Abstract
Rationale
The c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway and neurotrophic factor dysregulation play a critical role in the pathogenesis of neurobehavioral disorders (anxiety and depression). Targeting the JNK pathway and BDNF/VEGF signaling may signify a new avenue for the treatment of neurobehavioral disorders.
Objectives
The present study investigated the effect of matrine (Mat) against anxiety- and depressive-like emotional status in an acute mouse model of burn injury and explores its underlying mechanism.
Methods
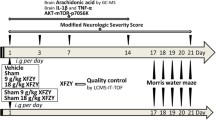
In the mouse model of thermal injury, anxiety- and depression-related behaviors were evaluated using the elevated plus-maze test, the light-dark box test, the open-field test, the forced swimming test, and the tail suspension test. The JNK/caspase-3 and BDNF/VEGF proteins were determined by immunohistochemistry. Additionally, proinflammatory cytokine, antioxidant, nitric oxide, and corticosterone levels were also measured.
Results
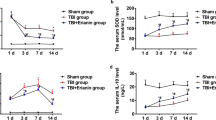
The results showed that treatment with Mat significantly improves anxiety- and depressive-like behaviors. It remarkably reduced the levels of proinflammatory cytokines, malondialdehyde, and nitric oxide in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of a mouse brain. It considerably improved burn-induced alteration in the antioxidant status, corticosterone, and BDNF/VEGF. It also inhibited burn-induced apoptotic signaling by downregulating the expression of JNK/caspase-3. Similarly, it prevented DNA damage and histopathological changes in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. Furthermore, molecular docking results showed that Mat possess better binding affinity for JNK/caspase-3 and BDNF/VEGF proteins.
Conclusions
These findings provide convincing evidence that Mat improves anxiety- and depressive-like emotional status through modulation of JNK-mediated inflammatory, oxidative stress, apoptotic, and BDNF/VEGF signaling in an acute mouse model of burn injury.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad A, Herndon DN, Szabo C (2019) Oxandrolone protects against the development of multiorgan failure, modulates the systemic inflammatory response and promotes wound healing during burn injury. Burns 45:671–681
Arif M, Ramprasad K (2013) Prevalence of anxiety and depression in burns patients in a tertiary care hospital. Religion 26:74
Atiq A, Shal B, Naveed M, Khan A, Ali J, Zeeshan S, Al-Sharari SD, Kim YS, Khan S (2019) Diadzein ameliorates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators in rodents. Eur J Pharmacol 843:292–306
Cederholm JM, Froud KE, Wong AC, Ko M, Ryan AF, Housley GD (2012) Differential actions of isoflurane and ketamine-based anaesthetics on cochlear function in the mouse. Hear Res 292:71–79
Chen X, Zhi X, Pan P, Cui J, Cao L, Weng W, Zhou Q, Wang L, Zhai X, Zhao Q (2017) Matrine prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice by inhibiting RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. FASEB J 31:4855–4865
Cheng J, Dong S, Yi L, Geng D, Liu Q (2018) Magnolol abrogates chronic mild stress-induced depressive-like behaviors by inhibiting neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in the prefrontal cortex of mice. Int Immunopharmacol 59:61–67
Choi RJ, Chun J, Khan S, Kim YS (2014) Desoxyrhapontigenin, a potent anti-inflammatory phytochemical, inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory responses via suppressing NF-κB and MAPK pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol 18:182–190
Deniz S, Arslan S (2017) Pain and anxiety in burn patients. Int J 10:1723
Dhanasekaran DN, Reddy EP (2017) JNK-signaling: a multiplexing hub in programmed cell death. Genes Cancer 8:682
Ding X-F, Liu Y, Yan Z-Y, Li X-J, Ma Q-Y, Jin Z-Y, Li Y-H, Liu Y-Y, Xue Z, Chen J-X (2017) Involvement of normalized glial fibrillary acidic protein expression in the hippocampi in antidepressant-like effects of xiaoyaosan on chronically stressed mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017:1960584
Duman RS, Li N (2012) A neurotrophic hypothesis of depression: role of synaptogenesis in the actions of NMDA receptor antagonists. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367:2475–2484
Flierl MA, Stahel PF, Touban BM, Beauchamp KM, Morgan SJ, Smith WR, Ipaktchi KR (2009) Bench-to-bedside review: burn-induced cerebral inflammation–a neglected entity? Crit Care 13:215
Furtado M, Katzman MA (2015) Examining the role of neuroinflammation in major depression. Psychiatry Res 229:27–36
Gao Y-J, Ji R-R (2008) Activation of JNK pathway in persistent pain. Neurosci Lett 437:180–183
Gao W, Wang W, Peng Y, Deng Z (2019) Antidepressive effects of kaempferol mediated by reduction of oxidative stress, proinflammatory cytokines and up-regulation of AKT/β-catenin cascade. Metab Brain Dis 34:485–494
