Abstract
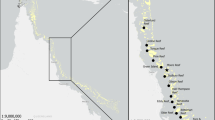
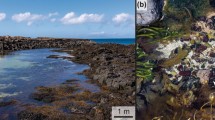
Biofilm microbial communities play an important role in the larval settlement response of marine invertebrates. However, the underlying mechanism has yet to be resolved, mainly because of the uncertainties in characterizing members in the communities using traditional 16S rRNA gene-based molecular methods and in identifying the chemical signals involved. In this study, pyrosequencing was used to characterize the bacterial communities in intertidal and subtidal marine biofilms developed during two seasons. We revealed highly diverse biofilm bacterial communities that varied with season and tidal level. Over 3,000 operational taxonomic units with estimates of up to 8,000 species were recovered in a biofilm sample, which is by far the highest number recorded in subtropical marine biofilms. Nineteen phyla were found, of which Cyanobacteria and Proteobacteria were the most dominant one in the intertidal and subtidal biofilms, respectively. Apart from these, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Planctomycetes were the major groups recovered in both intertidal and subtidal biofilms, although their relative abundance varied among samples. Full-length 16S rRNA gene clone libraries were constructed for the four biofilm samples and showed similar bacterial compositions at the phylum level to those revealed by pyrosequencing. Laboratory assays confirmed that cyrids of the barnacle Balanus amphitrite preferred to settle on the intertidal rather than subtidal biofilms. This preference was independent of the biofilm bacterial density or biomass but was probably related to the biofilm community structure, particularly, the Proteobacterial and Cyanobacterial groups.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann R, Ludwig W, Schleifer K (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 59:143
Ashelford KE, Chuzhanova NA, Fry JC, Jones AJ, Weightman AJ (2005) At least 1 in 20 16S rRNA sequence records currently held in public repositories is estimated to contain substantial anomalies. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7724–7736
Biddle J, Fitz-Gibbon S, Schuster S, Brenchley J, House C (2008) Metagenomic signatures of the Peru Margin subseafloor biosphere show a genetically distinct environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:10583
Bitton G (1994) Role of microorganisms in biogeochemical cycles. Wastewater microbiology. Wiley-Liss, New York, USA, pp 51–73
Capone D, Carpenter E (1982) Nitrogen fixation in the marine environment. Science 217:1140
Chao A (1984) Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand J Stat 11:265–270
Chao A, Yang M (1993) Stopping rules and estimation for recapture debugging with unequal failure rates. Biometrika 80:193–201
Chung H, Lee O, Huang Y, Mok S, Kolter R, Qian P (2010) Bacterial community succession and chemical profiles of subtidal biofilms in relation to larval settlement of the polychaete Hydroides elegans. ISME J 4(6):817–828
Cole J, VanRaden P, O'Connell J, Van Tassell C, Sonstegard T, Schnabel R, Taylor J, Wiggans G (2009) Distribution and location of genetic effects for dairy traits. J Dairy Sci 92:2931
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The ribosomal database project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucl Acids Res 37:141–145
Costerton J, Cheng K, Geesey G, Ladd T, Nickel J, Dasgupta M, Marrie T (1987) Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol 41:435–464
Dang H, Lovell C (2002) Numerical dominance and phylotype diversity of marine Rhodobacter species during early colonization of submerged surfaces in coastal marine waters as determined by 16S ribosomal DNA sequence analysis and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:496
Darwin C (1854) A monograph on the sub class Cirripedia. Trans Zool Soc London 22
Denef V, Mueller R, Banfield J (2010) AMD biofilms: using model communities to study microbial evolution and ecological complexity in nature. ISME J 4:599–610
Dobretsov S, Qian PY (2006) Facilitation and inhibition of larval attachment of the bryozoan Bugula neritina in association with mono-species and multi-species biofilms. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 333:263–274
Donlan R (2002) Biofilms: microbial life on surfaces. Emerg Infect Dis 8:881–890
Edgar R (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucl Acids Res 32:1792
Edwards R, Rodriguez-Brito B, Wegley L, Haynes M, Breitbart M, Peterson D, Saar M, Alexander S, Alexander E, Rohwer F (2006) Using pyrosequencing to shed light on deep mine microbial ecology. BMC Genom 7:57
Egert M, Friedrich M (2003) Formation of pseudo-terminal restriction fragments, a PCR-related bias affecting terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of microbial community structure. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2555
Grosberg R (1982) Intertidal zonation of barnacles: the influence of planktonic zonation of larvae on vertical distribution of adults. Ecology 63:894–899
