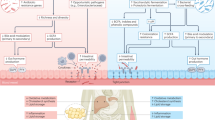
Abstract
Current advances on gut microbiota have broadened our view on host-microbiota interactions. As a microbiota-targeted approach, the use of antibiotics has been widely adopted to explore the role of gut microbiota in vivo. Antibiotics can change the microbial composition, resulting in varied effects, depending on the antibiotic class, dosage, and duration. Antibiotic intervention in early life leads to life-long phenotype alterations, including obesity. Antibiotic-induced changes in gut microbiota affect the epithelial utilization of both macronutrients (e.g., amino acids) and micronutrients (e.g., copper, vitamin E) and the redox homeostasis. Of particular interest is the regulation of gut anaerobiosis and aerobiosis by oxygen availability, which is closely related to epithelial metabolism. Additionally, antibiotic interventions enable to identify novel roles of gut microbiota in gut-liver axis and gut-brain axis. Indigenous antimicrobial molecules are produced by certain microbes, and they have the potential to affect function through eliciting changes in the gut microbiota. This review discusses at length these findings to gain a better and novel insight into microbiota-host interactions and the mechanisms involved.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azevedo AC, Bento CB, Ruiz JC, Queiroz MV, Mantovani HC (2015) Distribution and genetic diversity of bacteriocin gene clusters in rumen microbial genomes. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:7290–7304
Becattini S, Taur Y, Pamer EG (2016) Antibiotic-induced changes in the intestinal microbiota and disease. Trends Mol Med 22:458–478
Behr C, Slopianka M, Haake V, Strauss V, Sperber S, Kamp H, Walk T, Beekmann K, Rietjens I, van Ravenzwaay B (2019) Analysis of metabolome changes in the bile acid pool in feces and plasma of antibiotic-treated rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 363:79–87
Brussow H (2015) Growth promotion and gut microbiota: insights from antibiotic use. Environ Microbiol 17:2216–2227
Byndloss MX, Olsan EE, Rivera-Chávez F, Tiffany CR, Cevallos SA, Lokken KL, Torres TP, Byndloss AJ, Faber F, Gao Y (2017) Microbiota-activated PPAR-γ signaling inhibits dysbiotic Enterobacteriaceae expansion. Science 357:570–575
Caputi V, Marsilio I, Filpa V, Cerantola S, Orso G, Bistoletti M, Paccagnella N, De Martin S, Montopoli M, Dall'Acqua S, Crema F, Di Gangi IM, Galuppini F, Lante I, Bogialli S, Rugge M, Debetto P, Giaroni C, Giron MC (2017) Antibiotic-induced dysbiosis of the microbiota impairs gut neuromuscular function in juvenile mice. Br J Pharmacol 174:3623–3639
Champagne-Jorgensen K, Kunze WA, Forsythe P, Bienenstock J, McVey Neufeld KA (2019) Antibiotics and the nervous system: more than just the microbes? Brain Behav Immun 77:7–15
Chatzispyrou IA, Held NM, Mouchiroud L, Auwerx J, Houtkooper RH (2015) Tetracycline antibiotics impair mitochondrial function and its experimental use confounds research. Cancer Res 75:4446–4449
Chevalier C, Stojanovic O, Colin DJ, Suarez-Zamorano N, Tarallo V, Veyrat-Durebex C, Rigo D, Fabbiano S, Stevanovic A, Hagemann S, Montet X, Seimbille Y, Zamboni N, Hapfelmeier S, Trajkovski M (2015) Gut microbiota orchestrates energy homeostasis during cold. Cell 163:1360–1374
Dapito DH, Mencin A, Gwak GY, Pradere JP, Jang MK, Mederacke I, Caviglia JM, Khiabanian H, Adeyemi A, Bataller R, Lefkowitch JH, Bower M, Friedman R, Sartor RB, Rabadan R, Schwabe RF (2012) Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma by the intestinal microbiota and TLR4. Cancer Cell 21:504–516
Desbonnet L, Clarke G, Traplin A, O’Sullivan O, Crispie F, Moloney RD, Cotter PD, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2015) Gut microbiota depletion from early adolescence in mice: implications for brain and behaviour. Brain Behav Immun 48:165–173
Djaldetti M, Nachmias N, Bessler H (2016) The effect of antibiotics on cytokine production by mononuclear cells and the cross-talk with colon cancer cells. J Pharm Pharmacog Res 4:134–143
Espey MG (2013) Role of oxygen gradients in shaping redox relationships between the human intestine and its microbiota. Free Radic Biol Med 55:130–140
