Abstract
Purpose
To meta-statistically compare the efficiency of hypoxia-induced factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor on hemoglobin, ferritin, hepcidin rate, and adverse events.
Methods
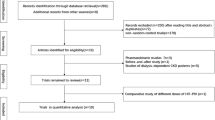
A systematic identification of literature was performed according to PRISMA guidelines on 4 academic databases: MEDLINE, Scopus, EMBASE, and CENTRAL. A meta-analysis evaluating the influence of hypoxia-induced factors was performed for patients undergoing/not undergoing hemodialysis. The analysis evaluated the efficacy of hypoxia-induced factors on hemoglobin, ferritin, hepcidin rate, and the number of adverse events.
Results
Out of 1052 records, 15 articles including 2045 patients (mean age 62.1 ± 5.4 years) were included in this review. The systematic review presents a 1a level of evidence supporting the use of hypoxia-induced factor for mediating anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. The meta-analysis reveals medium to large beneficial effects of the hypoxia-induced factor on hemoglobin rate for patients receiving (0.72) and not receiving (1.04) hemodialysis. Moreover, the administration of hypoxia-induced factors was reported to reduce ferritin rate and the hepcidin rate, and the number of adverse events in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Conclusion
The current meta-analysis recommends the use of hypoxia-induced factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor for managing anemia in chronic kidney disease.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hill NR, Fatoba ST, Oke JL, Hirst JA, O’Callaghan CA, Lasserson DS, Hobbs FDR (2016) Global prevalence of chronic kidney disease – a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 11:e0158765. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158765
Luyckx VA, Tonelli M, Stanifer JW (2018) The global burden of kidney disease and the sustainable development goals. Bull World Health Organ 96:414–422D. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.17.206441
Thomas C, Thomas L (2009) Renal failure—measuring the glomerular filtration rate. Dtsch Arztebl Int 106:849–854. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2009.0849
Abramson JL, Jurkovitz CT, Vaccarino V, Weintraub WS, Mcclellan W (2003) Chronic kidney disease, anemia, and incident stroke in a middle-aged, community-based population: the ARIC study. Kidney Int 64:610–615. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00109.x
McCullough PA, Lepor NE (2005) Piecing together the evidence on anemia: the link between chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease. Rev Cardiovasc Med 6(Suppl 3):S4–S12
O’Mara NB (2008) Anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Spectrum 21:12–19. https://doi.org/10.2337/diaspect.21.1.12
Souma T, Suzuki N, Yamamoto M (2015) Renal erythropoietin-producing cells in health and disease. Front Physiol 6:167. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00167
Hedley BD, Allan AL, Xenocostas A (2011) The role of erythropoietin and erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res 17:6373–6380. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2577
Malyszko J, Mysliwiec M (2007) Hepcidin in anemia and inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Blood Press Res 30:15–30. https://doi.org/10.1159/000098522
van der Weerd NC, Grooteman MPC, Nubé MJ, ter Wee P, Swinkels DW, Gaillard CA (2015) Hepcidin in chronic kidney disease: not an anaemia management tool, but promising as a cardiovascular biomarker. Neth J Med 73:108–118
Eschbach JW, Funk D, Adamson J et al (1967) Erythropoiesis in patients with renal failure undergoing chronic dialysis. N Engl J Med 276:653–658. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM196703232761202
Lasch KF, Evans CJ, Schatell D (2009) A qualitative analysis of patient-reported symptoms of anemia. Nephrol Nurs J 36(621–624):631–632 quiz 633
Kurella Tamura M, Vittinghoff E, Yang J, Go AS, Seliger SL, Kusek JW, Lash J, Cohen DL, Simon J, Batuman V, Ordonez J, Makos G, Yaffe K (2016) Anemia and risk for cognitive decline in chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol 17:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-016-0226-6
Virani SA, Khosla A, Levin A (2008) Chronic kidney disease, heart failure and anemia. Can J Cardiol 24:22B–24B
Collister D, Rigatto C, Tangri N (2017) Anemia management in chronic kidney disease and dialysis: a narrative review. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 26:214–218. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNH.0000000000000317
Belonje AMS, de Boer RA, Voors AA (2008) Recombinant human Epo treatment: beneficial in chronic kidney disease, chronic heart failure, or both? Editorial to: “Correction of anemia with erythropoietin in chronic kidney disease (stage 3 or 4): effects on cardiac performance by Pappas et al.” Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 22:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-008-6079-x
Gupta N, Wish JB (2017) Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors: a potential new treatment for anemia in patients with CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 69:815–826. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.12.011
