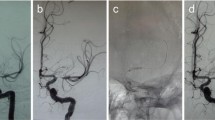
Abstract
Intracranial arterial stenosis is a frequently misdiagnosed cause of ischemic stroke, associated with high rates of recurrence under medical therapy alone. Endovascular intracranial angioplasty and stenting has increasingly been used worldwide for treatment of symptomatic intracranial stenoses, despite controversial results of the first randomized trials. Lesion morphology and etiology must be considered during endovascular treatment planning. Complex morphologies can lead to serious complications during the endovascular procedure. We present a case of a symptomatic complex middle cerebral artery stenosis that was successfully treated with a double stenting in T configuration, using a safety micro-guidewire technique. During follow-up, intracranial Doppler revealed a non-significant residual stenosis and the patient remained asymptomatic.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu W, Jiang WJ (2018) Stenting for intracranial stenosis: potential future for the prevention of disabling or fatal stroke. Stroke Vasc Neurol 3(3):140–146
Asaithambi G, Saravanapavan P, Rastogi V, Khan S, Bidari S, Khanna AY, Ganti L, Qureshi AI, Hedna VS (2014) Isolated middle cerebral artery dissection: a systemic review. Int J Emerg Med 7(1):44
Alexander MJ, Zauner A, Chaloupka JC et al (2019) WEAVE trial: final results in 152 on-label patients. Stroke 50(4):889–894
Kim JS, Bang OY (2017) Medical treatment of intracranial atherosclerosis: an update. J Stroke 19(3):261–270
Jiang WJ, Wang YJ, Du B et al (2004) Stenting of symptomatic M1 stenosis of middle cerebral artery: an initial experience of 40 patients. Stroke. 35(6):1375–1380
Derdeyn CP, Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ et al (2014) Aggressive medical treatment with or without stenting in high-risk patients with intracranial artery stenosis (SAMMPRIS): the final results of a randomised trial. Lancet 383:333–341
Zaidat OO, Fitzsimmons BF, Woodward BK et al (2015) Effect of a balloon-expandable intracranial stent vs medical therapy on risk of stroke in patients with symptomatic intracranial stenosis: the VISSIT randomized clinical trial. JAMA 313:1240–1248
Miao Z, Zhang Y, Shuai J, Jiang C, Zhu Q, Chen K, Liu L, Li B, Shi X, Gao L, Liu Y, Wang F, Li Y, Liu T, Zheng H, Wang Y, Wang Y, Study Group of Registry Study of Stenting for Symptomatic Intracranial Artery Stenosis in China (2015) Thirty-day outcome of a multicenter registry study of stenting for symptomatic intracranial artery stenosis in China. Stroke. 46(10):2822–2829
Kwak HS, Hwang SB, Chung GH, Jeong SK (2014) High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of symptomatic middle cerebral artery dissection. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 23(3):550–553
Mandell DM, Mossa-Basha M, Qiao Y et al (2017) Intracranial vessel wall MRI: principles and expert consensus recommendations of the American Society of Neuroradiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 38(2):218–229
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, M., Figueiredo, S., Rocha, J. et al. Double stenting in T configuration with safety micro-guidewire technique in a complex middle cerebral artery stenosis. Neuroradiology 62, 757–760 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02400-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02400-4