Han M, Ban J-J, Bae J-S, Shin C-Y, Lee DH, Chung JH (2017) UV irradiation to mouse skin decreases hippocampal neurogenesis and synaptic protein expression via HPA axis activation. Sci Rep 7:15574
Hollos P, Marchisella F, Coffey ET (2018) JNK regulation of depression and anxiety. Brain Plast 3:145–155
Jangra A, Lukhi MM, Sulakhiya K, Baruah CC, Lahkar M (2014) Protective effect of mangiferin against lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive and anxiety-like behaviour in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 740:337–345
Jangra A, Sriram CS, Lahkar M (2016) Lipopolysaccharide-induced behavioral alterations are alleviated by sodium phenylbutyrate via attenuation of oxidative stress and neuroinflammatory cascade. Inflammation 39:1441–1452
Khalid S, Ullah MZ, Khan AU, Afridi R, Rasheed H, Khan A, Ali H, Kim YS, Khan S (2018) Antihyperalgesic properties of honokiol in inflammatory pain models by targeting of NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling. Front Pharmacol 9:140
Khalid S, Khan A, Shal B, Ali H, Kim YS, Khan S (2019) Suppression of TRPV1 and P2Y nociceptors by honokiol isolated from Magnolia officinalis in 3rd degree burn mice by inhibiting inflammatory mediators. Biomed Pharmacother 114:108777
Khan S, Shehzad O, Chun J, Kim YS (2013) Mechanism underlying anti-hyperalgesic and anti-allodynic properties of anomalin in both acute and chronic inflammatory pain models in mice through inhibition of NF-κB, MAPKs and CREB signaling cascades. Eur J Pharmacol 718:448–458
Khan S, Shehzad O, Lee KJ, Tosun A, Kim YS (2014) Anti-inflammatory properties of samidin from Seseli resinosum through suppression of NF-κB and AP-1-mediated-genes in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Arch Pharm Res 37:1496–1503
Khan S, Choi RJ, Lee J, Kim YS (2016) Attenuation of neuropathic pain and neuroinflammatory responses by a pyranocoumarin derivative, anomalin in animal and cellular models. Eur J Pharmacol 774:95–104
Khan A, Khan S, Ali H, Shah KU, Ali H, Shehzad O, Onder A, Kim YS (2019a) Anomalin attenuates LPS-induced acute lungs injury through inhibition of AP-1 signaling. Int Immunopharmacol 73:451–460
Khan A, Shal B, Naveed M, Shah FA, Atiq A, Khan NU, Kim YS, Khan S (2019b) Matrine ameliorates anxiety and depression-like behaviour by targeting hyperammonemia-induced neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in CCl4 model of liver injury. Neurotoxicology 72:38–50
Kitazumi I, Tsukahara M (2011) Regulation of DNA fragmentation: the role of caspases and phosphorylation. FEBS J 278:427–441
Kumar S, Saini V, Maurya IK, Sindhu J, Kumari M, Kataria R, Kumar V (2018) Design, synthesis, DFT, docking studies and ADME prediction of some new coumarinyl linked pyrazolylthiazoles: potential standalone or adjuvant antimicrobial agents. PLoS One 13:e0196016
Lee E-G, Son H (2009) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and related neurotrophic factors. BMB Rep 42:239–244
Lei Z, Liu X, Ma J, Zhu J (2009) Effects of matrine on airway inflammation and early airway remodeling in asthmatic mice. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi 32:165–170
Li J, Xu B, Chen Z, Zhou C, Liao L, Qin Y, Yang C, Zhang X, Hu Z, Sun L (2018) PI 3K/AKT/JNK/p38 signalling pathway-mediated neural apoptosis in the prefrontal cortex of mice is involved in the antidepressant-like effect of pioglitazone. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 45:525–535
Liu L, Song H, Duan H, Chai J, Yang J, Li X, Yu Y, Zhang X, Hu X, Xiao M (2016) TSG-6 secreted by human umbilical cord-MSCs attenuates severe burn-induced excessive inflammation via inhibiting activations of P38 and JNK signaling. Sci Rep 6:30121
Lu S, Xiao X, Cheng M (2015) Matrine inhibits IL-1β-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases by suppressing the activation of MAPK and NF-κB in human chondrocytes in vitro. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:4764
Mane DR, Kale AD, Belaldavar C (2017) Validation of immunoexpression of tenascin-C in oral precancerous and cancerous tissues using ImageJ analysis with novel immunohistochemistry profiler plugin: an immunohistochemical quantitative analysis. J Oral And Maxillofac Pathol 21:211–217
Mohammadi AB, Torbati M, Farajdokht F, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Fazljou SMB, Vatandoust SM, Golzari SE, Mahmoudi J (2019) Sericin alleviates restraint stress induced depressive-and anxiety-like behaviors via modulation of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and apoptosis in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Brain Res 1715:47–56
Naveed M, Khan SZ, Zeeshan S, Khan A, Shal B, Atiq A, Ali H, Ullah R, Khan S (2019) A new cationic palladium (II) dithiocarbamate exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities through inhibition of inflammatory mediators in in vivo models. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 392:961–977
