Abstract
Rationale
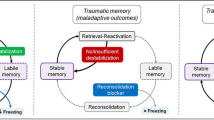
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) kinase is known to mediate consolidation and reconsolidation of aversive memories. Most studies in this area use a forward conditioning paradigm in which the conditioned stimulus (CS) precedes the unconditioned stimulus (US). Little is known, however, about the neurobiological underpinnings of backwards (BW) conditioning paradigms, particularly in female mice. In BW conditioning, the CS does not become directly associated with the US; it instead evokes conditioned fear by reactivating a memory of the conditioning context and indirectly retrieving a memory of the aversive US.
Objectives
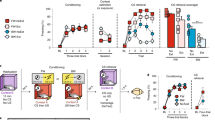
We sought to examine BW conditioned fear memory processes in female mice. First, we examined whether freezing to a BW CS is mediated by fear to the conditioning context. Second, we tested whether blocking consolidation of a BW CS attenuated memory of the CS and conditioning context. Finally, we tested whether blocking reconsolidation of a BW CS attenuated memory of the conditioning context.
Results
We show that conditioned freezing to a BW CS is mediated by fear to the conditioning context. Furthermore, rapamycin—an mTOR inhibitor, when given immediately following BW conditioning, impairs consolidation of both cued and contextual fear memory. Similarly, rapamycin given following retrieval of a BW CS blocks context recall. Rapamycin is acting on reconsolidation as CS retrieval is necessary to see the effects of rapamycin on context memory recall.
Conclusions
Our study provides novel evidence that indirect retrieval cues are sensitive to rapamycin in female mice. The capacity to indirectly reactivate memories and render them susceptible to disruption is critical in the translation of reconsolidation-based approaches to the clinic.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adkins JM, Halcomb CJ, Rogers D, Jasnow AM (2022) Stress and sex-dependent effects on conditioned inhibition of fear. Learn Mem 29(9):246–255. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.053508.121
Bekinschtein P, Cammarota M, Igaz LM, Bevilaqua LR, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (2007) Persistence of long-term memory storage requires a late protein synthesis- and BDNF- dependent phase in the hippocampus. Neuron 53(2):261–277. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Citation&list_uids=17224407
Bernier BE, Lacagnina AF, Ayoub A, Shue F, Zemelman BV, Krasne FB, Drew MR (2017) Dentate gyrus contributes to retrieval as well as encoding: evidence from context fear conditioning, recall, and extinction. J Neurosci 37(26):6359–6371. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3029-16.2017
Blair RS, Acca GM, Tsao B, Stevens N, Maren S, Nagaya N (2022) Estrous cycle contributes to state-dependent contextual fear in female rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 141:105776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2022.105776
Blundell J, Kouser M, Powell CM (2008) Systemic inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin inhibits fear memory reconsolidation. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90(1):28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2007.12.004
Breslau N, Kessler RC, Chilcoat HD, Schultz LR, Davis GC, Andreski P (1998) Trauma and posttraumatic stress disorder in the community: the 1996 Detroit Area Survey of Trauma. Arch Gen Psychiatry 55(7):626–632. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.55.7.626
Byers SL, Wiles MV, Dunn SL, Taft RA (2012) Mouse estrous cycle identification tool and images. The Jackson Laboratory
Cai W-H, Blundell J, Han J, Greene RW, Powell CM (2006) Postreactivation glucocorticoids impair recall of established fear memory. J Neurosci 26(37):9560–9566. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2397-06.2006
Chang YJ, Yang CH, Liang YC, Yeh CM, Huang CC, Hsu KS (2009) Estrogen modulates sexually dimorphic contextual fear extinction in rats through estrogen receptor beta. Hippocampus 19(11):1142–1150. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20581
Christiansen DM (2017) Sex and gender differences in trauma victims presenting for treatment. In: Legato MJ (ed) Principles of gender-specific medicine, 3rd edn. Academic Press (Elsevier), p 497–511
Cora MC, Kooistra L, Travlos G (2015) Vaginal cytology of the laboratory rat and mouse: review and criteria for the staging of the estrous cycle using stained vaginal smears. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health
Debiec J and Ledoux JE (2004) Disruption of reconsolidation but not consolidation of auditory fear conditioning by noradrenergic blockade in the amygdala. Neurosci 129(2):267–272 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Citation&list_uids=15501585
Dudai Y, Karni A, Born J (2015) The consolidation and transformation of memory. Neuron 88(1):20–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.09.004
Duvarci S, Nader K, LeDoux JE (2008) De novo mRNA synthesis is required for both consolidation and reconsolidation of fear memories in the amygdala. Learn Mem 15(10):747–755. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.1027208
Gafford GM, Parsons RG, Helmstetter FJ (2011) Consolidation and reconsolidation of contextual fear memory requires mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent translation in the dorsal hippocampus. Neurosci 182:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.03.023
Glover EM, Ressler KJ, Davis M (2010) Differing effects of systemically administered rapamycin on consolidation and reconsolidation of context vs cued fear memories. Learn Mem 17(11):577–581. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.1908310
Goode TD, Ressler RL, Acca GM, Miles OW, Maren S (2019) Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis regulates fear to unpredictable threat signals. Elife 8:20190404. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46525
Hapke U, Schumann A, Rumpf H, John U, Meyer C (2006) Post-traumatic stress disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 256:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-006-0654-6
Jobim PF, Pedroso TR, Christoff RR, Werenicz A, Maurmann N, Reolon GK, Roesler R (2012) Inhibition of mTOR by rapamycin in the amygdala or hippocampus impairs formation and reconsolidation of inhibitory avoidance memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 97(1):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2011.10.002
