Abstract
Rationale
Psychiatric disorders such as anxiety and depression are frequently observed in neuropathic pain patients, and negatively impact their quality of life. Mirogabalin is a novel ligand for the α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels and has unique binding characteristics to α2δ subunits and potent and long-lasting analgesic effects in neuropathic pain models.
Objectives
To provide further information on the pharmacological profile of mirogabalin and its utility for chronic pain therapy, we investigated its anxiolytic effects in an experimental animal model for neuropathic pain.
Methods
In chronic constriction injury (CCI) model rats, mechanical hypersensitivity was determined by the von Frey test. Anxiety- and depression-related behaviours were evaluated using the elevated plus maze test and forced swimming test, respectively.
Results
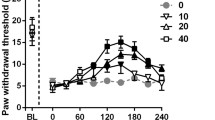
CCI model rats showed sustained tactile allodynia followed by anxiety-related behaviours, not depression-related behaviours. The tactile allodynia (significant decreases in paw withdrawal threshold) developed within 2 weeks after model preparation, whereas the anxiety-related behaviours (significant decreases in the number of entries and time spent in open arms and significant increases in time spent in closed arms) were observed at 5 weeks but not 4 weeks after model preparation. Single oral administration of mirogabalin (3 or 10 mg/kg) dose-dependently alleviated the above-mentioned anxiety-related behaviours and tactile allodynia.
Conclusions
CCI model rats showed anxiety-related behaviours in a time-dependent manner in the elevated plus maze test. Mirogabalin alleviated both the anxiety-related behaviours and tactile allodynia in CCI model rats. Mirogabalin may provide effective anxiety relief as well as pain relief in patients with neuropathic pain.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alba-Delgado C, Cebada-Aleu A, Mico JA, Berrocoso E (2016) Comorbid anxiety-like behavior and locus coeruleus impairment in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a comparative study with the chronic constriction injury model. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 71:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2016.06.007
Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, Haanpää M, Hansson P, Jensen TS, Nurmikko T (2010) EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol 17:1113–1123. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.02999.x
Attal N, Lanteri-Minet M, Laurent B, Fermanian J, Bouhassira D (2011) The specific disease burden of neuropathic pain: results of a French nationwide survey. Pain 152:2836–2843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2011.09.014
Baastrup C, Jensen TS, Finnerup NB (2011) Pregabalin attenuates place escape/avoidance behavior in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Brain Res 1370:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.11.008
Belliotti TR, Capiris T, Ekhato IV, Kinsora JJ, Field MJ, Heffner TG, Meltzer LT, Schwarz JB, Taylor CP, Thorpe AJ, Vartanian MG, Wise LD, Zhi-Su T, Weber ML, Wustrow DJ (2005) Structure-activity relationships of pregabalin and analogues that target the α2-δ protein. J Med Chem 48:2294–2307. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm049762l
Benbouzid M, Pallage V, Rajalu M, Waltisperger E, Doridot S, Poisbeau P, Freund-Mercier MJ, Barrot M (2008) Sciatic nerve cuffing in mice: a model of sustained neuropathic pain. Eur J Pain 12:591–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpain.2007.10.002
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33:87–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(88)90209-6
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(94)90144-9
Colloca L, Ludman T, Bouhassira D, Baron R, Dickenson AH, Yarnitsky D, Freeman R, Truini A, Attal N, Finnerup NB, Eccleston C, Kalso E, Bennett DL, Dworkin RH, Raja SN (2017) Neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3:17002. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.2
Cruccu G, Truini A (2017) A review of neuropathic pain: from guidelines to clinical practice. Pain Ther 6(Suppl 1):S35–S42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40122-017-0087-0
Deeks ED (2019) Mirogabalin: first global approval. Drugs. 79:463–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-019-01070-8
Dixon WJ (1980) Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 20:441–462. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.002301
Domon Y, Arakawa N, Inoue T, Matsuda F, Takahashi M, Yamamura N, Kai K, Kitano Y (2018a) Binding characteristics and analgesic effects of mirogabalin, a novel ligand for the α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 365:573–582. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.117.247551
