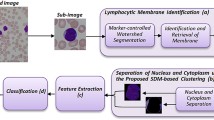
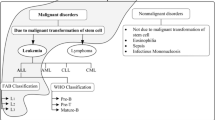
Abstract
Microscopic examination of stained peripheral blood smears is, nowadays, an indispensable tool in the evaluation of patients with hematological and non-hematological diseases. While a rapid automated quantification of the regular blood cells is available, recognition and counting of immature white blood cells (WBC) still relies mostly on the microscopic examination of blood smears by an experienced observer. Recently, there are efforts to improve the prediction by various machine learning approaches. An open dataset collection including the recently digitalized single-cell images for 200 patients, from peripheral blood smears at 100 × magnification, was used. We studied different morphological, fractal, and textural descriptors for WBC classification, with an aim to indicate the most reliable parameters for the recognition of certain cell types. Structural properties of both the mature and non-mature leukocytes obtained from (i) acute myeloid leukemia patients, or (ii) non-malignant controls, were studied in depth, with a sample size of about 25 WBC per group. We quantified structural and textural differences and, based on the statistical ranges of parameters for different WBC types, selected eight features for classification: Cell area, Nucleus-to-cell ratio, Nucleus solidity, Fractal dimension, Correlation, Contrast, Homogeneity, and Energy. Classification Precision of up to 100% (80% on average) was achieved.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
This research utilized a data set available from The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA).
Code availability
ImageJ software (NIH, Bethesda, MD), Self-written procedures (Haralick et al. 1973).
References
Acute Myeloid Leukemia—Cancer Stat Facts (2020) SEER. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html. Accessed 28 Jul 2020
Amin MM, Kermani S, Talebi A, Oghli MG (2015) Recognition of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells in microscopic images using K-means clustering and support vector machine classifier. J Med Signals Sens 5:49–58. https://doi.org/10.4103/2228-7477.150428
Bagge U, Born GVR, Gaehtgens P (1982) White blood cells: morphology and rheology as related to function. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-7585-9 (978-94-009-7587-3)
Bain BJ, Béné MC (2019) Morphological and immunophenotypic clues to the WHO categories of acute myeloid leukaemia. Acta Haematol 141:232–244. https://doi.org/10.1159/000496097
Betz BL, Hess JL (2010) Acute myeloid leukemia diagnosis in the 21st century. Arch Pathol Lab Med 134:1427–1433. https://doi.org/10.1043/2010-0245-RA.1
Carrotta R, Barthès J, Longo A, Martorana V, Manno M, Portale G, San Biagio PL (2007) Large size fibrillar bundles of the Alzheimer amyloid beta-protein. Eur Biophys J 36(7):701–709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-007-0164-0
Clark K, Vendt B, Smith K, Freymann J, Kirby J, Koppel P, Moore S, Phillips S, Maffitt D, Pringle M, Tarbox L, Prior F (2013) The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): maintaining and operating a public information repository. J Digit Imaging 26:1045–1057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-013-9622-7
Dasariraju S, Huo M, McCalla S (2020) Detection and classification of immature leukocytes for diagnosis of acute myeloid leukemia using random forest algorithm. Bioengineering 7:120. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7040120
De Angelis C, Pacheco C, Lucchini G, Arguello M, Conter V, Flores A, Biondi A, Masera G, Baez F (2012) The experience in Nicaragua: childhood leukemia in low income countries—the main cause of late diagnosis may be “medical delay.” Int J Pediatr 2012:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/129707
Dinčić M, Todorović J, Nešović Ostojić J, Kovačević S, Dunđerović D, Lopičić S, Spasić S, Radojević-Škodrić S, Stanisavljević D, Ilić A (2020) The fractal and GLCM textural parameters of chromatin may be potential biomarkers of papillary thyroid carcinoma in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis specimens. Microsc Microanal 26(4):717–730. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1431927620001683
Ferro DP, Falconi MA, Adam RL, Ortega MM, Lima CP, de Souza CA, Lorand-Metze I, Metze K (2011) Fractal characteristics of May– Grunwald-Giemsa stained chromatin are independent prognostic factors for survival in multiple myeloma. PLoS ONE 6(6):e20706. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020706