Guckert J, Antworth C, Nichols P, White D (1985) Phospholipid, ester-linked fatty acid profiles as reproducible assays for changes in prokaryotic community structure of estuarine sediments. FEMS Microbiol Lett 31:147–158
Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton J, Stoodley P (2004) Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:95–108
Hansen M, Tolker-Nielsen T, Givskov M, Molin S (1998) Biased 16S rDNA PCR amplification caused by interference from DNA flanking the template region. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 26:141–149
Harder T, Thiyagarajan V, Qian P (2001) Effect of cyprid age on the settlement of Balanus amphitrite Darwin in response to natural biofilms. Biofouling 17:211–219
Holmstrom C, Rittschof D, Kjelleberg S (1992) Inhibition of settlement by larvae of Balanus amphitrite and Ciona intestinalis by a surface-colonizing marine bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2111
Huang Y, Dobretsov S, Ki J, Yang L, Qian P (2007) Presence of acyl-homoserine lactone in subtidal biofilm and the implication in larval behavioral response in the polychaete Hydroides elegans. Microb Ecol 54:384–392
Huang Y, Ki J, Case R, Qian P (2008) Diversity and acyl-homoserine lactone production among subtidal biofilm- forming bacteria. Aquat Microb Ecol 52:185–193
Huggett M, Nedved B, Hadfield M (2009) Effects of initial surface wettability on biofilm formation and subsequent settlement of Hydroides elegans. Biofouling 25:387–399
Hung O, Thiyagarajan V, Qian P (2008) Preferential attachment of barnacle larvae to natural multi-species biofilms: does surface wettability matter? J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 361:36–41
Hung O, Thiyagarajan V, Zhang R, Wu R, Qian P (2007) Attachment of Balanus amphitrite larvae to biofilms originating from contrasting environments. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 333:229–242
Kaeberlein T, Lewis K, Epstein S (2002) Isolating “uncultivable” microorganisms in pure culture in a simulated natural environment. Science 296:1127
Kemp P, Aller J (2004) Estimating prokaryotic diversity: when are 16 S rDNA libraries large enough? Limnol Oceanogr Methods 2:114–125
Kirchman D, Graham S, Reish D, Mitchell R (1981) Bacteria induce settlement and metamorphosis of Janua (Dexiospira) brasiliensis Grube (Polychaeta: Spirprbidae). J Exp Biol Ecol 56:153–163
Kisand V, Wikner J (2003) Limited resolution of 16S rDNA DGGE caused by melting properties and closely related DNA sequences. J Microbiol Methods 54:183–191
Kitamura H, Kitahara S, Koh H (1993) The induction of larval settlement and metamorphosis of two sea urchins, Pseudocentrotus depressus and Anthocidaris crassispina, by free fatty acids extracted from the coralline red alga Corallina pilulifera. Mar Biol 115:387–392
Kumar C, Anand S (1998) Significance of microbial biofilms in food industry: a review. Int J Food Microbiol 42:9–27
Lane D (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, UK, pp 115–175
Lau S, Thiyagarajan V, Cheung S, Qian P (2005) Roles of bacterial community composition in biofilms as a mediator for larval settlement of three marine invertebrates. Aquat Microb Ecol 38:41–51
Lau S, Thiyagarajan V, Qian P (2003) The bioactivity of bacterial isolates in Hong Kong waters for the inhibition of barnacle (Balanus amphitrite Darwin) settlement. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 282:43–60
Lee O, Wong Y, Qian P (2009) Inter- and intraspecific variations of bacterial communities associated with marine sponges from San Juan Island, Washington. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3513
Lewandowski Z (2000) Structure and function of biofilms. In: Evans L (ed) Biofilms: recent advances in their study and control. CRC Press, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp 1–17
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8228
Maki J, Rittschof D, Samuelsson M, Szewzyk U, Yule A, Kjelleberg S, Costlow J, Mitchell R (1990) Effect of marine bacteria and their exopolymers on the attachment of barnacle cypris larvae. Bull Mar Sci 46:499–511
Miyamoto Y, Noda T, Nakao S (1999) Zonation of two barnacle species not determined by competition. J Mar Biol Assoc U K 79:621–628
Morse A, Froyd C, Morse D (1984) Molecules from cyanobacteria and red algae that induce larval settlement and metamorphosis in the mollusc Haliotis rufescens. Mar Biol 81:293–298
Morton L, Surman S (1994) Biofilms in biodeterioration — a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 34:203–221
Murray AE, Preston CM, Massana R, Taylor LT, Blakis A, Wu K, DeLong EF (1998) Seasonal and spatial variability of bacterial and archaeal assemblages in the coastal waters near Anvers Island, Antarctica. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2585–2595
Muyzer G, Smalla K (1998) Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis (TGGE) in microbial ecology. Anton Leeuwenh 73:127–141
Nicolella C, Van Loosdrecht M, Heijnen J (2000) Wastewater treatment with particulate biofilm reactors. J Biotechnol 80:1–33
