Abstract
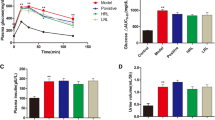
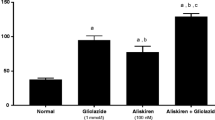
Reactive oxygen species via NADPH oxidase (NOX) activation are involved in the pathogenesis of many disease conditions such as diabetes and its complications. In the present study, we have examined the effect of daidzein in the management of diabetic cystopathy. Diabetes was induced in male Sprague Dawley rats via intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (STZ) at a dose of 55 mg/kg. After 6 weeks of diabetes induction, animals were treated with daidzein orally at a dose of 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg for 4 weeks. Diabetic animals showed increase (p < 0.001) in bladder capacity (4.32 ± 0.43 mL) and residual volume (2.53 ± 0.19 mL) when compared with normal control animals (2.10 ± 0.40 mL and 0.51 ± 0.12 mL res). Treatment with daidzein at dose of 50 and 100 mg/kg significantly reduced the elevated bladder capacity (2.91 ± 0.11 mL, p < 0.01 and 2.65 ± 1.13 mL, p < 0.001) and residual volume (1.40 ± 0.15 mL, p < 0.001 and 1.15 ± 0.05 mL, p < 0.001). Daidzein-treated animals also showed improvement in voiding efficiency. Elevated threshold and baseline pressure were also found to be reduced in diabetic animals after 4 weeks of daidzein treatment. Daidzein treatment also prevented the loss of antioxidant enzymes in the urinary bladder and also reduced the expression of NOX-4 and RAC-1 in the bladder. From the results, it can be concluded that daidzein showed a beneficial effect on urinary bladder dysfunction in diabetic animals.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
Code availability
Not applicable.
Change history
13 October 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02777-y
References
Andersson KE, Wein AJ (2004) Pharmacology of the lower urinary tract: basis for current and future treatments of urinary incontinence. Pharmacol Rev 56(4):581–631. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.56.4.4
Arioglu Inan E, Ellenbroek JH, Michel MC (2018) A systematic review of urinary bladder hypertrophy in experimental diabetes: Part I. Streptozotocin-induced rat models. Neurourol Urodyn 37(4):1212–1219. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.23490
Blaha I, López-Oliva ME, Martínez MP, et al (2019) Bladder dysfunction in an obese Zucker rat: the role of TRPA1 channels, oxidative stress, and hydrogen sulfide. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019. 5641645. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5641645
Cantley J, Ashcroft FM (2015) Q&A: Insulin secretion and type 2 diabetes: why do β-cells fail? BMC Biol. 33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-015-0140-6
Chen W, Ma X, Lin Y et al (2016) Dietary supplementation with a high dose of daidzein enhances the antioxidant capacity in swine muscle but experts pro-oxidant function in liver and fat tissues. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40104-016-0102-z
Cho AJ, Cho ST, Lee YK et al (2015) The association between an abnormal post-voiding urine volume and a lower estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with type 2 diabetes with no voiding symptoms. Korean J Intern Med 30:82–87. https://doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2015.30.1.82
Choi EJ, Kim GH (2014) The antioxidant activity of daidzein metabolites, O-desmethylangolensin and equol, in HepG2 cells. Mol Med Rep 9:328–332. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2013.1752
Choi MS, Jung UJ, Yeo J et al (2008) Genistein and daidzein prevent diabetes onset by elevating insulin level and altering hepatic gluconeogenic and lipogenic enzyme activities in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 24:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.780
Corrêa LBNS, Ramos CSCB, de Abboud RS et al (2020) Influence of alpha lipoic acid supplementation on urinary bladder morphology of diabetic rats. Int J Morphol 38:627–633. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-95022020000300627
Damasceno DC, Netto AO, Iessi IL et al (2014) Streptozotocin-induced diabetes models: pathophysiological mechanisms and fetal outcomes. Biomed Res Int 2014:819065. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/819065
Daneshgari F, Liu G, Birder L et al (2009) Diabetic bladder dysfunction: current translational knowledge. J Urol 182(6 Suppl):S18-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.08.070
Ellenbroek JH, Arioglu Inan E, Michel MC (2018) A systematic review of urinary bladder hypertrophy in experimental diabetes: Part 2. Comparison of animal models and functional consequences. Neurourol Urodyn 37:2346–2360. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.23786
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
Elumalai S, Karunakaran U, Lee IK et al (2017) Rac1-NADPH oxidase signaling promotes CD36 activation under glucotoxic conditions in pancreatic beta cells. Redox Biol 11:126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2016.11.009
Evcim AS, Micili SC, Karaman M et al (2015) The role of Rac1 on Carbachol-induced contractile activity in detrusor smooth muscle from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 116:476–484. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.12346
Fayyad AM, Hill SR, Jones G (2009) Prevalence and risk factors for bothersome lower urinary tract symptoms in women with diabetes mellitus from hospital-based diabetes clinic. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 20:1339–1344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-009-0949-z
Frimodt Moller C (1976) Diabetic cystopathy I: a clinical study of the frequency of bladder dysfunction in diabetics. Dan Med Bull 23:267–278
Garud MS, Kulkarni YA (2017) Attenuation of renal damage in type I diabetic rats by umbelliferone – a coumarin derivative. Pharmacol Reports 69:1263–1269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.06.014
Golbidi S, Laher I (2010) Bladder dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Front Pharmacol 1(36):1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2010.00136