Kainz A, Mayer B, Kramar R, Oberbauer R (2010) Association of ESA hypo-responsiveness and haemoglobin variability with mortality in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:3701–3706. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfq287
Joharapurkar AA, Pandya VB, Patel VJ, Desai RC, Jain MR (2018) Prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors: a breakthrough in the therapy of anemia associated with chronic diseases. J Med Chem 61:6964–6982. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01686
Chen N, Hao C, Peng X, Lin H, Yin A, Hao L, Tao Y, Liang X, Liu Z, Xing C, Chen J, Luo L, Zuo L, Liao Y, Liu BC, Leong R, Wang C, Liu C, Neff T, Szczech L, Yu KHP (2019) Roxadustat for anemia in patients with kidney disease not receiving dialysis. N Engl J Med 381:1001–1010. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1813599
Akizawa T, Nangaku M, Yamaguchi T, Arai M, Koretomo R, Matsui A, Hirakata H (2019) A placebo-controlled, randomized trial of enarodustat in patients with chronic kidney disease followed by long-term trial. Am J Nephrol 49:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1159/000496929
Holdstock L, Cizman B, Meadowcroft AM, Biswas N, Johnson BM, Jones D, Kim SG, Zeig S, Lepore JJ, Cobitz AR (2019) Daprodustat for anemia: a 24-week, open-label, randomized controlled trial in participants with chronic kidney disease. Clin Kidney J 12:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1093/ckj/sfy013
Xie D, Wang J, Wu X, Li M (2018) Effect of daprodustat on anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 50:2201–2206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1940-8
Zhong H, Zhou T, Li H, Zhong Z (2018) The role of hypoxia-inducible factor stabilizers in the treatment of anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Drug Des Devel Ther 12:3003–3011. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S175887
Martin ER, Smith MT, Maroni BJ, Zuraw QC, deGoma EM (2017) Clinical trial of vadadustat in patients with anemia secondary to stage 3 or 4 chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol 45:380–388. https://doi.org/10.1159/000464476
Akizawa T, Nangaku M, Yamaguchi T, Arai M, Koretomo R, Maeda K, Miyazawa Y, Hirakata H (2019) Enarodustat, conversion and maintenance therapy for anemia in hemodialysis patients: a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial followed by long-term trial. Nephron 143:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1159/000500487
Bailey CK, Caltabiano S, Cobitz AR, Huang C, Mahar KM, Patel VV (2019) A randomized, 29-day, dose-ranging, efficacy and safety study of daprodustat, administered three times weekly in patients with anemia on hemodialysis. BMC Nephrol 20:372. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-019-1547-z
Haase VH, Chertow GM, Block GA, Pergola PE, deGoma EM, Khawaja Z, Sharma A, Maroni BJ, McCullough PA (2019) Effects of vadadustat on hemoglobin concentrations in patients receiving hemodialysis previously treated with erythropoiesis-stimulating agents. Nephrol Dial Transplant 34:90–99. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfy055
Meadowcroft AM, Cizman B, Holdstock L, Biswas N, Johnson BM, Jones D, Nossuli AK, Lepore JJ, Aarup M, Cobitz AR (2019) Daprodustat for anemia: a 24-week, open-label, randomized controlled trial in participants on hemodialysis. Clin Kidney J 12:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1093/ckj/sfy014
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Jørgensen L, Paludan-Müller AS, Laursen DRT, Savović J, Boutron I, Sterne JAC, Higgins JPT, Hróbjartsson A (2016) Evaluation of the Cochrane tool for assessing risk of bias in randomized clinical trials: overview of published comments and analysis of user practice in Cochrane and non-Cochrane reviews. Syst Rev:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0259-8
Viswanathan M, Ansari MT, Berkman ND, et al (2008) Assessing the risk of bias of individual studies in systematic reviews of health care interventions. In: Methods Guide for Effectiveness and Comparative Effectiveness Reviews. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US), Rockville (MD)
Burns PB, Rohrich RJ, Chung KC (2011) The levels of evidence and their role in evidence-based medicine. Plast Reconstr Surg 128:305–310. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e318219c171
Bax L, Yu L-M, Ikeda N, Moons KG (2007) A systematic comparison of software dedicated to meta-analysis of causal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol 7:40. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-7-40
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Spiegelhalter DJ (2009) A re-evaluation of random-effects meta-analysis. J R Stat Soc Ser A Stat Soc 172:137–159. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-985X.2008.00552.x
Rosenthal R (1994) Parametric measures of effect size. In: The handbook of research synthesis. Russell Sage Foundation, New York, NY, US, pp 231–244
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21:1539–1558. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186
