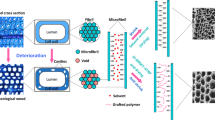
Abstract
Controls over the dimensions of waterlogged archaeological wood (WAW) upon drying are a critical issue for its conservation. Surface-initiated activator regenerated by electron transfer atom transfer radical polymerization (SI-ARGET ATRP) has been proven to be an effective consolidation method to increase the dimensional stability. However, the drawback of the current method is that the expansion stress generated during graft polymerization cannot be well controlled. An improved SI-ARGET ATRP system using a bifunctional monomer ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) to introduce a cross-linking process during the polymerization is presented in this paper. Both Pinus massoniana and Sapium sp. samples with different maximum moisture contents as 507% and 863%, respectively, show a reduced volumetric shrinkage of around 5% without any expansion phenomenon after the treatment. This method shows potential applications in the field of WAW conservation and may provide a new solution for consolidation of other organic archaeological objects as well as developing new wood-based materials.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Babiński L (2015) Dimensional changes of waterlogged archaeological hardwoods pre-treated with aqueous mixtures of lactitol/trehalose and mannitol/trehalose before freeze-drying. J Cult Herit 16(6):876–882
Björdal CG (2012) Microbial degradation of waterlogged archaeological wood. J Cult Herit 13:S118–S122
Björdal CG, Nilsson T, Daniel G (1999) Microbial decay of waterlogged archaeological wood found in Sweden applicable to archaeology and conservation. Int Biodeter Biodegr 43:63–73
Blanchette RA (2000) A review of microbial deterioration found in archaeological wood from different environments. Int Biodeter Biodegr 46:189–204
Broda M, Hill CAS (2021) Conservation of waterlogged wood—past, present and future perspectives. Forests 12:1193
Broda M, Mazela B (2017) Application of methyltrimethoxysilane to increase dimensional stability of waterlogged wood. J Cult Herit 25:149–156
Broda M, Yelle DJ (2022) Reactivity of waterlogged archaeological elm wood with organosilicon compounds applied as wood consolidants: 2D 1H–13C solution-state NMR studies. Molecules 27:3407
Broda M, Mazela B, Dutkiewicz A (2019a) Organosilicon compounds with various active groups as consolidants for the preservation of waterlogged archaeological wood. J Cult Herit 35:123–128
Broda M, Mazela B, Radka K (2019b) Methyltrimethoxysilane as a stabilising agent for archaeological waterlogged wood differing in the degree of degradation. J Cult Herit 35:129–139
Cavallaro G, Lazzara G, Milioto S, Parisi F, Sparacino V (2015) Thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of beeswax-halloysite nanocomposites for consolidating waterlogged archaeological woods. Polym Degrad Stabil 120:220–225
Cavallaro G, Lazzara G, Milioto S, Parisi F, Ruisi F (2017) Nanocomposites based on esterified colophony and halloysite clay nanotubes as consolidants for waterlogged archaeological woods. Cellulose 24:3367–3376
Christensen M, Larnøy E, Kutzke H, Hansen FK (2015) Treatment of waterlogged archaeological wood using chitosan- and modified chitosan solutions. part 1: chemical compatibility and microstructure. J American Inst Conserv 54:3–13
Endo R, Sugiyama J (2022) New attempts with the keratin-metal/magnesium process for the conservation of archaeological waterlogged wood. J Cult Herit 54:53–58
Endo R, Kamei K, Iida I, Kawahara Y (2008) Dimensional stability of waterlogged wood treated with hydrolyzed feather keratin. J Archaeol Sci 35:1240–1246
Endo R, Kamei K, Iida I, Yokoyama M, Kawahara Y (2010) Physical and mechanical properties of waterlogged wood treated with hydrolyzed feather keratin. J Archaeol Sci 37:1311–1316
Jones SPP, Slater NKH, Jones M et al (2009) Investigating the processes necessary for satisfactory freeze-drying of waterlogged archaeological wood. J Archaeol Sci 36(10):2177–2183
Kaye B, Cole-Hamilton DJ, Morphet K (2000) Supercritical drying: a new method for conserving waterlogged archaeological materials. Stud Conserv 45(4):233–252
Kennedy A, Pennington ER (2014) Conservation of chemically degraded waterlogged wood with sugars. Stud Conserv 59:194–201
Klaassen RKWM (2014) Speed of bacterial decay in waterlogged wood in soil and open water. Int Biodeter Biodegr 86:129–135
Lisuzzo L, Hueckel T, Cavallaro G, Sacanna S, Lazzara G (2021) Pickering emulsions based on wax and halloysite nanotubes: an ecofriendly protocol for the treatment of archaeological woods. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:1651–1661
Lisuzzo L, Cavallaro G, Milioto S, Lazzara G (2022) Pickering emulsions stabilized by halloysite nanotubes: from general aspects to technological applications. Adv Mater Interfaces 9:2102346
Liu L, Zhang L, Zhang B, Hu Y (2018) A comparative study of reinforcement materials for waterlogged wood relics in laboratory. J Cult Herit 36:94–102
Popescu CM, Broda M (2021) Interactions between different organosilicons and archaeological waterlogged wood evaluated by infrared spectroscopy. Forests 12:268
Tahira A, Howard W, Pennington ER, Kennedy A (2017) Mechanical strength studies on degraded waterlogged wood treated with sugars. Stud Conserv 62:223–228
Walsh Z, Janeček E, Jones M, Scherman OA (2015) Natural polymers as alternative consolidants for the preservation of waterlogged archaeological wood. Stud Conserv 54:45–56
Zhou Y, Wang K, Hu D (2019) High retreatability and dimensional stability of polymer grafted waterlogged archaeological wood achieved by ARGET ATRP. Sci Rep 9:9879
Zhou Y, Wang K, Hu D (2021) An aqueous approach to functionalize waterlogged archaeological wood followed by improved surface-initiated ARGET ATRP for maintaining dimensional stability. Cellulose 28:2433–2443
Zhou Y, Wang K, Hu D (2022) Surface-initiated arget atrp for maintaining the dimension of waterlogged archaeological wood (pinus massoniana): polymer distribution behaviors and anti-shrinkage mechanism. Wood Sci Technol 56(1):205–218
Acknowledgements
The research is supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2020YFC1521803) and National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 19CKG032).
Funding
The research is supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2020YFC1521803) and National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 19CKG032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ conducted the experiments and analysed the data. YZ and YZ wrote the main manuscript text and prepared the figures. KW and DH revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, K. et al. Well-controlled SI-ARGET ATRP of EGDMA for maintaining the dimensions of waterlogged archaeological wood. Wood Sci Technol 57, 523–535 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-023-01454-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-023-01454-w