Domon Y, Kitano Y, Makino M (2018b) Analgesic effects of the novel α2δ ligand mirogabalin in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Pharmazie 73:659–661. https://doi.org/10.1691/ph.2018.8550
Dooley DJ, Taylor CP, Donevan S, Feltner D (2007) Ca2+ channel α2δ ligands: novel modulators of neurotransmission. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2006.12.006
Failde I, Dueñas M, Ribera MV, Gálvez R, Mico JA, Salazar A, de Sola H, Pérez C (2018) Prevalence of central and peripheral neuropathic pain in patients attending pain clinics in Spain: factors related to intensity of pain and quality of life. J Pain Res 11:1835–1847. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S159729
Field MJ, Oles RJ, Singh L (2001) Pregabalin may represent a novel class of anxiolytic agents with a broad spectrum of activity. Br J Pharmacol 132:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0703794
Frampton JE (2014) Pregabalin: a review of its use in adults with generalized anxiety disorder. CNS Drugs 28:835–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-014-0192-0
Gee NS, Brown JP, Dissanayake VU, Offord J, Thurlow R, Woodruff GN (1996) The novel anticonvulsant drug, gabapentin (Neurontin), binds to the α2δ subunit of a calcium channel. J Biol Chem 271:5768–5776. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.10.5768
Grégoire S, Michaud V, Chapuy E, Eschalier A, Ardid D (2012) Study of emotional and cognitive impairments in mononeuropathic rats: effect of duloxetine and gabapentin. Pain 153:1657–1663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2012.04.023
Gustorff B, Dorner T, Likar R, Grisold W, Lawrence K, Schwarz F, Rieder A (2008) Prevalence of self-reported neuropathic pain and impact on quality of life: a prospective representative survey. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 52:132–136. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2007.01486.x
Harte SE, Meyers JB, Donahue RR, Taylor BK, Morrow TJ (2016) Mechanical conflict system: a novel operant method for the assessment of nociceptive behavior. PLoS One 11:e0150164. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150164
Hasnie FS, Breuer J, Parker S, Wallace V, Blackbeard J, Lever I, Kinchington PR, Dickenson AH, Pheby T, Rice AS (2007) Further characterization of a rat model of varicella zoster virus-associated pain: relationship between mechanical hypersensitivity and anxiety-related behavior, and the influence of analgesic drugs. Neuroscience 144:1495–1508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.11.029
Jensen TS, Baron R, Haanpää M, Kalso E, Loeser JD, Rice AS, Treede RD (2011) A new definition of neuropathic pain. Pain 152:2204–2205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2011.06.017
La Porta C, Lara-Mayorga IM, Negrete R, Maldonado R (2016) Effects of pregabalin on the nociceptive, emotional and cognitive manifestations of neuropathic pain in mice. Eur J Pain 20:1454–1466. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.868
Li Z, Taylor CP, Weber M, Piechan J, Prior F, Bian F, Cui M, Hoffman D, Donevan S (2011) Pregabalin is a potent and selective ligand for α2δ-1 and α2δ-2 calcium channel subunits. Eur J Pharmacol 667:80–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.05.054
Lotarski SM, Donevan S, El-Kattan A, Osgood S, Poe J, Taylor CP, Offord J (2011) Anxiolytic-like activity of pregabalin in the Vogel conflict test in α2δ-1 (R217A) and α2δ-2 (R279A) mouse mutants. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 338:615–621. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.111.180976
Montgomery SA (2006) Pregabalin for the treatment of generalised anxiety disorder. Expert Opin Pharmacother 7:2139–2154. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656566.7.15.2139
Narita M, Kaneko C, Miyoshi K, Nagumo Y, Kuzumaki N, Nakajima M, Nanjo K, Matsuzawa K, Yamazaki M, Suzuki T (2006) Chronic pain induces anxiety with concomitant changes in opioidergic function in the amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:739–750. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300858
O’Connor AB, Dworkin RH (2009) Treatment of neuropathic pain: an overview of recent guidelines. Am J Med 122(10 Suppl):S22–S32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.04.007
Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M (1977) Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 266:730–732
Radat F, Margot-Duclot A, Attal N (2013) Psychiatric co-morbidities in patients with chronic peripheral neuropathic pain: a multicentre cohort study. Eur J Pain 17:1547–1557. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00334.x
Roeska K, Doods H, Arndt K, Treede RD, Ceci A (2008) Anxiety-like behaviour in rats with mononeuropathy is reduced by the analgesic drugs morphine and gabapentin. Pain 139:349–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2008.05.003