Nowacka M, Obuchowicz E (2013) BDNF and VEGF in the pathogenesis of stress-induced affective diseases: an insight from experimental studies. Pharmacol Rep 65:535–546
Palmu R, Suominen K, Vuola J, Isometsä E (2011) Mental disorders after burn injury: a prospective study. Burns 37:601–609
Parihar A, Parihar MS, Milner S, Bhat S (2008) Oxidative stress and anti-oxidative mobilization in burn injury. Burns 34:6–17
Patki G, Solanki N, Atrooz F, Allam F, Salim S (2013) Depression, anxiety-like behavior and memory impairment are associated with increased oxidative stress and inflammation in a rat model of social stress. Brain Res 1539:73–86
Qu M, Nourbakhsh M (2017) Current experimental models of burns. Discov Med 23:95–103
Raone A, Cassanelli A, Scheggi S, Rauggi R, Danielli B, De Montis M (2007) Hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal modifications consequent to chronic stress exposure in an experimental model of depression in rats. Neuroscience 146:1734–1742
Renneberg B, Ripper S, Schulze J, Seehausen A, Weiler M, Wind G, Hartmann B, Germann G, Liedl A (2014) Quality of life and predictors of long-term outcome after severe burn injury. J Behav Med 37:967–976
Reyes R Jr, Wu Y, Lai Q, Mrizek M, Berger J, Jimenez DF, Barone CM, Ding Y (2006) Early inflammatory response in rat brain after peripheral thermal injury. Neurosci Lett 407:11–15
Schmidt HD, Banasr M, Duman RS (2008) Future antidepressant targets: neurotrophic factors and related signaling cascades. Drug Discov Today Ther Strateg 5:151–156
Shal B, Ding W, Ali H, Kim YS, Khan S (2018) Anti-neuroinflammatory potential of natural products in attenuation of Alzheimer's disease. Front Pharmacol 9:548
Shal B, Khan A, Naveed M, Khan NU, AlSharari SD, Kim YS, Khan S (2019) Effect of 25-methoxy hispidol a isolated from Poncirus trifoliate against bacteria-induced anxiety and depression by targeting neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 111:209–223
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31:455–461
Wang Z, Chen L, Rong X, Wang X (2017) Upregulation of MAOA in the hippocampus results in delayed depressive-like behaviors in burn mice. Burns. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2017.03.013
Weston CR, Davis RJ (2007) The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19:142–149
Wu S, Gao Q, Zhao P, Gao Y, Xi Y, Wang X, Liang Y, Shi H, Ma Y (2016) Sulforaphane produces antidepressant-and anxiolytic-like effects in adult mice. Behav Brain Res 301:55–62
Wu Z, You Z, Chen P, Chen C, Chen F, Shen J, Xu H (2018) Matrine exerts antidepressant-like effects on mice: role of the hippocampal PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 21:764–776
Xu M, Yang L, Hong L-Z, Zhao X-Y, Zhang H-L (2012) Direct protection of neurons and astrocytes by matrine via inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway contributes to neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 1454:48–64
Yang Y, Hu Z, Du X, Davies H, Huo X, Fang M (2017) miR-16 and fluoxetine both reverse autophagic and apoptotic change in chronic unpredictable mild stress model rats. Front Neurosci 11:428
Zeeshan S, Naveed M, Khan A, Atiq A, Arif M, Ahmed MN, Kim YS, Khan S (2019) N-Pyrazoloyl and N-thiopheneacetyl hydrazone of isatin exhibited potent anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive properties through suppression of NF-κB, MAPK and oxidative stress signaling in animal models of inflammation. Inflamm Res 68:613–632
Zhang J, Lin W (2018) The JNK signaling pathway as a potential new target for depression. Chin Sci Bull 63:1998–2009
Zhang J, Sio SWS, Moochhala S, Bhatia M (2010) Role of hydrogen sulfide in severe burn injury-induced inflammation in mice. Mol Med 16:417–424
Zhang Q-H, Li J-C, Dong N, Tang L-M, Zhu X-M, Sheng Z-Y, Yao Y-M (2013) Burn injury induces gelsolin expression and cleavage in the brain of mice. Neuroscience 228:60–72
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AK, BS, and MN designed and performed research including behavioral and biochemical assays. AK, BN, NI, HA, and SK analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. SK supervised the project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experimental manipulations were undertaken under the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, with the approval of the Bioethical Committee of Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad (Approval No. BEC-FBS-QAU 2017-60). Maximum care was made sure to minimize harm to animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., Shal, B., Naveed, M. et al. Matrine alleviates neurobehavioral alterations via modulation of JNK-mediated caspase-3 and BDNF/VEGF signaling in a mouse model of burn injury. Psychopharmacology 237, 2327–2343 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05537-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05537-5