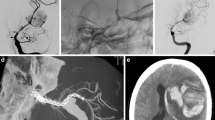
Abstract
Purpose
The management of residual or persistent intracranial aneurysms after flow-diversion therapy is not well defined in the literature. In this multicentric study, we report clinical and angiographic outcomes of 11 patients that underwent retreatment for 12 aneurysms initially treated with flow-diverter stents.
Methods
The median patient age was 53 years. Aneurysms (median size, 7.3 mm) were located at the internal carotid artery in 9 cases, and at the posterior circulation in 3. Treatment strategies, complications, and angiographic outcome were retrospectively assessed.
Results
Retreatment was feasible in all cases and performed by overlapping flow-diverter implantation. Overall, 12 side vessels were covered during retreatment, whereof 10 (83.3%) remained patent until mid-term follow-up. There were no further technical or symptomatic complications and no treatment-related morbidity. Angiographic follow-up (median, 17 months) showed improved aneurysm occlusion in all patients. Complete or near-complete aneurysm occlusion was achieved in 11 aneurysms (91.7%).
Conclusion
Required retreatment after failed flow-diversion therapy can be performed with adequate safety and efficacy by placement of additional flow-diverter stents.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wakhloo AK, Gounis MJ (2014) Revolution in aneurysm treatment: flow diversion to cure aneurysms: a paradigm shift. Neurosurgery 61(CN_suppl_1):111–120
Shankar JJS, Tampieri D, Iancu D, Cortes M, Agid R, Krings T, Wong J, Lavoie P, Ghostine J, Shettar B (2015) SILK flow diverter for complex intracranial aneurysms: a Canadian registry. J Neurointerv Surg. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2015-011708
Chalouhi N, Tjoumakaris S, Starke RM, Gonzalez LF, Randazzo C, Hasan D, McMahon JF, Singhal S, Moukarzel LA, Dumont AS (2013) Comparison of flow diversion and coiling in large unruptured intracranial saccular aneurysms. Stroke 44(8):2150–2154
Awad AJ, Mascitelli JR, Haroun RR, De Leacy RA, Fifi JT, Mocco J (2017) Endovascular management of fusiform aneurysms in the posterior circulation: the era of flow diversion. Neurosurg Focus 42(6):E14
Goertz L, Dorn F, Kraus B, Borggrefe J, Schlamann M, Forbrig R, Turowski B, Kabbasch C (2018) Safety and efficacy of the Derivo Embolization Device for the treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2018-014166
Kraus B, Goertz L, Turowski B, Borggrefe J, Schlamann M, Dorn F, Kabbasch C (2018) Safety and efficacy of the Derivo Embolization Device for the treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a multicentric study. J Neurointerv Surg. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2018-013963
Goertz L, Dorn F, Kraus B, Borggrefe J, Forbrig R, Schlamann M, Liebig T, Turowski B, Kabbasch C (2019) Improved occlusion rate of intracranial aneurysms treated with the Derivo Embolization Device: one-year clinical and angiographic follow-up in a multicenter study. World Neurosurg 126:e1503–e1509
Kallmes DF, Hanel R, Lopes D, Boccardi E, Bonafé A, Cekirge S, Fiorella D, Jabbour P, Levy E, McDougall C (2015) International retrospective study of the Pipeline Embolization Device: a multicenter aneurysm treatment study. Am J Neuroradiol 36(1):108–115
Brinjikji W, Murad MH, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF (2013) Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with flow diverters: a meta-analysis. Stroke 44(2):442–447
Chiu A, Cheung A, Wenderoth J, De Villiers L, Rice H, Phatouros C, Singh T, Phillips T, McAuliffe W (2015) Long-term follow-up results following elective treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms with the Pipeline Embolization Device. Am J Neuroradiol 36(9):1728–1734
Saatci I, Yavuz K, Ozer C, Geyik S, Cekirge H (2012) Treatment of intracranial aneurysms using the Pipeline flow-diverter embolization device: a single-center experience with long-term follow-up results. Am J Neuroradiol 33(8):1436–1446
Lubicz B, Collignon L, Raphaeli G, Pruvo J-P, Bruneau M, De Witte O, Leclerc X (2010) Flow-diverter stent for the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Stroke 41(10):2247–2253
Ding D, Starke RM, Liu KC (2014) Microsurgical strategies following failed endovascular treatment with the Pipeline Embolization Device: case of a giant posterior cerebral artery aneurysm. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg 16(1):26–31
Fahed R, Darsaut TE, Kotowski M, Salazkin I, Raymond J (2018) Re-treatment of residual aneurysms after flow diversion: an experimental study. Neuroradiol J 31(3):270–279
Kan P, Duckworth E, Puri A, Velat G, Wakhloo A (2016) Treatment failure of fetal posterior communicating artery aneurysms with the Pipeline Embolization Device. J Neurointerv Surg 8(9):945–948
Daou B, Atallah E, Chalouhi N, Starke RM, Oliver J, Montano M, Jabbour P, Rosenwasser RH, Tjoumakaris SI (2018) Aneurysms with persistent filling after failed treatment with the Pipeline Embolization Device. J Neurosurg 1(aop):1–7
Shapiro M, Becske T, Nelson PK (2017) Learning from failure: persistence of aneurysms following Pipeline embolization. J Neurosurg 126(2):578–585