Petitti DB (2001) Approaches to heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Stat Med 20:3625–3633. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1091
Duval S, Tweedie R (2000) Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 56:455–463. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0006-341x.2000.00455.x
Akizawa T, Tsubakihara Y, Nangaku M, Endo Y, Nakajima H, Kohno T, Imai Y, Kawase N, Hara K, Lepore J, Cobitz A (2017) Effects of daprodustat, a novel hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor on anemia management in Japanese hemodialysis subjects. Am J Nephrol 45:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1159/000454818
Besarab A, Provenzano R, Hertel J, Zabaneh R, Klaus SJ, Lee T, Leong R, Hemmerich S, Yu KHP, Neff TB (2015) Randomized placebo-controlled dose-ranging and pharmacodynamics study of roxadustat (FG-4592) to treat anemia in nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD) patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30:1665–1673. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfv302
Brigandi RA, Johnson B, Oei C, Westerman M, Olbina G, de Zoysa J, Roger SD, Sahay M, Cross N, McMahon L, Guptha V, Smolyarchuk EA, Singh N, Russ SF, Kumar S, Borsukov AV, Marasaev VV, Prasad G, Timokhovskaya GY, Kolmakova EV, Dobronravov VA, Zakharova EV, Abraham G, Packham D, Zateyshchikov DA, Arutyunov GP, Volgina GV, Lipatov KS, Perlin DV, Cooper B, Kumar Saha T, Zagrebelnaya OA, Mehta KS, Koziolova NA, Fassett R, Alexeeva NP, Lysenko LV (2016) A novel hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor (GSK1278863) for anemia in CKD: a 28-day, phase 2A randomized trial. Am J Kidney Dis 67:861–871. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.11.021
Chen N, Qian J, Chen J, Yu X, Mei C, Hao C, Jiang G, Lin H, Zhang X, Zuo L, He Q, Fu P, Li X, Ni D, Hemmerich S, Liu C, Szczech L, Besarab A, Neff TB, Peony Yu KH, Valone FH (2017) Phase 2 studies of oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor FG-4592 for treatment of anemia in China. Nephrol Dial Transplant 32:1373–1386. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfx011
Holdstock L, Meadowcroft AM, Maier R, Johnson BM, Jones D, Rastogi A, Zeig S, Lepore JJ, Cobitz AR (2016) Four-week studies of oral hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor GSK1278863 for treatment of anemia. J Am Soc Nephrol 27:1234–1244. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2014111139
Pergola PE, Spinowitz BS, Hartman CS, Maroni BJ, Haase VH (2016) Vadadustat, a novel oral HIF stabilizer, provides effective anemia treatment in nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 90:1115–1122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2016.07.019
Provenzano R, Besarab A, Wright S, Dua S, Zeig S, Nguyen P, Poole L, Saikali KG, Saha G, Hemmerich S, Szczech L, Yu KHP, Neff TB (2016) Roxadustat (FG-4592) versus epoetin alfa for anemia in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis: a phase 2, randomized, 6- to 19-week, open-label, active-comparator, dose-ranging, safety and exploratory efficacy study. Am J Kidney Dis 67:912–924. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.12.020
Seeley TW, Sternlicht MD, Klaus SJ, Neff TB, Liu DY (2017) Induction of erythropoiesis by hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors without promotion of tumor initiation, progression, or metastasis in a VEGF-sensitive model of spontaneous breast cancer. Hypoxia (Auckl) 5:1–9. https://doi.org/10.2147/HP.S130526
Zaritsky J, Young B, Wang H-J, Westerman M, Olbina G, Nemeth E, Ganz T, Rivera S, Nissenson AR, Salusky IB (2009) Hepcidin--a potential novel biomarker for iron status in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1051–1056. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.05931108
Becker K, Saad M (2017) A new approach to the management of anemia in CKD patients: a review on roxadustat. Adv Ther 34:848–853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-017-0508-9
van der Meer P, Voors AA, Lipsic E, Smilde TDJ, van Gilst WH, van Veldhuisen DJ (2004) Prognostic value of plasma erythropoietin on mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 44:63–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2004.03.052
Hwang S, Nguyen AD, Jo Y, Engelking LJ, Brugarolas J, DeBose-Boyd RA (2017) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α activates insulin-induced gene 2 (Insig-2) transcription for degradation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG)-CoA reductase in the liver. J Biol Chem 292:9382–9393. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.788562
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ML and PD conceived and designed the study; JL and FD did literature search and data analysis; ML wrote the paper; and PD reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 60 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Lan, J., Dong, F. et al. Effectiveness of hypoxia-induced factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor for managing anemia in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 77, 491–507 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-020-03037-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-020-03037-1