Abstract.
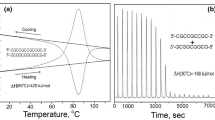
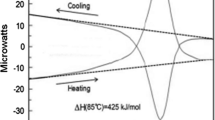
The dynamic behaviour of DNA is of fundamental importance to many cellular processes. One principal characteristic, central to transcription and replication, is the ability of the duplex to "melt". It has recently been shown that dynamic force spectroscopy provides information about the energetics of biomolecular dissociation. We have employed this technique to investigate the unbinding of single dodecanucleotide molecules. To separate the duplex to single-stranded DNA, forces ranging from 17 to 40 pN were required over a range of loading rates. Interpretation of the dependence of melting force on loading rate revealed that the energy barrier to rupture is between 9 and 13 kcal mol–1 in height and situated 0.58 nm from an intermediate structural state. Thermal melting studies show that, prior to dissociation, the oligonucleotide underwent a transition which required between 7 and 11 kcal mol–1 in energy. Through combined dynamic force spectroscopy and thermal melting studies we show the derivation of an energy landscape to dissociate a 12-mer duplex. Untilvery recently, this type of information was only accessible by computational analysis. Additionally, the force spectroscopy data allow an estimation of the kinetics of duplex formation and melting.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Revised version: 31 August 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pope, L., Davies, M., Laughton, C. et al. Force-induced melting of a short DNA double helix. Eur Biophys J 30, 53–62 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002490000107
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002490000107