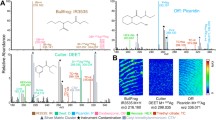
Abstract
Laser desorption laser postionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (L2MS) was applied for unambiguous discrimination of pigment-based inks in blue, black, and red gel pens and molecular imaging of equivocal documents in a quasi-non-destructive way. In comparison to laser desorption mass spectrometry (LD-MS), additional discriminatory information on ink components is acquired uniquely, facilitating the distinct differentiation of various pigmented gel inks. More importantly, diversified images of additional characteristic ions achieved using L2MS offer reliable support to discriminate forged documents and decipher important hidden contents. Apart from minimized matrix effect and maximized ionization yield, direct and confirmatory identification of forged documents is achieved successfully without solvent or matrix involved, not only eliminating unwanted damage and contamination to the samples but significantly shortening the overall analysis time. In addition, L2MS is a minimally destructive approach with tiny analyte consumption. With these appealing qualities, L2MS imaging is poised to be a powerful tool for confirmatory surface analysis of complex pigment-based samples.

Weight and see: Highly distinct and comprehensive images of counterfeit documents with blue-pigmented gel inks are achieved successfully, due to the high sensitivity and increased ion yield of laser desorption laser postionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The hidden important contents of the obliterated documents are visually deciphered with the help of the additional chemical information.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai Y, Huang Z, Cheung MHC, Motto Ros V, Chu PC, Wang Y, et al. Elemental analysis of Chinese black inks on Xuan Paper by ArF laser-excited plume fluorescence. Anal Chem. 2016;88:10971–8.
Calcerrada M, García-Ruiz C. Analysis of questioned documents: a review. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;853:143–66.
Alamilla F, Calcerrada M, García-Ruiz C, Torre M. Forensic discrimination of blue ballpoint pens on documents by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and multivariate analysis. Forensic Sci Int. 2013;228:1–7.
Creran B, Yan B, Moyano DF, Gilbert MM, Vachet RW, Rotello VM. Laser desorption ionization mass spectrometric imaging of mass barcoded gold nanoparticles for security applications. Chem Commun. 2012;48:4543–5.
Silva CS, Borba FSL, Pimentel MF, MJC P, Honorato RS, Pasquini C. Classification of blue pen ink using infrared spectroscopy and linear discriminant analysis. Microchem J. 2013;109:122–7.
Lee J, Lee C, Lee K, Lee Y. TOF-SIMS study of red sealing-inks on paper and its forensic applications. Appl Surf Sci. 2008;255:1523–6.
Sancey L, Motto Ros V, Busser B, Kotb S, Benoit JM, Piednoir A, et al. Laser spectrometry for multi-elemental imaging of biological tissues. Sci Rep UK. 2014;4:6065.
Dill AL, Eberlin LS, Ifa DR, Cooks RG. Perspectives in imaging using mass spectrometry. Chem Commun. 2011;47:2741–6.
Braz A, López López M, García Ruiz C. Raman imaging for determining the sequence of blue pen ink crossings. Forensic Sci Int. 2015;249:92–100.
Ewing AV, Kazarian SG. Infrared spectroscopy and spectroscopic imaging in forensic science. Analyst. 2017;142:257–72.
Tahtouh M, Despland P, Shimmon R, Kalman JR, Reedy BJ. The application of infrared chemical imaging to the detection and enhancement of latent fingerprints: method optimization and further findings. J Forensic Sci. 2007;52:1089–96.
Zieba Palus J, Borusiewicz R, Kunicki M. PRAXIS—combined μ-Raman and μ-XRF spectrometers in the examination of forensic samples. Forensic Sci Int. 2008;175:1–10.
Liu Y, Ma X, Lin Z, He M, Han G, Yang C, et al. Imaging mass spectrometry with a low-temperature plasma probe for the analysis of works of art. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2010;49:4435–7.
Greer T, Sturm R, Li L. Mass spectrometry imaging for drugs and metabolites. J Proteome. 2011;74:2617–31.
Rubakhin SS, Jurchen JC, Monroe EB, Sweedler JV. Imaging mass spectrometry: fundamentals and applications to drug discovery. Drug Discov Today. 2005;10:823–37.
Ifa DR, Gumaelius LM, Eberlin LS, Manicke NE, Cooks RG. Forensic analysis of inks by imaging desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) mass spectrometry. Analyst. 2007;132:461–7.
Tang HW, Wong MYM, Chan SLF, Che CM, Ng KM. Molecular imaging of banknote and questioned document using solvent-free gold nanoparticle-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2011;83:453–8.
