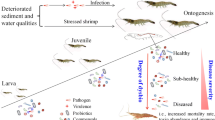
Abstract
One common notion is emerging that gut eukaryotes are commensal or beneficial, rather than detrimental. To date, however, surprisingly few studies have been taken to discern the factors that govern the assembly of gut eukaryotes, despite growing interest in the dysbiosis of gut microbiota-disease relationship. Herein, we firstly explored how the gut eukaryotic microbiotas were assembled over shrimp postlarval to adult stages and a disease progression. The gut eukaryotic communities changed markedly as healthy shrimp aged, and converged toward an adult-microbiota configuration. However, the adult-like stability was distorted by disease exacerbation. A null model untangled that the deterministic processes that governed the gut eukaryotic assembly tended to be more important over healthy shrimp development, whereas this trend was inverted as the disease progressed. After ruling out the baseline of gut eukaryotes over shrimp ages, we identified disease-discriminatory taxa (species level afforded the highest accuracy of prediction) that characteristic of shrimp health status. The profiles of these taxa contributed an overall 92.4% accuracy in predicting shrimp health status. Notably, this model can accurately diagnose the onset of shrimp disease. Interspecies interaction analysis depicted how the disease-discriminatory taxa interacted with one another in sustaining shrimp health. Taken together, our findings offer novel insights into the underlying ecological processes that govern the assembly of gut eukaryotes over shrimp postlarval to adult stages and a disease progression. Intriguingly, the established model can quantitatively and accurately predict the incidences of shrimp disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulsalam AM, Ithoi I, Al-Mekhlafi HM, Khan AH, Ahmed A, Surin J, Mak JW (2013) Prevalence, predictors and clinical significance of Blastocystis sp. in Sebha, Libya. Parasit Vectors 6(1):86
Andersen LO, Vedel NH, Stensvold CR (2013) Waiting for the human intestinal eukaryotome. ISME J 7(7):1253–1255
Ashbee HR, Evans EV (2002) Immunology of diseases associated with Malassezia species. Clin Microbiol Rev 15(1):21–57
Ávila-Villa LA, Fimbres-Olivarria D, García-Sánchez G, Gollas-Galván T, Hernández-López J, Martínez-Porchas M (2012) Physiological and immune responses of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) infected with necrotizing hepatopancreatitis bacterium. Aquaculture 324(3):14–19
Bledsoe JW, Peterson BC, Swanson KS, Small BC (2016) Ontogenetic characterization of the intestinal microbiota of channel catfish through 16S rRNA gene sequencing reveals insights on temporal shifts and the influence of environmental microbes. PLoS One 11(11):e0166379
Burns AR, Stephens WZ, Stagaman K, Wong S, Rawls JF, Guillemin K, Bohannan BJ (2016) Contribution of neutral processes to the assembly of gut microbial communities in the zebrafish over host development. ISME J 10(3):655–664
Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Desantis TZ, Andersen GL, Knight R (2009) PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 26(2):266–267
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Chase JM, Kraft NJB, Smith KG, Vellend M, Inouye BD (2011) Using null models to disentangle variation in community dissimilarity from variation in α-diversity. Ecosphere 2(2):24
Chayaburakul K, Nash G, Pratanpipat P, Sriurairatana S, Withyachumnarnkul B (2004) Multiple pathogens found in growth-retarded black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon cultivated in Thailand. Dis Aquat Org 60(2):89–96
Chen WY, Ng TH, Wu JH, Chen JW, Wang HC (2017) Microbiome dynamics in a shrimp grow-out pond with possible outbreak of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Sci Rep 7(1):9395
Churchill GA (2004) Using ANOVA to analyze microarray data. BioTechniques 37(2):173–177
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust Ecol 18(1):117–143
Cornejo-Granados F, Lopez-Zavala AA, Gallardo-Becerra L, Mendoza-Vargas A, Sánchez F, Vichido R, Brieba LG, Viana MT, Sotelo-Mundo RR, Ochoa-Leyva A (2017) Microbiome of Pacific Whiteleg shrimp reveals differential bacterial community composition between wild, aquacultured and AHPND/EMS outbreak conditions. Sci Rep 7(1):11783
Coyte KZ, Schluter J, Foster KR (2015) The ecology of the microbiome: networks, competition, and stability. Science 350(6261):663–666
Dai W, Yu W, Zhang J, Zhu J, Tao Z, Xiong J (2017) The gut eukaryotic microbiota influences the growth performance among cohabitating shrimp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(16):6447–6457
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26(19):2460–2461
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27(16):2194–2200
