Abstract
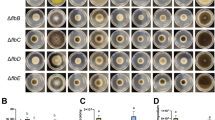
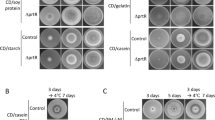
Aspergillus oryzae produces a large amount of secreted proteins in solid-state culture, and some proteins such as glucoamylase (GlaB) and acid protease (PepA) are specifically produced in solid-state culture, but rarely in submerged culture. From the disruption mutant library of A. oryzae transcriptional regulators, we successfully identified a disruption mutant showing an extremely low production level of GlaB but a normal level of α-amylase production. This strain was a disruption mutant of the C2H2-type transcription factor, FlbC, which is reported to be involved in the regulation of conidiospore development. Disruption mutants of other upstream regulators comprising a conidiation regulatory network had no apparent effect on GlaB production in solid-state culture. In addition to GlaB, the production of acid protease in solid-state culture was also markedly decreased by flbC disruption. Northern blot analyses revealed that transcripts of glaB and pepA were significantly decreased in the flbC disruption strain. These results suggested that FlbC is involved in the transcriptional regulation of genes specifically expressed under solid-state cultivation conditions, possibly independent of the conidiation regulatory network.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akao T, Gomi K, Goto K, Okazaki N, Akita O (2002) Subtractive cloning of cDNA from Aspergillus oryzae differentially regulated between solid-state culture and liquid (submerged) culture. Curr Genet 41:275–281
Anson ML (1938) Estimation of pepsin, papain and cathepsin with hemoglobin. J Gen Physiol 22:79–89
Cheevadhanarak S, Renno DV, Saunders G, Holt G (1991) Cloning and selective overexpression of an alkaline protease-encoding gene from Aspergillus oryzae. Gene 108:151–155
Fling M, Horowitz NH, Heinemann SF (1963) The isolation and properties of crystalline tyrosinase from Neurospora. J Biol Chem 238:2045–2053
Fujieda N, Murata M, Yabuta S, Ikeda T, Shimokawa C, Nakamura Y, Hata Y, Itoh S (2012) Multifunctions of MelB, a fungal tyrosinase from Aspergillus oryzae. Chembiochem 13:193–201
Gomi K, Iimura Y, Hara S (1987) Integrative transformation of Aspergillus oryzae with a plasmid containing the Aspergillus nidulans argB gene. Agric Biol Chem 51:2549–2555
Gomi K, Arikawa K, Kamiya N, Kitamoto K, Kumagai C (1993) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the acid protease-encoding gene (pepA) from Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 57:1095–1100
Gomi K, Akeno T, Minetoki T, Ozeki K, Kumagai C, Okazaki N, Iimura Y (2000) Molecular cloning and characterization of a transcriptional activator gene, amyR, involved in the amylolytic gene expression in Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:816–827
Guo JP, Ma Y (2008) High-level expression, purification and characterization of recombinant Aspergillus oryzae alkaline protease in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 58:301–308
Hata Y, Ishida H, Kojima Y, Ichikawa E, Kawano A, Suginami K, Imayasu S (1997) Comparison of two glucoamylase produced by Aspergillus oryzae in solid-state culture (koji) and in submerged culture. J Ferment Bioeng 84:532–537
Hata Y, Ishida H, Ichikawa E, Kawato A, Suginami K, Imayasu S (1998) Nucleotide sequence of an alternative glucoamylase-encoding gene (glaB) expressed in solid-state culture of Aspergillus oryzae. Gene 207:127–134
Hatamoto O, Umitsüki G, Machida M, Sano M, Tanaka A, Oka C, Maeda H, Tainaka H, Ito T, Uchikawa T, Masuda T, Matsushima K (2010) Recombinant vector capable of increasing secretion of Koji mold protease. U.S. patent US7842799 B2
Hisada H, Sano M, Ishida H, Hata Y, Machida M (2013) Identification of regulatory elements in the glucoamylase-encoding gene (glaB) promoter from Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:4951–4956
Ichinose S, Tanaka M, Shintani T, Gomi K (2014) Improved α-amylase production by Aspergillus oryzae after a double deletion of genes involved in carbon catabolite repression. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:335–343
Ishida H, Hata Y, Ichikawa E, Kawato A, Abe Y, Suginami K, Imayasu S (1998) Regulation of the glucoamylase-encoding gene (glaB), expressed in solid-state culture (koji) of Aspergillus oryzae. J Ferment Bioeng 86:301–307
Ishida H, Hata Y, Kawato A, Abe Y, Suginami K, Imayasu S (2000) Identification of functional elements that regulate the glucoamylase-encoding gene (glaB) expressed in solid-state culture of Aspergillus oryzae. Curr Genet 37:373–379
Jin FJ, Nishida M, Hara S, Koyama Y (2011) Identification and characterization of a putative basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor involved in the early stage of conidiophore development in Aspergillus oryzae. Fungal Genet Biol 48:1108–1115
Kitano H, Kataoka K, Furukawa K, Hara S (2002) Specific expression and temperature-dependent expression of the acid protease-encoding gene (pepA) in Aspergillus oryzae in solid-state culture (Rice-Koji). J Biosci Bioeng 93:563–567
Kwon NJ, Garzia A, Espeso EA, Ugalde U, Yu JH (2010) FlbC is a putative nuclear C2H2 transcription factor regulating development in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 77:1203–1219