Kessler RC, Sonnega A, Bromet E, Hughes M, Nelson CB (1995) Posttraumatic stress disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52(12):1048–1060. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.1995.03950240066012
Kheirbek MA, Drew LJ, Burghardt NS, Costantini DO, Tannenholz L, Ahmari SE, Zeng H, Fenton AA, Hen R (2013) Differential control of learning and anxiety along the dorsoventral axis of the dentate gyrus. Neuron 77(5):955–968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.12.038
Kida S (2023) Interaction between reconsolidation and extinction of fear memory. Brain Res Bull 195:141–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2023.02.009
Kilpatrick DG, Resnick HS, Milanak ME, Miller MW, Keyes KM, Friedman MJ (2013) National estimates of exposure to traumatic events and PTSD prevalence using DSM-IV and DSM-5 criteria. J Trauma Stress 26(5):537–547. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.21848
Lana D, Di Russo J, Mello T, Wenk GL, Giovannini MG (2017) Rapamycin inhibits mTOR/p70S6K activation in CA3 region of the hippocampus of the rat and impairs long term memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 137:15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2016.11.006
Leal G, Comprido D, Duarte CB (2014) BDNF-induced local protein synthesis and synaptic plasticity. Neuropharmacol 76:639–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.005
Mac Callum PE, Hebert M, Adamec RE, Blundell J (2014) Systemic inhibition of mTOR kinase via rapamycin disrupts consolidation and reconsolidation of auditory fear memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 112:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2013.08.014
MacCallum P, Blundell JJ (2020) The mTORC1 inhibitor rapamycin and the mTORC1/2 inhibitor AZD2014 impair the consolidation and persistence of contextual fear memory. Psychopharmacol 237 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05573-1
Mamlouk GM, Dorris DM, Barrett LR, Meitzen J (2020) Sex bias and omission in neuroscience research is influenced by research model and journal, but not reported NIH funding. Front Neuroendocrinol 57:100835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2020.100835
Milad MR, Igoe SA, Lebron-Milad K, Novales JE (2009) Estrous cycle phase and gonadal hormones influence conditioned fear extinction. Neurosci 164(3):887–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.09.011
Myskiw JC, Rossato JI, Bevilaqua LR, Medina JH, Izquierdo I, Cammarota M (2008) On the participation of mTOR in recognition memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 89(3):338–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2007.10.002
Nascimento EB, Dierschnabel AL, Lima RH, Sousa MBC, Suchecki D, Silva RH, Ribeiro AM (2022) Stress-related impairment of fear memory acquisition and disruption of risk assessment behavior in female but not in male mice. Behav Processes 199:104660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beproc.2022.104660
Olivera-Pasilio V, Dabrowska J (2023) Fear-conditioning to unpredictable threats reveals sex differences in rat fear-potentiated startle (FPS). bioRxiv 20230308 https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.06.531430
Parsons RG, Gafford GM, Baruch DE, Riedner BA, Helmstetter FJ (2006) Long-term stability of fear memory depends on the synthesis of protein but not mRNA in the amygdala. Eur J Neurosci 23(7):1853–1859. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04723.x
Peyrot C, Brouillard A, Morand-Beaulieu S, Marin MF (2020) A review on how stress modulates fear conditioning: let’s not forget the role of sex and sex hormones. Behav Res Ther 129:103615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2020.103615
Radiske A, Gonzalez MC, Noga DA, Rossato JI, Bevilaqua LRM, Cammarota M (2021) mTOR inhibition impairs extinction memory reconsolidation. Learn Mem 28(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.052068.120
Ressler RL, Goode TD, Evemy C, Maren S (2020) NMDA receptors in the CeA and BNST differentially regulate fear conditioning to predictable and unpredictable threats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 174:107281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2020.107281
Ressler RL, Goode TD, Kim S, Ramanathan KR, Maren S (2021) Covert capture and attenuation of a hippocampus-dependent fear memory. Nat Neurosci 24:677–684. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-021-00825-5
Saxe MD, Battaglia F, Wang JW, Malleret G, David DJ, Monckton JE, Garcia AD, Sofroniew MV, Kandel ER, Santarelli L, Hen R, Drew MR (2006) Ablation of hippocampal neurogenesis impairs contextual fear conditioning and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(46):17501–17506. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0607207103
Schratt GM, Nigh EA, Chen WG, Hu L, Greenberg ME (2004) BDNF regulates the translation of a select group of mRNAs by a mammalian target of rapamycin-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway during neuronal development. J Neurosci 24(33):7366–7377. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1739-04.2004
Slipczuk L, Bekinschtein P, Katche C, Cammarota M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (2009) BDNF activates mTOR to regulate GluR1 expression required for memory formation. PLoS ONE 4(6):e6007. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006007
Switon K, Kotulska K, Janusz-Kaminska A, Zmorzynska J, Jaworski J (2017) Molecular neurobiology of mTOR. Neuroscience 341:112–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.11.017
Takei N, Inamura N, Kawamura M, Namba H, Hara K, Yonezawa K, Nawa H (2004) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent local activation of translation machinery and protein synthesis in neuronal dendrites. J Neurosci 24(44):9760–9769. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Citation&list_uids=15525761
Tolin DF, Foa EB (2006) Sex differences in trauma and posttraumatic stress disorder: a quantitative review of 25 years of research. Psychol Bull 132(6):959–992. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.132.6.959
Zucker I, Beery AK (2010) Males still dominate animal studies. Nature 465:690. https://doi.org/10.1038/465690a
Funding
NSERC Discovery Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Trask, J., MacCallum, P.E., Rideout, H. et al. Rapamycin attenuates reconsolidation of a backwards-conditioned aversive stimuli in female mice. Psychopharmacology 241, 601–612 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-024-06544-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-024-06544-6