Gao LS, Li F, Yang Y, Xing J, Hammoudi AA, Zhao H, Fan Y, Wong KK, Wang Z, Wong ST, Thrall MJ, Cagle PT, Massoud Y (2011) On-the-spot lung cancer differential diagnosis by label-free, molecular vibrational imaging and knowledge-based classification. J Biomed Opt 16:096004. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.3619294
Gmachowski L (2018) Fractal analysis of lateral movement in biomembranes. Eur Biophys J 47:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-017-1264-0
Gupta S, Gupta R, Singh S, Gupta K, Kudesia M (2010) Nuclear morphometry and texture analysis of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: utility in subclassification on cytosmears. Diagn Cytopathol 38:94–103. https://doi.org/10.1002/dc.21154
Haralick RM, Shanmugam K, Dinstein I (1973) Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 3:610–621. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1973.4309314
Heerema-McKenney A, Arber DA (2009) Acute myeloid leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am 23(633–654):2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hoc.2009.04.003
Helmy IM, Abdel Azim AM (2012) Efficacy of ImageJ in the assessment of apoptosis. Diagn Pathol 7:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-1596-7-15
Karperien AL, Jelinek HF (2016) Box-counting fractal analysis: a primer for the clinician. In: Di Ieva A (ed) The fractal geometry of the brain, vol 2016. Springer, New York, pp 91–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3995-4_6
Krasowska M, Grzywna ZJ, Mycielska ME, Djamgoz MB (2009) Fractal analysis and ionic dependence of endocytotic membrane activity of human breast cancer cells. Eur Biophys J 38(8):1115–1125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0516-z
Lahmiri S, Shmuel A (2019) Performance of machine learning methods applied to structural MRI and ADAS cognitive scores in diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Signal Proces Control 52:414–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2018.08.009
Landini G, Martinelli G, Piccinini F (2020) Colour deconvolution—stain unmixing in histological imaging. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa847
Lennon FE, Cianci GC, Cipriani NA, Hensing TA, Zhang HJ, Chen C-T, Murgu SD, Vokes EE, Vannier MW, Salgia R (2015) Lung cancer—a fractal viewpoint. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 12:664–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.108
Mashiah A, Wolach O, Sandbank J, Uziel O, Raanani P, Lahav M (2008) Lymphoma and leukemia cells possess fractal dimensions that correlate with their biological features. Acta Haematol 119:142–150. https://doi.org/10.1159/000125551
Matek C, Schwarz S, Marr C, Spiekermann K (2019a) A single-cell morphological dataset of leukocytes from AML patients and non-malignant controls [AML-Cytomorphology_LMU data set]. Cancer Imaging Arch. https://doi.org/10.7937/tcia.2019.36f5o9ld
Matek C, Schwarz S, Spiekermann K, Marr C (2019b) Human-level recognition of blast cells in acute myeloid leukaemia with convolutional neural networks. Nat Mach Intell 1:538–544. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-019-0101-9
Metze K, Adam R, Florindo JB (2019) The fractal dimension of chromatin—a potential molecular marker for carcinogenesis, tumor progression and prognosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 19(4):299–312. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737159.2019.1597707
Narayanan D, Weinberg OK (2020) How I investigate acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Lab Hematol 42:3–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijlh.13135
Nikitaev VG, Nagornov OV, Pronichev AN et al (2015) Study of the effectiveness of using wavelet analysis in data-acquisition systems for diagnosis of acute leukemias. Meas Tech 57:1203–1208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11018-015-0603-8
Oprić D, Stankovich AD, Nenadović A, Kovačević S, Obradović DD, de Luka S, Nešović-Ostojić J, Milašin J, Ilić AŽ, Trbovich AM (2020) Fractal analysis tools for early assessment of liver inflammation induced by chronic consumption of linseed, palm and sunflower oils. Biomed Signal Process Control 61:101959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101959
Orazi A (2007) Histopathology in the diagnosis and classification of acute myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndromes, and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases. Pathobiology 74:97–114. https://doi.org/10.1159/000101709