Oren A (2004) A proposal for further integration of the cyanobacteria under the Bacteriological Code. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1895
Hung OS, Lee OO, Thiyagarajan V, He HP, Xu Y, Chung HC, Qiu JW, Qian PY (2009) Characterization of cues from natural multi-species biofilms that induce larval attachment of the polychaete Hydroides elegans. Aquat Biol 4:253–262
Pawlik J (1986) Chemical induction of larval settlement and metamorphosis in the reef-building tube worm Phragmatopoma californica (Sabellariidae: Polychaeta). Mar Biol 91:59–68
Pommier T, Canback B, Riemann L, Bostrom KH, Simu K, Lundberg P, Tunlid A, Hagstrom Å (2007) Global patterns of diversity and community structure in marine bacterioplankton. Mol Ecol 16:867–880
Qian P (1999) Larval settlement of polychaetes. Hydrobiologia 402:239–253
Qian P, Thiyagarajan V, Lau S, Cheung S (2003) Relationship between bacterial community profile in biofilm and attachment of the acorn barnacle Balanus amphitrite. Aquat Microb Ecol 33:225–237
Saeed A, Bhagabati N, Braisted J, Liang W, Sharov V, Howe E, Li J, Thiagarajan M, White J, Quackenbush J (2006) TM4 microarray software suite. Methods Enzymol 411:134–193
Schloss P, Handelsman J (2005) Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1501
Siebel MA, Charaklis W, Prieur D (1989) Seasonal variations in bacterial colonisation of stainless steel, aluminium and polycarbonate surfaces in sea water flow system. Biofouling 1:251–261
Singleton DR, Furlong MA, Rathbun SL, Whitman WB (2001) Quantitative comparisons of 16S rRNA gene sequence libraries from environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4374–4376
Sogin M, Morrison H, Huber J, Welch D, Huse S, Neal P, Arrieta J, Herndl G (2006) Microbial diversity in the deep sea and the underexplored “rare biosphere”. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:12115
Steinberg P, de Nys R, Kjelleberg S (2002) Chemical cues for surface colonization. J Chem Ecol 28:1935–1951
Thiyagarajan V, Harder T, Qiu J, Qian P (2003) Energy content at metamorphosis and growth rate of the early juvenile barnacle Balanus amphitrite. Mar Biol 143:543–554
Thiyagarajan V, Lau S, Cheung S, Qian P (2006) Cypris habitat selection facilitated by microbial films influences the vertical distribution of subtidal barnacle Balanus trigonus. Microb Ecol 51:431–440
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tyson G, Lo I, Baker B, Allen E, Hugenholtz P, Banfield J (2005) Genome-directed isolation of the key nitrogen fixer Leptospirillum ferrodiazotrophum sp. nov. from an acidophilic microbial community. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6319
Unabia C, Hadfield M (1999) Role of bacteria in larval settlement and metamorphosis of the polychaete Hydroides elegans. Mar Biol 133:55–64
Wagner M, Smidt H, Loy A, Zhou J (2007) Unravelling microbial communities with DNA-microarrays: challenges and future directions. Microb Ecol 53:498–506
Wang G, Kennedy S, Fasiludeen S, Rensing C, DasSarma S (2004) Arsenic resistance in Halobacterium sp. strain NRC-1 examined by using an improved gene knockout system. J Bacteriol 186:3187
Wieczoreck S, Clare A, Tood C (1995) Inhibitory and facilitatory effects of microbial films on settlement of Balanus amphitrite larvae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 119:221–228
Wieczorek S, Todd C (1998) Inhibition and facilitation of settlement of epifaunal marine invertebrate larvae by microbial biofilm cues. Biofouling 12:81–118
Zar J (1999) Biostatistical analysis, 4th edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Zelles L, Bai Q, Beck T, Beese F (1992) Signature fatty acids in phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides as indicators of microbial biomass and community structure in agricultural soils. Soil Biol Biochem 24:317–323
Zhou J (2003) Microarrays for bacterial detection and microbial community analysis. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:288–294
Zhou J, Bruns M, Tiedje J (1996) DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:316–322
Zimmer R, Butman C (2000) Chemical signaling processes in the marine environment. Biol Bull 198:168
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2012CB417304), COMRA project of China (COMRRDA12SC02), and awards from the Deep Sea Institute of Science and Engineering, the Chinese Academy of Science (SIDSSE-201206) and from the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology granted to P.Y. Qian (SA-C0040/UK-C0016) and grant from HKSAR government (GRF661611) for Biofilm study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lee and Chung made equal contributions to the work
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 2167 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, O.O., Chung, H.C., Yang, J. et al. Molecular Techniques Revealed Highly Diverse Microbial Communities in Natural Marine Biofilms on Polystyrene Dishes for Invertebrate Larval Settlement. Microb Ecol 68, 81–93 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0348-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0348-3