Machida M, Asai K, Sano M, Tanaka T, Kumagai T, Terai G, Kusumoto K, Arima T, Akita O, Kashiwagi Y, Abe K, Gomi K, Horiuchi H, Kitamoto K, Kobayashi T, Takeuchi M, Denning DW, Galagan JE, Nierman WC, Yu J, Archer DB, Bennett JW, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE, Fedorova ND, Gotoh O, Horikawa H, Hosoyama A, Ichinomiya M, Igarashi R, Iwashita K, Juvvadi PR, Kato M, Kato Y, Kin T, Kokubun A, Maeda H, Maeyama N, Maruyama J, Nagasaki H, Nakajima T, Oda K, Okada K, Paulsen I, Sakamoto K, Sawano T, Takahashi M, Takase K, Terabayashi Y, Wortman JR, Yamada O, Yamagata Y, Anazawa H, Hata Y, Koide Y, Komori T, Koyama Y, Minetoki T, Suharnan S, Tanaka A, Isono K, Kuhara S, Ogasawara N, Kikuchi H (2005) Genome sequencing and analysis of Aspergillus oryzae. Nature 438:1157–1161
Machida M, Yamada O, Gomi K (2008) Genomics of Aspergillus oryzae: learning from the history of koji mold and exploration of its future. DNA Res 15:173–183
Mizutani O, Masaki K, Gomi K, Iefuji H (2012) Modified cre-loxP recombination in Aspergillus oryzae by direct introduction of cre recombinase for marker gene rescue. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:4126–4133
Murakami K, Ishida Y, Masaki A, Tatsumi H, Murakami S, Nakano E, Motai H, Kawabe H, Arimura H (1991) Isolation and characterization of the alkaline protease gene of Aspergillus oryzae. Agric Biol Chem 55:2807–2811
Obata H, Ishida H, Hata Y, Kawato A, Abe Y, Akao T, Akita O, Ichishima E (2004) Cloning of a novel tyrosinase-encoding gene (melB) from Aspergillus oryzae and its overexpression in solid-state culture (Rice Koji). J Biosci Bioeng 97:400–405
Oda K, Kakizono D, Yamada O, Iefuji H, Akita O, Iwashita K (2006) Proteomic analysis of extracellular proteins from Aspergillus oryzae grown under submerged and solid-state culture conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3448–3457
Ogawa M, Tokuoka M, Jin FJ, Takahashi T, Koyama Y (2010) Genetic analysis of conidiation regulatory pathways in koji-mold Aspergillus oryzae. Fungal Genet Biol 47:10–18
Ogawa M, Kobayashi T, Koyama Y (2012) ManR, A novel Zn(II)2Cys6 transcriptional activator, controls the β-mannan utilization system in Aspergillus oryzae. Fungal Genet Biol 49:987–995
Park HS, Yu JH (2012) Genetic control of asexual sporulation in filamentous fungi. Curr Opin Microbiol 15:669–677
Petersen KL, Lehmbeck J, Christensen J (1999) A new transcriptional activator for amylase genes in Aspergillus. Mol Gen Genet 262:668–676
Sato H, Toyoshima Y, Shintani T, Gomi K (2011) Identification of potential cell wall component that allows taka-amylase A adsorption in submerged cultures of Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:961–969
Suzuki K, Tanaka M, Konno Y, Ichikawa T, Ichinose S, Hasegawa-Shiro S, Shintani T, Gomi K (2015) Distinct mechanism of activation of two transcription factors, AmyR and MalR, involved in amylolytic enzyme production in Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1805–1815
Takahashi T, Jin FJ, Sunagawa M, Machida M, Koyama Y (2008) Generation of large chromosomal deletions in koji molds Aspergillus oryzae and Aspergillus sojae via a loop-out recombination. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:7684–7693
Tanaka M, Tokuoka M, Shintani T, Gomi K (2012) Transcripts of a heterologous gene encoding mite allergen der f 7 are stabilized by codon optimization in Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:1275–1282
Tatsumi H, Murakami S, Tsuji RF, Ishida Y, Murakami K, Masaki A, Kawabe H, Arimura H, Nakano E, Motai H (1991) Cloning and expression in yeast of a cDNA clone encoding Aspergillus oryzae neutral protease II, a unique metalloprotease. Mol Gen Genet 228:97–103
Te Biesebeke R, van Biezen N, de Vos WM, van den Hondel CAMJJ, Punt PJ (2005) Different control mechanisms regulate glucoamylase and protease gene transcription in Aspergillus oryzae in solid-state and submerged fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:75–82
Watanabe J, Tanaka H, Mogi Y, Yamazaki T, Suzuki K, Watanabe T, Yamada O, Akita O (2011) Loss of Aspergillus oryzae amyR function indirectly affects hemicellulolytic and cellulolytic enzyme production. J Biosci Bioeng 111:408–413
Yamada O, Lee BR, Gomi K (1997) Transformation system for Aspergillus oryzae with double auxortophic mutations, niaD and sC. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:1367–1369
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Yoji Hata for kindly providing the anti-GlaB antibody and Yukihiro Nakamura for technical advice about the tyrosinase activity assay. We also thank Takeshi Akao for technical advice about total RNA extraction from A. oryzae cultured in solid-state culture and Osamu Mizutani for kindly providing the ∆ligD::loxP pyrG − strain. This study was supported by the Program for Promotion of Basic and Applied Researches for Innovations in Bio-oriented Industry and the Science and Technology Research Promotion Program for Agriculture, Forestry, Fisheries and Food Industry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any study with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Mizuki Tanaka and Midori Yoshimura contributed equally to this article.
Electronic supplementary materials
ESM 1
(PDF 371 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, M., Yoshimura, M., Ogawa, M. et al. The C2H2-type transcription factor, FlbC, is involved in the transcriptional regulation of Aspergillus oryzae glucoamylase and protease genes specifically expressed in solid-state culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 5859–5868 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7419-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7419-6