O’kelly C, Krings T, Fiorella D, Marotta T (2010) A novel grading scale for the angiographic assessment of intracranial aneurysms treated using flow diverting stents. Interv Neuroradiol 16(2):133–137
Schwarz UR, Geiger J, Walter U, Eigenthaler M (1999) Flow cytometry analysis of intracellular VASP phosphorylation for the assessment of activating and inhibitory signal transduction pathways in human platelets. Thromb Haemost 81(03):1145–1152
Kallmes DF, Brinjikji W, Cekirge S, Fiorella D, Hanel RA, Jabbour P, Lopes D, Lylyk P, McDougall CG, Siddiqui A (2017) Safety and efficacy of the Pipeline Embolization Device for treatment of intracranial aneurysms: a pooled analysis of 3 large studies. J Neurosurg 127(4):775–780. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.8.jns16467
Chalouhi N, Jabbour P, Singhal S, Drueding R, Starke RM, Dalyai RT, Tjoumakaris S, Gonzalez LF, Dumont AS, Rosenwasser R (2013) Stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms: predictors of complications, recanalization, and outcome in 508 cases. Stroke 44(5):1348–1353
Chalouhi N, Tjoumakaris S, Gonzalez L, Dumont A, Starke R, Hasan D, Wu C, Singhal S, Moukarzel L, Rosenwasser R (2014) Coiling of large and giant aneurysms: complications and long-term results of 334 cases. Am J Neuroradiol 35(3):546–552
Piotin M, Blanc R, Spelle L, Mounayer C, Piantino R, Schmidt PJ, Moret J (2010) Stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms: clinical and angiographic results in 216 consecutive aneurysms. Stroke 41(1):110–115
Cebral J, Mut F, Raschi M, Scrivano E, Ceratto R, Lylyk P, Putman C (2011) Aneurysm rupture following treatment with flow-diverting stents: computational hemodynamics analysis of treatment. Am J Neuroradiol 32(1):27–33
Turowski B, Macht S, Kulcsár Z, Hänggi D, Stummer W (2011) Early fatal hemorrhage after endovascular cerebral aneurysm treatment with a flow diverter (SILK-Stent). Neuroradiology 53(1):37–41
Kulcsár Z, Houdart E, Bonafé A, Parker G, Millar J, Goddard A, Renowden S, Gal G, Turowski B, Mitchell K (2011) Intra-aneurysmal thrombosis as a possible cause of delayed aneurysm rupture after flow-diversion treatment. Am J Neuroradiol 32(1):20–25
Brinjikji W, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Siddiqui AH, Boccardi E, Cekirge S, Fiorella D, Hanel R, Jabbour P, Levy E, Lopes D, Lylyk P, Szikora I, Kallmes DF (2016) Risk factors for ischemic complications following Pipeline Embolization Device treatment of intracranial aneurysms: results from the IntrePED study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37(9):1673–1678. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4807
Algra AM, Lindgren A, Vergouwen MDI, Greving JP, van der Schaaf IC, van Doormaal TPC, Rinkel GJE (2018) Procedural clinical complications, case-fatality risks, and risk factors in endovascular and neurosurgical treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.4165
Kallmes DF, Brinjikji W, Boccardi E, Ciceri E, Diaz O, Tawk R, Woo H, Jabbour P, Albuquerque F, Chapot R (2016) Aneurysm study of Pipeline in an observational registry (ASPIRe). Int Neurol 5(1–2):89–99
Chalouhi N, Tjoumakaris S, Phillips J, Starke R, Hasan D, Wu C, Zanaty M, Kung D, Gonzalez L, Rosenwasser R (2014) A single Pipeline Embolization Device is sufficient for treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Am J Neuroradiol 35(8):1562–1566
Rouchaud A, Leclerc O, Benayoun Y, Saleme S, Camilleri Y, D’Argento F, Boncoeur M-P, Robert P-Y, Mounayer C (2015) Visual outcomes with flow-diverter stents covering the ophthalmic artery for treatment of internal carotid artery aneurysms. Am J Neuroradiol 36(2):330–336
Bhogal P, Ganslandt O, Bäzner H, Henkes H, Pérez MA (2017) The fate of side branches covered by flow diverters–results from 140 patients. World Neurosurg 103:789–798
Puffer RC, Kallmes DF, Cloft HJ, Lanzino G (2012) Patency of the ophthalmic artery after flow diversion treatment of paraclinoid aneurysms. J Neurosurg 116(4):892–896
Brinjikji W, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF (2014) Patency of the posterior communicating artery after flow diversion treatment of internal carotid artery aneurysms. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 120:84–88
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LG, NH, TL, WA, NA, and BK acquired the data. LG, CK, and FD developed the project, analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript. All authors revised the paper critically for important intellectual content and provided final approval of the version published. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
FD and CK serve as consultants for Acandis GmbH (Pforzheim, Germany). CK and TL serve as proctors for MicroVention Inc./Sequent Medical (Aliso Viejo, CA, USA). The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goertz, L., Hesse, N., Liebig, T. et al. Retreatment strategies for recurrent and residual aneurysms after treatment with flow-diverter devices. Neuroradiology 62, 1019–1028 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02389-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02389-w