adipate-degradation pathway. Metab Eng 47:254–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.04.002
Zhao M, Li G, Deng Y (2018b) Engineering Escherichia coli for glutarate production as the C5 platform backbone. Appl Environ Microbiol 84(16):e00814–e00818. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00814-18
Zhou S, Hao T, Xu S, Deng Y (2020a) Coenzyme A thioester-mediated carbon chain elongation as a paintbrush to draw colorful chemical compounds. Biotechnol Adv 43:107575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107575
Zhou Y, Zhao M, Zhou S, Zhao Y, Li G, Deng Y (2020b) Biosynthesis of adipic acid by a highly efficient induction-free system in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 314-315:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.03.011
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFA0905502), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21877053, 31900066), the Top-Notch Academic Programs Project of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (TAPP), the National First-class Discipline Program of Light Industry Technology and Engineering (LITE2018-24), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JUSRP12056, JUSRP51705A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y. D. and S. Z. designed the structure of this review. Y. D. and S. Z. revised the manuscript. L.L. wrote the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Zhou, S. & Deng, Y. The 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase: an engineered enzyme for carbon chain elongation of chemical compounds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 8117–8129 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10848-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10848-w