Fenton A, Perkins SE (2010) Applying predator-prey theory to modelling immune-mediated, within-host interspecific parasite interactions. Parasitology 137(6):1027–1038
Fjellheim AJ, Playfoot KJ, Skjermo J, Vadstein O (2012) Inter-individual variation in the dominant intestinal microbiota of reared Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) Aquac Res 43(10):1499–1508
Fry L, Baker BS (2007) Triggering psoriasis: the role of infections and medications. Clin Dermatol 25(6):606–615
Gomathi V, Saravanakumar K, Kathiresan K (2013) Production of polyunsaturated fatty acid (DHA) by mangrove-derived Aplanochytrium sp. Afr J Microbiol Res 7(13):1098–1103
Goslee SC, Urban DL, Leeuw JD, Zeileis A (2007) The ecodist package for dissimilarity-based analysis of ecological data. J Stat Softw 22(7):1–19
Greenhalgh K, Meyer KM, Aagaard KM, Wilmes P (2016) The human gut microbiome in health: establishment and resilience of microbiota over a lifetime. Environ Microbiol 18(7):2103–2116
Gutiérrez-Salazar GJ, Molina-Garza ZJ, Hernández-Acosta M, García-Salas JA, Mercado-Hernández R, Galaviz-Silva L (2011) Pathogens in Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei Boone, 1931) and their relationship with physicochemical parameters in three different culture systems in Tamaulipas, Mexico. Aquaculture 321(1):34–40
Hugerth LW, Muller EE, Hu YO, Lebrun LA, Roume H, Lundin D, Wilmes P, Andersson AF (2014) Systematic design of 18S rRNA gene primers for determining eukaryotic diversity in microbial consortia. PLoS One 9(4):e95567
Jiravanichpaisal P, Puanglarp N, Petkon S, Donnuea S, Söderhäll I, Söderhäll K (2007) Expression of immune-related genes in larval stages of the giant tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon. Fish Shellfish Immunol 23(4):815–824
Johnson PT, Hoverman JT (2012) Parasite diversity and coinfection determine pathogen infection success and host fitness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(23):9006–9011
Kamada N, Chen GY, Inohara N, Núñez G (2013) Control of pathogens and pathobionts by the gut microbiota. Nat Immunol 14(7):685–690
Karthikeyan V, Selvakumar P, Gopalakrishnan A (2015) A novel report of fungal pathogen Aspergillus awamori causing black gill infection on Litopenaeus vannamei (Pacific white shrimp). Aquaculture 444:36–40
Legendre P, Gallagher ED (2001) Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 129(2):271–280
Liaw A, Wiener M (2002) Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2(3):18–22
Lukeš J, Stensvold CR, Parfrey LW (2015) Are human intestinal eukaryotes beneficial or commensals? PLoS Pathog 11(8):e1005039
Mallon CA, Elsas JD, Salles JF (2015) Microbial invasions: the process, patterns, and mechanisms. Trends Microbiol 23(11):719–729
Massana R, Logares R (2013) Eukaryotic versus prokaryotic marine picoplankton ecology. Environ Microbiol 15(5):1254–1261
Morton ER, Lynch J, Froment A, Lafosse S, Heyer E, Przeworski M, Ran B, Segurel L (2015) Variation in rural African gut microbiomes is strongly shaped by parasitism and diet. PLoS Gent 11:e1005658
Nakabayashi A, Sei Y, Guillot J (2000) Identification of Malassezia species isolated from patients with seborrhoeic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, pityriasis versicolor and normal subjects. Med Mycol 38(5):337–341
Nie L, Zhou Q, Qiao Y, Chen J (2017) Interplay between the gut microbiota and immune responses of ayu (Plecoglossus altivelis) during Vibrio anguillarum infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 68:479–487
Nunan L, Lightner D, Pantoja C, Gomez-Jimenez S (2014) Detection of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in Mexico. Dis Aquat Org 111(1):81–86
Ohkuma M (2008) Symbioses of flagellates and prokaryotes in the gut of lower termites. Trends Microbiol 16(7):345–352
Parfrey LW (2015) Mock communities highlight the diversity of host-associated eukaryotes. Mol Ecol 24(17):4337–4339
Parfrey LW, Walters WA, Knight R (2011) Microbial eukaryotes in the human microbiome: ecology, evolution, and future directions. Front Microbiol 2:153
Parfrey LW, Walters WA, Lauber CL, Clemente JC, Berg-Lyons D, Teiling C, Kodira C, Mohiuddin M, Brunelle J, Driscoll M (2014) Communities of microbial eukaryotes in the mammalian gut within the context of environmental eukaryotic diversity. Front Microbiol 5:298
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41(1):590–596
R Core Team (2015) A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: The R Foundation for Statistical Computing. ISBN: 3-900051-07-0. http://www.R-project.org/
Refaeilzadeh P, Tang L, Liu H (2009) Cross-validation encyclopedia of database systems. Springer, pp 532–538