Gort E, Güell R, Valls O (1984) Diagnosis of urinary bladder disorders in diabetic children. Acta Diabetol Lat 21:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02591104
GraphPad-Software (2012) Outlier calculator. In: QuickCalcs. https://www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/grubbs1/. Accessed 17 Apr 2022
Jiang YJ, Gong DX, Liu HB et al (2008) Ability of alpha-lipoic acid to reverse the diabetic cystopathy in a rat model. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29:713–719. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00790.x
Kaplan SA, Blaivas JG (1988) Diabetic cystopathy. J Diabet Complications 2:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-6632(88)80024-2
Kaplan SA, Te AE, Blaivas JG, McGuire EJ (1995) Urodynamic findings in patients with diabetic cystopathy. J Urol 153:342–344. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005392-199502000-00013
Laddha AP, Murugesan S, Kulkarni YA (2020) In-vivo and in-silico toxicity studies of daidzein: an isoflavone from soy. Drug Chem Toxicol 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/01480545.2020.1833906
Laddha AP, Kulkarni YA (2019) Tannins and vascular complications of diabetes: an update. Phytomedicine 56:229–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2018.10.026
Laddha AP, Kulkarni YA (2020) NADPH oxidase: a membrane-bound enzyme and its inhibitors in diabetic complications. Eur J Pharmacol 881:173206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173206
Laddha AP, Kulkarni YA (2021a) Daidzein ameliorates diabetic retinopathy in experimental animals. Life Sci 265:118779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118779
Laddha AP, Kulkarni YA (2021b) Daidzein mitigates myocardial injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Life Sci 284:119664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119664
Liu G, Daneshgari F (2014) Diabetic bladder dysfunction. Chin Med J (engl) 127:1357–1364
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/0922-338X(96)89160-4
Mann PC, Vahle J, Keenan CM et al (2012) International harmonization of toxicologic pathology nomenclature: an overview and review of basic principles. Toxicol Pathol 40:7S-13S. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623312438738
Mastri AR (1980) Neuropathology of diabetic neurogenic bladder. Ann Intern Med 92:316–318. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-92-2-316
Melman A, Zotova E, Kim M et al (2009) Longitudinal studies of time-dependent changes in both bladder and erectile function after streptozotocin-induced diabetes in Fischer 344 male rats. BJU Int 104:1292–1300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08573.x
Miyata Y, Matsuo T, Mitsunari K et al (2019) A review of oxidative stress and urinary dysfunction caused by bladder outlet obstruction and treatments using antioxidants. Antioxidants 8(5):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8050132
Murthy KS, Zhou H, Grider JR et al (2003) Differential signalling by muscarinic receptors in smooth muscle: m2-mediated inactivation of myosin light chain kinase via Gi3, Cdc42/Rac1 and p21-activated kinase 1 pathway, and m3-mediated MLC20 (20 kDa regulatory light chain of myosin II) phosphorylat. Biochem J 374:145–155. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20021274
Nasiry D, Khalatbary AR, Ahmadvand H et al (2017) Protective effects of methanolic extract of Juglans regia L. leaf on streptozotocin-induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 17:476. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-017-1983-x
NIH (2021) National Institutes of Health (NIH) | Turning Discovery Into Health. https://www.nih.gov/. Accessed 9 Jan 2022
Noriega-López L, Tovar AR, Gonzalez-Granillo M et al (2007) Pancreatic insulin secretion in rats fed a soy protein high fat diet depends on the interaction between the amino acid pattern and isoflavones. J Biol Chem 282:20657–20666. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M701045200
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Paoletti F, Mocali A, Aldinucci D (1990) Superoxide-driven NAD(P)H oxidation induced by EDTA-manganese complex and mercaptoethanol. Chem Biol Interact 76:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2797(90)90030-Q
Saito M, Nakamura I, Miyagawa I (1997) Autoradiographic localization of muscarinic receptors in diabetic rat bladder. Japanese J Urol 88:858–867. https://doi.org/10.5980/jpnjurol1989.88.858
Shimada K, Fujii T, Anai S et al (2011) ROS generation via NOX4 and its utility in the cytological diagnosis of urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder. BMC Urol 11:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2490-11-22
Starer P, Libow L (1990) Cystometric evaluation of bladder dysfunction in elderly diabetic patients. Arch Intern Med 150:810–813. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.150.4.810
Van Poppel H, Stessens R, Van Damme B et al (1988) Diabetic cystopathy: neuropathological examination of urinary bladder biopsies. Eur Urol 15:128–131. https://doi.org/10.1159/000473412
Wang Y, Deng GG, Davies KP (2016) Novel insights into development of diabetic bladder disorder provided by metabolomic analysis of the rat nondiabetic and diabetic detrusor and urothelial layer. Am J Physiol - Endocrinol Metab 311:E471–E479. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00134.2016
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Dr. Shailesh Khade for technical help in the surgical procedure.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YK and AL designed the experiments. AL conducted the experiments. AL and YK interpreted the results and wrote the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The experimental protocol was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) (approval no: CPCSEA/IAEC/P-75/2018).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Laddha, A.P., Kulkarni, Y.A. Daidzein attenuates urinary bladder dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats by NOX-4 and RAC-1 inhibition. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 395, 975–986 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-022-02246-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-022-02246-y