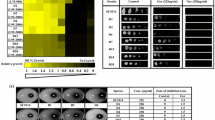
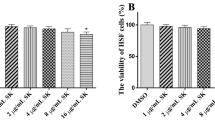
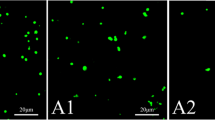
Abstract
Candida albicans is the most common clinical pathogenic fungus, which is highly susceptible to immunodeficiency. Development of novel antifungal agents has become a growing trend in the treatment of Candida infections. C16-Fengycin A, a lipopeptide isolated from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens fmb60 showed significant fungicidal activity against C. albicans. In the study, we explored the possible antifungal mode of C16-Fengycin A. It was predicted that C16-Fengycin A had the ability to disrupt the cell wall due to its alterations of cell ultrastructure, and reduction of cell wall hydrophobicity. This was further confirmed by the changes in the exposure of the cell wall components and down-regulation of the genes related in the cell wall synthesis. Meanwhile, with the treatment of C16-Fengycin A, the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) increased, resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction in the cells. We hypothesized that the antifungal mechanism of C16-Fengycin A might be via the destruction of the cell wall and the accumulation of ROS, which could activate the High-Osmolarity Glycerol Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (HOG-MAPK) pathway. Our findings indicated that C16-Fengycin A could be a potential antifungal agent that could be used to treat candida infections.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
An AM, Francois IE, Meert EM, Li QT, Cammue BP, Thevissen K (2007) The antifungal activity of RsAFP2, a plant defensin from Raphanus sativus, involves the induction of reactive oxygen species in Candida albicans. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 13(4):243–247. https://doi.org/10.1159/000104753
Anderson JB (2005) Evolution of antifungal-drug resistance: mechanisms and pathogen fitness. Nat Rev Microbiol 3(7):547–556. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1179
Andres MT, Viejo-Diaz M, Fierro JF (2008) Human lactoferrin induces apoptosis-like cell death in Candida albicans: critical role of K+-channel-mediated K+ efflux. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52(11):4081–4088. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.01597-07
Arima K, Kakinuma A, Tamura G (1968) Surfactin, a crystalline peptidelipid surfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis: isolation, characterization and its inhibition of fibrin clot formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 31(3):488–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291X(68)90503-2
Bauer KD (1993) Quality control issues in DNA content flow cytometry. Ann N Y Acad Sci 677:59–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb38765.x
Bayhan GI, Garipardic M, Karaman K, Akbayram S (2016) Voriconazole-associated visual disturbances and hallucinations. Cutan Ocul Toxicol 35(1):80–82. https://doi.org/10.3109/15569527.2015.1020544
Besson F, Peypoux F, Michel G, Delcambe L (1976) Characterization of iturin a in antibiotics from various strains of Bacillus subtilis. J Antibiot 29(10):1043–1049. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.29.1043
Brewster JL, de Valoir T, De DND, Winter E, Gustin MC (1993) An osmosensing signal transduction pathway in yeast. Science 259(5102):1760–1763. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7681220
Calderone R, Sun N, Gay-Andrieu F, Groutas W, Weerawarna P, Prasad S, Alex D, Li D (2014) Antifungal drug discovery: the process and outcomes. Future Microbiol 9(6):791–805. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb.14.32
Cheetham J, MacCallum DM, Doris KS, da Silva Dantas A, Scorfield S, Odds F, Smith DA, Quinn J (2011) MAPKKK-independent regulation of the Hog1 stress-activated protein kinase in Candida albicans. J Biol Chem 286(49):42002–42016. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.265231
Cheng W, Feng YQ, Ren J, Jing D, Wang C (2016) Anti-tumor role of Bacillus subtilis fmbJ-derived fengycin on human colon cancer HT29 cell line. Neoplasma 63(2):215–222. https://doi.org/10.4149/206_150518N270
Chin VK, Lee TY, Rusliza B, Chong PP (2016) Dissecting Candida albicans infection from the perspective of C. albicans virulence and omics approaches on host-pathogen interaction: a review. Int J Mol Sci 17(10):1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101643
Costa V, Moradas-Ferreira P (2001) Oxidative stress and signal transduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: insights into ageing, apoptosis and diseases. Mol Asp Med 22(4):217–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-2997(01)00012-7
Ene IV, Walker LA, Schiavone M, Lee KK, Martin-Yken H, Dague E, Gow NA, Munro CA, Brown AJ (2015) Cell wall remodeling enzymes modulate fungal cell wall elasticity and osmotic stress resistance. MBio 6(4):e00986. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00986-15
