Abstract
Background
Thiamine deficiency disease may occur in infants from thiamine-deficient mothers in developing countries, as well as in infants fed solely with soy-based formula. Thiamine deficiency in infants may present with acute neurological manifestations of infantile encephalitic beriberi.
Objective
To review the role of noncontrast CT brain findings in infantile encephalitic beriberi in early diagnosis.
Materials and methods
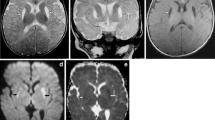
A retrospective review of noncontrast CT scans of the brain in 21 infants with acute-onset infantile encephalitic beriberi was carried out.
Results
On noncontrast-enhanced CT brain, hypodense lesions were seen symmetrically in the putamen in all the babies; symmetric hypodensities were seen in the caudate nuclei in 14/21 (67%), in dorsomedial thalami/hypothalamic/subthalamic area in 4/21 (19%), and in the globi pallidi in 2/21 (9.5%) of the infants.
Conclusion
Recognition of symmetrical hypodense lesions in the basal ganglia and medial thalami/hypothalamic/subthalamic area on noncontrast CT scan of the brain are important early features to recognize in encephalitic beriberi in at-risk infants.
Advances in knowledge
IEBB is a cause of hypodense bilateral basal ganglia and may be identified by this finding in the appropriate clinical settings.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith TJ, Hess SY (2021) Infantile thiamine deficiency in South and Southeast Asia: an age-old problem needing new solutions. Nutr Bull 46(1):12–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/nbu.12481
Qureshi UA, Sami A, Altaf U, Ahmad K, Iqbal J, Wani NA et al (2016) Thiamine responsive acute life threatening metabolic acidosis in exclusively breast-fed infants. Nutrition 32:213–216
Fattal-Valevski A, Kesler A, Sela BA, Nitzan-Kaluski D, Rotstein M, Mesterman R et al (2005) Outbreak of life-threatening thiamine deficiency in infants in Israel caused by a defective soy-based formula. Pediatrics 115(2):e233-8
Bhat JI, Rather HA, Ahangar AA, Qureshi UA, Dar P, Ahmed QI et al (2017) Shoshin beriberi-thiamine responsive pulmonary hypertension in exclusively breastfed infants: a study from northern India. Indian Heart J 69:24–27
Qureshi UA, Wani NA, Ahmad K, Irshad M, Ali I (2015) Infantile Wernicke’s encephalopathy. Arch Dis Child 100:648. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2014-307949
Kornreich L, Bron-Harlev E, Hoffmann C, Schwarz M, Konen O, Schoenfeld T et al (2005) Thiamine deficiency in infants: MR findings in the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26(7):1668–1674
Wani NA, Qureshi UA, Ahmad K, Choh NA (2016) Cranial ultrasonography in infantile encephalitic beriberi: a useful first-line imaging tool for screening and diagnosis in suspected cases. Am J Neuroradiol 37:1535–1540
Wani NA, Qureshi UA, Jehangir M, Ahmad K, Ahmad W (2016) Infantile encephalitic beriberi: magnetic resonance imaging findings. Pediatr Radiol 46:96–103
Rao SN, Mani S, Madap K, Kumar MV, Singh L, Chandak GR (2008) High prevalence of infantile encephalitic beriberi with overlapping features of Leigh’s disease. J Trop Pediatr 54(5):328–332
Wyalt DT, Michael JN, Hillman RE (1987) Infantile beriberi presenting as subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy. J Pediatr 110:888–889
Coe M, Carfagnini F, Tani G, Ambrosetto P (2001) Wernicke’s encephalopathy in a child: case report and MR findings. Pediatr Radiol 31:167–168
Zuccoli G, Siddiqui N, Bailey A, Bartoletti SC (2010) Neuroimaging findings in pediatric Wernicke encephalopathy: a review. Neuroradiology 52(6):523–529
Khan YR, Mehraj J, Ahmad K (2023) Thiamine deficiency in exclusive breastfed infants with encephalopathy attending Govind Ballabh Path children hospital, Srinagar. Int J Contemporary Pediatrics 10(4):554–558
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Approval was obtained from the institutional ethical committee.
Informed consent
As we compiled data in a retrospective manner, informed consent from subjects could not be obtained and a waiver for the same was provided by the institutional ethical committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wani, N.A., Malik, I., Tariq, S. et al. The role of CT brain findings in the early diagnosis of infantile encephalitic beriberi. Neuroradiology (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-024-03346-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-024-03346-7