Saeki K, Yasuda SI, Kato M, Kano M, Domon Y, Arakawa N, Kitano Y (2019) Analgesic effects of mirogabalin, a novel ligand for α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels, in experimental animal models of fibromyalgia. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 392:723–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01628-z
Sawada A, Niiyama Y, Ataka K, Nagaishi K, Yamakage M, Fujimiya M (2014) Suppression of bone marrow-derived microglia in the amygdala improves anxiety-like behavior induced by chronic partial sciatic nerve ligation in mice. Pain 155:1762–1772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2014.05.031
Schaefer C, Mann R, Sadosky A, Daniel S, Parsons B, Nieshoff E, Tuchman M, Nalamachu S, Anschel A, Stacey BR (2014) Burden of illness associated with peripheral and central neuropathic pain among adults seeking treatment in the United States: a patient-centered evaluation. Pain Med 15:2105–2119. https://doi.org/10.1111/pme.12502
Shimamura M, Kuratani K, Kinoshita M (2007) A new automated and high-throughput system for analysis of the forced swim test in mice based on magnetic field changes. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 55:332–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vascn.2006.11.003
Stahl SM, Porreca F, Taylor CP, Cheung R, Thorpe AJ, Clair A (2013) The diverse therapeutic actions of pregabalin: is a single mechanism responsible for several pharmacological activities? Trends Pharmacol Sci 34:332–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2013.04.001
Suzuki T, Amata M, Sakaue G, Nishimura S, Inoue T, Shibata M, Mashimo T (2007) Experimental neuropathy in mice is associated with delayed behavioral changes related to anxiety and depression. Anesth Analg 104:1570–1577. https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ane.0000261514.19946.66
Wallace VC, Segerdahl AR, Blackbeard J, Pheby T, Rice AS (2008) Anxiety-like behaviour is attenuated by gabapentin, morphine and diazepam in a rodent model of HIV anti-retroviral-associated neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett 448:153–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2008.10.005
Wang XQ, Zhong XL, Li ZB, Wang HT, Zhang J, Li F, Zhang JY, Dai RP, Xin-Fu Z, Li CQ, Li ZY, Bi FF (2015) Differential roles of hippocampal glutamatergic receptors in neuropathic anxiety-like behavior after partial sciatic nerve ligation in rats. BMC Neurosci 16:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-015-0150-x
Wu Y, Yao X, Jiang Y, He X, Shao X, Du J, Shen Z, He Q, Fang J (2017) Pain aversion and anxiety-like behavior occur at different times during the course of chronic inflammatory pain in rats. J Pain Res 10:2585–2593. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S139679
Yalcin I, Barthas F, Barrot M (2014) Emotional consequences of neuropathic pain: insight from preclinical studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 47:154–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.08.002
Yalcin I, Bohren Y, Waltisperger E, Sage-Ciocca D, Yin JC, Freund-Mercier MJ, Barrot M (2011) A time-dependent history of mood disorders in a murine model of neuropathic pain. Biol Psychiatry 70:946–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.07.017
Acknowledgements
We thank Asuka Kawamura and Kousei Shimada for help with the chemical synthesis. We also thank Miki Sugiyama, Katsuhiro Higuchi and Yuri Noda for their expertise in the experiments. In addition, we thank Masami Kato, Mayumi Kano, Jun Harada, Mitsuhiro Makino, Kaori Ito, Yuki Domon, Naohisa Arakawa and Kazufumi Kubota for all of their support in this study. Finally, we wish to express our gratitude to Scientific Language Co., Ltd. (Ibaraki, Japan), for reviewing and editing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HM and YK conceived and designed the research. HM, HK and KS performed the experiments and analysed the data. HM and YK wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the Guidelines for Management and Welfare of Experimental Animals (Hashima Laboratory, Nihon Bioresearch Inc.; April 2, 2007, modified on August 27, 2010), and the Guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd. This article does not describe any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
HM, HK and KS are employees of Nihon Bioresearch Inc., while YK is an employee of Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd. This study was sponsored by Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 55.7 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murasawa, H., Kobayashi, H., Saeki, K. et al. Anxiolytic effects of the novel α2δ ligand mirogabalin in a rat model of chronic constriction injury, an experimental model of neuropathic pain. Psychopharmacology 237, 189–197 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05356-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05356-3