Fernandes C, Anjos J, Walker LA, Silva BM, Cortes L, Mota M, Munro CA, Gow NA, Gonçalves T (2014) Modulation of Alternaria infectoria cell wall chitin and glucan synthesis by cell wall synthase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(5):2894–2904. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02647-13
Ford CB, Funt JM, Abbey D, Issi L, Guiducci C, Martinez DA, Delorey T, Li BY, White TC, Cuomo C, Rao RP, Berman J, Thompson DA, Regev A (2015) The evolution of drug resistance in clinical isolates of Candida albicans. Elife 4:e00662. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00662
Gregori C, Schuller C, Roetzer A, Schwarzmuller T, Ammerer G, Kuchler K (2007) The high-osmolarity glycerol response pathway in the human fungal pathogen Candida glabrata strain ATCC 2001 lacks a signaling branch that operates in baker's yeast. Eukaryot Cell 6(9):1635–1645. https://doi.org/10.1128/EC.00106-07
Helmerhorst EJ, Troxler RF, Oppenheim FG (2001) The human salivary peptide histatin 5 exerts its antifungal activity through the formation of reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(25):14637–14642. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.141366998
Horowitz S, Griffin WM (1991) Structural analysis of Bacillus licheniformis 86 surfactant. J Ind Microbiol 7(1):45–52
Hultmark D, Engstrom Å, Bennich H, Kapur R, Boman HG (1982) Insect immunity: isolation and structure of cecropin D and four minor antibacterial components from Cecropia pupae. Eur J Biochem 127(1):207–217. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06857.x
Hwang B, Hwang JS, Lee J, Lee DG (2010) Antifungal properties and mode of action of psacotheasin, a novel knottin-type peptide derived from Psacothea hilaris. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 400(3):352–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.08.063
Kullberg BJ, Arendrup MC (2015) Invasive candidiasis. N Engl J Med 373(15):1445–1456. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1315399
Lee HS, Kim Y (2017) Paeonia lactiflora inhibits cell wall synthesis and triggers membrane depolarization in Candida albicans. J Microbiol Biotechnol 27(2):395–404. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1611.11064
Liu Y, Lu J, Sun J, Lu F, Bie X, Lu Z (2019) Membrane disruption and DNA binding of Fusarium graminearum cell induced by C16-Fengycin A produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Food Control 102:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.03.031
Lu Y, Su C, Unoje O, Liu H (2014) Quorum sensing controls hyphal initiation in Candida albicans through Ubr1-mediated protein degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(5):1975–1980. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1318690111
Lu H, Qian S, Muhammad U, Jiang X, Han J, Lu Z (2016) Effect of fructose on promoting fengycin biosyntesis in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens fmb-60. J Appl Microbiol 121(6):1653–1664. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13291
Mandal SM, Porto WF, Dey P, Maiti MK, Ghosh AK, Franco OL (2013) The attack of the phytopathogens and the trumpet solo: identification of a novel plant antifungal peptide with distinct fold and disulfide bond pattern. Biochimie 95(10):1939–1948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2013.06.027
Miao H, Zhao L, Li C, Shang Q, Lu H, Fu Z, Wang L, Jiang Y, Cao Y (2012) Inhibitory effect of Shikonin on Candida albicans growth. Biol Pharm Bull 35(11):1956–1963. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b12-00338
Mouyna I, Fontaine T, Vai M, Monod M, Fonzi WA, Diaquin M, Popolo L, Hartland RP, Latge JP (2000) Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored glucanosyltransferases play an active role in the biosynthesis of the fungal cell wall. J Biol Chem 275(20):14882–14889. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.20.14882
Naito Y, Tohda H, Okuda K, Takazoe I (1993) Adherence and hydrophobicity of invasive and noninvasive strains of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Oral Microbiol Immunol 8(4):195–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-302X.1993.tb00559.x
Newman DJ (2008) Natural products as leads to potential drugs: an old process or the new hope for drug discovery? J Med Chem 51(9):2589–2599. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm0704090
Nishikiori T, Naganawa H, Muraoka Y, Aoyagi T, Umezawa H (1986) Plipastatins: new inhibitors of phospholipase A2, produced by Bacillus Cereus BMG302-fF67. III. Structural elucidation of plipastins. J Antibiot 39(6):755–761. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.39.755
Odds FC, Brown AJ, Gow NA (2003) Antifungal agents: mechanisms of action. Trends Microbiol 11(6):272–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0966-842X(03)00117-3
Papon N, Courdavault V, Clastre M, Bennett RJ (2013) Emerging and emerged pathogenic Candida species: beyond the Candida albicans paradigm. PLoS Pathog 9(9):e1003550. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003550