Osowski S, Siroic R, Markiewicz T, Siwek K (2009) Application of support vector machine and genetic algorithm for improved blood cell recognition. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 58(7):2159–2168. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2008.2006726
Pathan S, Prabhu KG, Siddalingaswamy PC (2018) A methodological approach to classify typical and atypical pigment network patterns for melanoma diagnosis. Biomed Signal Process Control 44:25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2018.03.017
Pietruszka M, Olszewska M (2020) Extracellular ionic fluxes suggest the basis for cellular life at the 1/f ridge of extended criticality. Eur Biophys J 49:239–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-020-01430-3
Raccosta S, Manno M, Bulone D, Giacomazza D, Militello V, Martorana V, San Biagio PL (2010) Irreversible gelation of thermally unfolded proteins: structural and mechanical properties of lysozyme aggregates. Eur Biophys J 39(6):1007–1017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0503-4
Rawat J, Singh A, Bhadauria HS, Virmani J, Devgun JS (2017) Classification of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia using hybrid hierarchical classifiers. Multimed Tools Appl 76:19057–19085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4478-3
Ruifrok AC, Johnston DA (2001) Quantification of histochemical staining by color deconvolution. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 23:291–299
Şen EH, Ide S, Bayari SH, Hill M (2016) Micro- and nano-structural characterization of six marine sponges of the class Demospongiae. Eur Biophys J 45:831–842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-016-1127-0
Shirvaikar M, Huang N, Dong XN (2016) The measurement of bone quality using gray level co-occurrence matrix textural features. J Med Imaging Health Inform 6:1357–1362. https://doi.org/10.1166/jmihi.2016.1812
Sikdar D, Roy R, Mahadevappa M (2018) Epilepsy and seizure characterisation by multifractal analysis of EEG subbands. Biomed Signal Proces Control 41:264–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2017.12.006
Tél T (1988) Fractals, multifractals, and thermodynamics. Zeitschrift Für Naturforschung A 43(12):1154–1174. https://doi.org/10.1515/zna-1988-1221
Theera-Umpon N, Dhompongsa S (2007) Morphological granulometric features of nucleus in automatic bone marrow white blood cell classification. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 11(3):353–359. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2007.892694
Xie S, Girshick R, Dollár P, Tu Z, He K (2017) Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, vol 2017, pp 5987–5995. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.634
Zhang L, Lin X (2013) Some considerations of classification for high dimension low-sample size data. Stat Methods Med Res 22(5):537–550. https://doi.org/10.1177/0962280211428387
Acknowledgements
A.Ž.I. acknowledges funding provided by the Institute of Physics Belgrade, University of Belgrade, through the grants by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia. This study was also supported by the grants No III-45003, and 451-03-68/2020-14/200015, from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of Serbia.
Funding
A.Ž.I. acknowledges funding provided by the Institute of Physics Belgrade, University of Belgrade, through the grants by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development (MESTD) of the Republic of Serbia. This study was also supported by the Grant No. 451-03-68/2020-14/200015, from the MESTD of Serbia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AI, MD, TP. Formal analysis: AI, MD, MK. Investigation: AI, MD, MK, TP. Methodology: AI, MD. Software: AI, MD. Resources: AI, TP, MD. Funding acquisition: AI, TP. Project administration: AI, TP. Supervision: AI. Visualization: AI, MD. Writing—original draft: AI, MD, TP, AT. Writing—review and editing: AI, MD, TP, AT.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Ethics approval
Not applicable. This research utilized a data set available from The Cancer Imaging Archive.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinčić, M., Popović, T.B., Kojadinović, M. et al. Morphological, fractal, and textural features for the blood cell classification: the case of acute myeloid leukemia. Eur Biophys J 50, 1111–1127 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-021-01574-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-021-01574-w