Gao K, Pi Y, Mu CL, Peng Y, Huang Z, Zhu WY (2018) Antibiotics-induced modulation of large intestinal microbiota altered aromatic amino acid profile and expression of neurotransmitters in the hypothalamus of piglets. J Neurochem 146:219–234
Gao K, Pi Y, Mu CL, Farzi A, Liu Z, Zhu WY (2019) Increasing carbohydrate availability in the hindgut promotes hypothalamic neurotransmitter synthesis: aromatic amino acids linking the microbiota-brain axis. J Neurochem 149:641–659
Garcia-Gutierrez E, Mayer MJ, Cotter PD, Narbad A (2019) Gut microbiota as a source of novel antimicrobials. Gut Microbes 10:1–21
Guida F, Turco F, Iannotta M, De Gregorio D, Palumbo I, Sarnelli G, Furiano A, Napolitano F, Boccella S, Luongo L, Mazzitelli M, Usiello A, De Filippis F, Iannotti FA, Piscitelli F, Ercolini D, de Novellis V, Di Marzo V, Cuomo R, Maione S (2018) Antibiotic-induced microbiota perturbation causes gut endocannabinoidome changes, hippocampal neuroglial reorganization and depression in mice. Brain Behav Immun 67:230–245
Hildebrand F, Moitinho-Silva L, Blasche S, Jahn MT, Gossmann TI, Heuerta-Cepas J, Hercog R, Luetge M, Bahram M, Pryszlak A, Alves RJ, Waszak SM, Zhu A, Ye L, Costea PI, Aalvink S, Belzer C, Forslund SK, Sunagawa S, Hentschel U, Merten C, Patil KR, Benes V, Bork P (2019) Antibiotics-induced monodominance of a novel gut bacterial order. Gut 68:1781–1790
Hoban AE, Stilling RM, Moloney GM, Moloney RD, Shanahan F, Dinan TG, Cryan JF, Clarke G (2017) Microbial regulation of microRNA expression in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Microbiome 5:102
Ianiro G, Tilg H, Gasbarrini A (2016) Antibiotics as deep modulators of gut microbiota: between good and evil. Gut 65:1906–1915
Inoue Y, Fukui H, Xu X, Kondo T, Kono T, Tozawa K, Ohda Y, Tomita T, Oshima T, Watari J (2018) Sa1592-Antibiotics treatment prolongs gastrointestinal transit time accompanied by increase of colonic Glp-1/Gpr43 expression. Gastroenterology 154:S-324
Johnson TA, Looft T, Severin AJ, Bayles DO, Nasko DJ, Wommack KE, Howe A,Allen HK (2017) The in-feed antibiotic carbadox induces phage gene transcription in the swine gut microbiome. MBio 8:e00709-17
Kang JD, Myers CJ, Harris SC, Kakiyama G, Lee I-K, Yun B-S, Matsuzaki K, Furukawa M, Min H-K, Bajaj JS (2019) Bile acid 7α-dehydroxylating gut bacteria secrete antibiotics that inhibit Clostridium difficile: Role of secondary bile acids. Cell Chem Biol 26:27–34 e24
Kuno T, Hirayama-Kurogi M, Ito S, Ohtsuki S (2019) Proteomic analysis of small intestinal epithelial cells in antibiotic-treated mice: changes in drug transporters and metabolizing enzymes. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 34(2):159–162
Leclercq S, Mian FM, Stanisz AM, Bindels LB, Cambier E, Ben-Amram H, Koren O, Forsythe P, Bienenstock J (2017) Low-dose penicillin in early life induces long-term changes in murine gut microbiota, brain cytokines and behavior. Nat Commun 8:15062
Ling LL, Schneider T, Peoples AJ, Spoering AL, Engels I, Conlon BP, Mueller A, Schäberle TF, Hughes DE, Epstein S (2015) A new antibiotic kills pathogens without detectable resistance. Nature 517:455–459
Litvak Y, Byndloss MX, Tsolis RM, Baumler AJ (2017) Dysbiotic Proteobacteria expansion: a microbial signature of epithelial dysfunction. Curr Opin Microbiol 39:1–6
Litvak Y, Byndloss MX, Baumler AJ (2018) Colonocyte metabolism shapes the gut microbiota. Science 362(6418):eaat9076
Liu J, Wu M, He J, Xiao C, Xue Y, Fu T, Lin C, Dong D, Li Z (2018) Antibiotic-induced dysbiosis of gut microbiota impairs corneal nerve regeneration by affecting CCR2-negative macrophage distribution. Am J Pathol 188:2786–2799
Livanos AE, Greiner TU, Vangay P, Pathmasiri W, Stewart D, McRitchie S, Li H, Chung J, Sohn J, Kim S, Gao Z, Barber C, Kim J, Ng S, Rogers AB, Sumner S, Zhang XS, Cadwell K, Knights D, Alekseyenko A, Backhed F, Blaser MJ (2016) Antibiotic-mediated gut microbiome perturbation accelerates development of type 1 diabetes in mice. Nat Microbiol 1:16140
Looft T, Johnson TA, Allen HK, Bayles DO, Alt DP, Stedtfeld RD, Sul WJ, Stedtfeld TM, Chai B, Cole JR, Hashsham SA, Tiedje JM, Stanton TB (2012) In-feed antibiotic effects on the swine intestinal microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:1691–1696