Peleg AY, Hogan DA, Mylonakis E (2010) Medically important bacterial-fungal interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(5):340–349. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2313
Perlin DS (2015) Mechanisms of echinocandin antifungal drug resistance. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1354:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12831
Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ (2010) Epidemiology of invasive mycoses in North America. Crit Rev Microbiol 36(1):1–53. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408410903241444
Phillips AJ, Sudbery I, Ramsdale M (2003) Apoptosis induced by environmental stresses and amphotericin B in Candida albicans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(24):14327–14332. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2332326100
Qi X, Zhou C, Li P, Xu W, Cao Y, Ling H, Ning Chen W, Ming Li C, Xu R, Lamrani M, Mu Y, Leong SS, Wook Chang M, Chan-Park MB (2010) Novel short antibacterial and antifungal peptides with low cytotoxicity: efficacy and action mechanisms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 398(3):594–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.06.131
Rajasekharan SK, Kamalanathan C, Ravichandran V, Ray AK, Satish AS, Mohanvel SK (2018) Mannich base limits Candida albicans virulence by inactivating Ras-cAMP-PKA pathway. Sci Rep 8(1):14972. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32935-9
Shai Y (1995) Molecular recognition between membrane-spanning polypeptides. Trends Biochem Sci 20(11):460–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0004(00)89101-X
Sherrington SL, Sorsby E, Mahtey N, Kumwenda P, Lenardon MD, Brown I, Ballou ER, MacCallum DM, Hall RA (2017) Adaptation of Candida albicans to environmental pH induces cell wall remodelling and enhances innate immune recognition. PLoS Pathog 13(5):e1006403. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006403
Stein T (2005) Bacillus subtilis antibiotics: structures, syntheses and specific functions. Mol Microbiol 56(4):845–857. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04587.x
Sun L, Lu Z, Bie X, Lu F, Yang S (2006) Isolation and characterization of a co-producer of fengycins and surfactins, endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ES-2, from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22(12):1259–1266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9170-0
Tang Q, Bie X, Lu Z, Lv F, Tao Y, Qu X (2014) Effects of fengycin from Bacillus subtilis fmbJ on apoptosis and necrosis in Rhizopus stolonifer. J Microbiol 52(8):675–680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-014-3605-3
Turner SA, Butler G (2014) The Candida pathogenic species complex. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 4(9):a019778. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a019778
Vanittanakom N, Loeffler W, Koch U, Jung G (1986) Fengycin-A novel antifungal lipopeptide antibiotic produced by Bacillus Subtillis F-29-3. J Antibiot 39(7):888–901. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.39.888
Vincent BM, Lancaster AK, Scherz-Shouval R, Whitesell L, Lindquist S (2013) Fitness trade-offs restrict the evolution of resistance to amphotericin B. PLoS Biol 11(10):e1001692. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001692
Wei YH, Wang LC, Chen WC, Chen SY (2010) Production and characterization of fengycin by indigenous Bacillus subtilis F29-3 originating from a potato farm. Int J Mol Sci 11(11):4526–4538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11114526
Yin H, Guo C, Wang Y, Liu D, Lv Y, Lv F, Lu Z (2013) Fengycin inhibits the growth of the human lung cancer cell line 95D through reactive oxygen species production and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Anti-Cancer Drugs 24(6):587–598. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0b013e3283611395
Zhu X, Zhang L, Wang J, Ma Z, Xu W, Li J, Shan A (2015) Characterization of antimicrobial activity and mechanisms of low amphipathic peptides with different alpha-helical propensity. Acta Biomater 18:155–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2015.02.023
Zoratti M, Szabo I (1995) The mitochondrial permeability transition. Biochim Biophys Acta 1241(2):139–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4157(95)00003-A
Funding
This work was financially supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31571887).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 205 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Lu, J., Sun, J. et al. C16-Fengycin A affect the growth of Candida albicans by destroying its cell wall and accumulating reactive oxygen species. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 8963–8975 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10117-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10117-5