Soltwisch J, Kettling H, Vens Cappell S, Wiegelmann M, Müthing J, Dreisewerd K. Mass spectrometry imaging with laser-induced postionization. Science. 2015;348:211–5.
Kalberer M, Morrical BD, Sax M, Zenobi R. Picogram quantitation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorbed on aerosol particles by two-step laser mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2002;74:3492–7.
Akhmetov A, Moore JF, Gasper GL, Koin PJ, Hanley L. Laser desorption postionization for imaging MS of biological material. J Mass Spectrom. 2010;45:137–45.
Pallix JB, Becker CH, Newman N. Surface analysis by laser ionization. MRS Bull. 1987;12:52–9.
Mibuka R, Hassaballa S, Uchino K, Yurimoto H, Todokoro R, Kumondai K, et al. Characteristics of post-ionization using a femto-second laser. Appl Surf Sci. 2008;255:1595–8.
Thomson K, Ziskind M, Mihesan C, Therssen E, Desgroux P, Focsa C. Influence of the photoionization process on the fragmentation of laser desorbed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Surf Sci. 2007;253:6435–41.
Voumard P, Zhan Q, Zenobi R. A new instrument for spatially resolved laser desorption/laser multiphoton ionization mass spectrometry. Rev Sci Instrum. 1993;64:2215–20.
Chen J, Hu Y, Lu Q, Wang P, Zhan H. Determination of proflavine in rat whole blood without sample pretreatment by laser desorption postionization mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017;409:2813–9.
Chen J, Hu Y, Lu Q, Wang P, Zhan H. Molecular imaging of small molecule drugs in animal tissues using laser desorption postionization mass spectrometry. Analyst. 2017;142:1119–24.
Behm JM, Hemminger JC, Lykke KR. Microscopic laser desorption/postionization Fourier transform mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1996;68:713–9.
Cui Y, Bhardwaj C, Milasinovic S, Carlson RP, Gordon RJ, Hanley L. Molecular imaging and depth profiling of biomaterials interfaces by femtosecond laser desorption postionization mass spectrometry. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:9269–75.
Liu Y, Yu J, Xie M, Chen Y, Jiang G, Gao Y. Studies on the degradation of blue gel pen dyes by ion-pairing high performance liquid chromatography and electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2006;1125:95–103.
Wu Y, Zhou CX, Yu J, Liu HL, Xie MX. Differentiation and dating of gel pen ink entries on paper by laser desorption ionization- and quadruple-time of flight mass spectrometry. Dyes Pigments. 2012;94:525–32.
Denman JA, Skinner WM, Kirkbride KP, Kempson IM. Organic and inorganic discrimination of ballpoint pen inks by ToF-SIMS and multivariate statistics. Appl Surf Sci. 2010;256:2155–63.
Weyermann C, Bucher L, Majcherczyk P. A statistical methodology for the comparison of blue gel pen inks analyzed by laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Sci Justice. 2011;51:122–30.
Trejos T, Flores A, Almirall JR. Micro-spectrochemical analysis of document paper and gel inks by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B. 2010;65:884–95.
Dawson JHJ, Guilhaus M. Orthogonal-acceleration time-of-flight mass spectrometer. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1989;3:155–9.
Trejos T, Montero S, Almirall JR. Analysis and comparison of glass fragments by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) and ICP-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2003;376:1255–64.
He M, Xiao Y, Zhang S, Liu R, Hang W, Huang B. Composition analysis of ancient celadon via femtosecond laser ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Appl Surf Sci. 2015;351:624–34.
Weyermann C, Bucher L, Majcherczyk P, Mazzella W, Roux C, Esseiva P. Statistical discrimination of black gel pen inks analysed by laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci Int. 2012;217:127–33.
Sun Q, Luo Y, Xiang P, Yang X, Shen M. Analysis of PEG oligomers in black gel inks: discrimination and ink dating. Forensic Sci Int. 2017;277:1–9.
Silva CS, Pimentel MF, Honorato RS, Pasquini C, Prats Montalban JM, Ferrer A. Near infrared hyperspectral imaging for forensic analysis of document forgery. Analyst. 2014;139:5176–84.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (21427813), the Program for Changjiang Scholars and the Innovative Research Team in University (IRT13036), and the Foundation for Innovative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21521004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 261 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, R., Yin, Z., Cheng, X. et al. Confirmatory surface analysis of equivocal documents with pigment-based gel inks via laser desorption laser postionization mass spectrometry imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem 410, 1445–1452 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0781-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0781-0