Sanchez A, Pascual C, Sanchez A, Vargasalbores F, Le MG, Rosas C (2001) Hemolymph metabolic variables and immune response in Litopenaeus setiferus adult males: the effect of acclimation. Aquaculture 198(1):13–28
Scanlan PD, Marchesi JR (2008) Micro-eukaryotic diversity of the human distal gut microbiota: qualitative assessment using culture-dependent and -independent analysis of faeces. ISME J 2(12):1183–1193
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504
Shaw TW, Pao YY, Wang D (2016) MetaMIS: a metagenomic microbial interaction simulator based on microbial community profiles. BMC Bioinformatics 17(1):488
Stecher B, Chaffron S, Käppeli R, Hapfelmeier S, Freedrich S, Weber TC, Kirundi J, Suar M, McCoy KD, von Mering C, Macpherson AJ, Hardt WD (2010) Like will to like: abundances of closely related species can predict susceptibility to intestinal colonization by pathogenic and commensal bacteria. PLoS Pathog 6(1):e1000711
Strobl C, Boulesteix A-L, Zeileis A, Hothorn T (2007) Bias in random forest variable importance measures. BMC Bioinformatics 8:1–10
Thitamadee S, Prachumwat A, Srisala J, Jaroenlak P, Salachan PV, Sritunyalucksana K, Flegel TW, Itsathitphaisarn O (2016) Review of current disease threats for cultivated penaeid shrimp in Asia. Aquaculture 452:69–87
Tourtip S, Wongtripop S, Stentiford GD, Bateman KS, Sriurairatana S, Chavadej J, Sritunyalucksana K, Withyachumnarnkul B (2009) Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei sp. nov. (Microsporida: Enterocytozoonidae), a parasite of the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon (Decapoda: Penaeidae): fine structure and phylogenetic relationships. J Invertebr Pathol 102(1):21–29
Valentini D, Vittucci AC, Grandin A, Tozzi AE, Russo C, Onori M, Menichella D, Bartuli A, Villani A (2013) Coinfection in acute gastroenteritis predicts a more severe clinical course in children. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 32(7):909–915
Wagner MB, Waite DW, Hoggard M, Douglas RG, Taylor MW, Biswas K (2017) Bacterial community collapse: a meta-analysis of the sinonasal microbiota in chronic rhinosinusitis. Environ Microbiol 19(1):381–392
Wells ML, Potin P, Craigie JS, Raven JA, Merchant SS, Helliwell KE, Smith AG, Camire ME, Brawley SH (2017) Algae as nutritional and functional food sources: revisiting our understanding. J Appl Phycol 29(2):1–34
Winter SE, Bäumler AJ (2014) Why related bacterial species bloom simultaneously in the gut: principles underlying the ‘Like will to like’ concept. Cell Microbiol 16(2):179–184
Xiong J, Zhu J, Zhang D (2014) The application of bacterial indicator phylotypes to predict shrimp health status. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(19):8291–8299
Xiong J, Wang K, Wu J, Qiuqian L, Yang K, Qian Y, Zhang D (2015) Changes in intestinal bacterial communities are closely associated with shrimp disease severity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(16):6911–6919
Xiong J, Dai W, Li C (2016) Advances, challenges, and directions in shrimp disease control: the guidelines from an ecological perspective. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(16):6947–6954
Xiong J, Dai W, Zhu J, Liu K, Dong C, Qiu Q (2017a) The underlying ecological processes of gut microbiota among cohabitating retarded, overgrown and normal shrimp. Microb Ecol 73(4):988–999
Xiong J, Zhu J, Dai W, Dong C, Qiu Q, Li C (2017b) Integrating gut microbiota immaturity and disease-discriminatory taxa to diagnose the initiation and severity of shrimp disease. Environ Microbiol 19(4):1490–1501
Yan Q, Li J, Yu Y, Wang J, He Z, Van Nostrand JD, Kempher ML, Wu L, Wang Y, Liao L (2016) Environmental filtering decreases with fish development for the assembly of gut microbiota. Environ Microbiol 18(12):4739–4754
Zhang M, Sun Y, Chen K, Yu N, Zhou Z, Chen L, Du Z, Li E (2014) Characterization of the intestinal microbiota in Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, fed diets with different lipid sources. Aquaculture 434:449–455
Zhu J, Dai W, Qiu Q, Dong C, Zhang J, Xiong J (2016) Contrasting ecological processes and functional compositions between intestinal bacterial community in healthy and diseased shrimp. Microb Ecol 72(4):975–985
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Project of Science and Technology Department of Ningbo (2017C10044), the Zhejiang Province Public Welfare Technology Application Research Project (2016C32063), and the K.C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 939 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, J., Yu, W., Dai, W. et al. Quantitative prediction of shrimp disease incidence via the profiles of gut eukaryotic microbiota. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 3315–3326 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8874-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8874-z