Looft T, Allen HK, Cantarel BL, Levine UY, Bayles DO, Alt DP, Henrissat B, Stanton TB (2014) Bacteria, phages and pigs: the effects of in-feed antibiotics on the microbiome at different gut locations. ISME J 8:1566
Lowe PP, Gyongyosi B, Satishchandran A, Iracheta-Vellve A, Cho Y, Ambade A, Szabo G (2018) Reduced gut microbiome protects from alcohol-induced neuroinflammation and alters intestinal and brain inflammasome expression. J Neuroinflammation 15:298
Ma C, Han M, Heinrich B, Fu Q, Zhang Q, Sandhu M, Agdashian D, Terabe M, Berzofsky JA, Fako V, Ritz T, Longerich T, Theriot CM, McCulloch JA, Roy S, Yuan W, Thovarai V, Sen SK, Ruchirawat M, Korangy F, Wang XW, Trinchieri G,Greten TF (2018) Gut microbiome-mediated bile acid metabolism regulates liver cancer via NKT cells. Science 360:eaan5931
Manrique P, Bolduc B, Walk ST, van der Oost J, de Vos WM, Young MJ (2016) Healthy human gut phageome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:10400–10405
Miller KA, Vicentini FA, Hirota SA, Sharkey KA, Wieser ME (2019) Antibiotic treatment affects the expression levels of copper transporters and the isotopic composition of copper in the colon of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:5955–5960
Modi SR, Lee HH, Spina CS, Collins JJ (2013) Antibiotic treatment expands the resistance reservoir and ecological network of the phage metagenome. Nature 499:219–222
Mu C, Yang Y, Zhu W (2016) Gut microbiota: the brain peacekeeper. Front Microbiol 7:345
Mu C, Yang Y, Su Y, Zoetendal EG, Zhu W (2017a) Differences in microbiota membership along the gastrointestinal tract of piglets and their differential alterations following an early-life antibiotic intervention. Front Microbiol 8:797
Mu C, Yang Y, Yu K, Yu M, Zhang C, Su Y, Zhu W (2017b) Alteration of metabolomic markers of amino-acid metabolism in piglets with in-feed antibiotics. Amino Acids 49:771–781
Nogacka AM, Salazar N, Arboleya S, Suarez M, Fernandez N, Solis G, de Los Reyes-Gavilan CG, Gueimonde M (2018) Early microbiota, antibiotics and health. Cell Mol Life Sci 75:83–91
Olishevska S, Nickzad A, Deziel E (2019) Bacillus and Paenibacillus secreted polyketides and peptides involved in controlling human and plant pathogens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:1189–1215
Ooijevaar RE, Terveer EM, Verspaget HW, Kuijper EJ, Keller JJ (2019) Clinical application and potential of fecal microbiota transplantation. Annu Rev Med 70:335–351
Palleja A, Mikkelsen KH, Forslund SK, Kashani A, Allin KH, Nielsen T, Hansen TH, Liang S, Feng Q, Zhang C, Pyl PT, Coelho LP, Yang H, Wang J, Typas A, Nielsen MF, Nielsen HB, Bork P, Wang J, Vilsboll T, Hansen T, Knop FK, Arumugam M, Pedersen O (2018) Recovery of gut microbiota of healthy adults following antibiotic exposure. Nat Microbiol 3:1255–1265
Pi Y, Gao K, Peng Y, Mu CL, Zhu WY (2019) Antibiotic-induced alterations of the gut microbiota and microbial fermentation in protein parallel the changes in host nitrogen metabolism of growing pigs. Animal 13:262–272
Ran L, Liu AB, Lee MJ, Xie P, Lin Y, Yang CS (2019) Effects of antibiotics on degradation and bioavailability of different vitamin E forms in mice. Biofactors 45:450–462
Reese AT, Cho EH, Klitzman B, Nichols SP, Wisniewski NA, Villa MM, Durand HK, Jiang S, Midani FS, Nimmagadda SN, O’Connell TM, Wright JP, Deshusses MA,David LA (2018) Antibiotic-induced changes in the microbiota disrupt redox dynamics in the gut. Elife 7:e35987
Rivera-Chavez F, Zhang LF, Faber F, Lopez CA, Byndloss MX, Olsan EE, Xu G, Velazquez EM, Lebrilla CB, Winter SE, Baumler AJ (2016) Depletion of butyrate-producing Clostridia from the gut microbiota drives an aerobic luminal expansion of Salmonella. Cell Host Microbe 19:443–454
Rizzatti G, Ianiro G, Gasbarrini A (2018) Antibiotic and modulation of microbiota: a new paradigm? J Clin Gastroenterol 52:S74–S77
Roychowdhury S, Cadnum J, Glueck B, Obrenovich M, Donskey C, Cresci GAM (2018) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and a prebiotic protect intestinal health in a mouse model of antibiotic and Clostridium difficile exposure. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 42:1156–1167
Schulfer AF, Battaglia T, Alvarez Y, Bijnens L, Ruiz VE, Ho M, Robinson S, Ward T, Cox LM, Rogers AB, Knights D, Sartor RB, Blaser MJ (2018) Intergenerational transfer of antibiotic-perturbed microbiota enhances colitis in susceptible mice. Nat Microbiol 3:234–242
Schulfer AF, Schluter J, Zhang Y, Brown Q, Pathmasiri W, McRitchie S, Sumner S, Li H, Xavier JB, Blaser MJ (2019) The impact of early-life sub-therapeutic antibiotic treatment (STAT) on excessive weight is robust despite transfer of intestinal microbes. ISME J 13(5):1280–1292
Sherwin E, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2018) Recent developments in understanding the role of the gut microbiota in brain health and disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1420:5–25
Soto M, Herzog C, Pacheco JA, Fujisaka S, Bullock K, Clish CB, Kahn CR (2018) Gut microbiota modulate neurobehavior through changes in brain insulin sensitivity and metabolism. Mol Psychiatry 23:2287
Sprockett D, Fukami T, Relman DA (2018) Role of priority effects in the early-life assembly of the gut microbiota. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:197–205
Stanisavljevic S, Cepic A, Bojic S, Veljovic K, Mihajlovic S, Dedovic N, Jevtic B, Momcilovic M, Lazarevic M, Mostarica Stojkovic M, Miljkovic D, Golic N (2019) Oral neonatal antibiotic treatment perturbs gut microbiota and aggravates central nervous system autoimmunity in Dark Agouti rats. Sci Rep 9:918
Stark CM, Susi A, Emerick J, Nylund CM (2019) Antibiotic and acid-suppression medications during early childhood are associated with obesity. Gut 68:62–69
Suter PM, Golner BB, Goldin BR, Morrow FD, Russell RM (1991) Reversal of protein-bound vitamin B12 malabsorption with antibiotics in atrophic gastritis. Gastroenterology 101:1039–1045
Swann JR, Want EJ, Geier FM, Spagou K, Wilson ID, Sidaway JE, Nicholson JK, Holmes E (2011) Systemic gut microbial modulation of bile acid metabolism in host tissue compartments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(Suppl 1):4523–4530
Tripathi A, Debelius J, Brenner DA, Karin M, Loomba R, Schnabl B, Knight R (2018) The gut-liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:397–411
Ubeda C, Pamer EG (2012) Antibiotics, microbiota, and immune defense. Trends Immunol 33:459–466
Vrieze A, Out C, Fuentes S, Jonker L, Reuling I, Kootte RS, van Nood E, Holleman F, Knaapen M, Romijn JA, Soeters MR, Blaak EE, Dallinga-Thie GM, Reijnders D, Ackermans MT, Serlie MJ, Knop FK, Holst JJ, van der Ley C, Kema IP, Zoetendal EG, de Vos WM, Hoekstra JB, Stroes ES, Groen AK, Nieuwdorp M (2014) Impact of oral vancomycin on gut microbiota, bile acid metabolism, and insulin sensitivity. J Hepatol 60:824–831
Xiao H, Shao F, Wu M, Ren W, Xiong X, Tan B, Yin Y (2015) The application of antimicrobial peptides as growth and health promoters for swine. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 6:19
Yu M, Mu C, Yang Y, Zhang C, Su Y, Huang Z, Yu K, Zhu W (2017a) Increases in circulating amino acids with in-feed antibiotics correlated with gene expression of intestinal amino acid transporters in piglets. Amino Acids 49:1587–1599
Yu M, Zhang C, Yang Y, Mu C, Su Y, Yu K, Zhu W (2017b) Long-term effects of early antibiotic intervention on blood parameters, apparent nutrient digestibility, and fecal microbial fermentation profile in pigs with different dietary protein levels. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 8:60
Zarrinpar A, Chaix A, Xu ZZ, Chang MW, Marotz CA, Saghatelian A, Knight R, Panda S (2018) Antibiotic-induced microbiome depletion alters metabolic homeostasis by affecting gut signaling and colonic metabolism. Nat Commun 9:2872
Funding
This work was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China (31430082) and National Key Basic Research Program of China (2013CB127300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, C., Zhu, W. Antibiotic effects on gut microbiota, metabolism, and beyond. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 9277–9285 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10165-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10165-x