Abstract
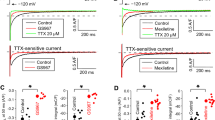
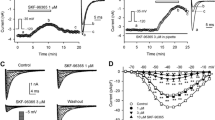
Tacrolimus is a commonly used immunosuppressive agent which causes cardiovascular complications, e.g., hypertension and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In spite of it, there is little information on the cellular cardiac effects of the immunosuppressive agent tacrolimus in larger mammals. In the present study, therefore, the concentration-dependent effects of tacrolimus on action potential morphology and the underlying ion currents were studied in canine ventricular cardiomyocytes. Standard microelectrode, conventional whole cell patch clamp, and action potential voltage clamp techniques were applied in myocytes enzymatically dispersed from canine ventricular myocardium. Tacrolimus (3–30 μM) caused a concentration-dependent reduction of maximum velocity of depolarization and repolarization, action potential amplitude, phase-1 repolarization, action potential duration, and plateau potential, while no significant change in the resting membrane potential was observed. Conventional voltage clamp experiments revealed that tacrolimus concentrations ≥3 μM blocked a variety of ion currents, including ICa, Ito, IK1, IKr, and IKs. Similar results were obtained under action potential voltage clamp conditions. These effects of tacrolimus developed rapidly and were fully reversible upon washout. The blockade of inward currents with the concomitant shortening of action potential duration in canine myocytes is the opposite of those observed previously with tacrolimus in small rodents. It is concluded that although tacrolimus blocks several ion channels at higher concentrations, there is no risk of direct interaction with cardiac ion channels when applying tacrolimus in therapeutic concentrations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage JM, Kormos RL, Fung J, Starzl TE (1991) The clinical trial of FK506 as primary and rescue immunosuppression in adult cardiac transplantation. Transplant Proc 23:3054–3057
Atkison P, Joubert G, Barron A, Grant D, Paradis K, Seidman E, Wall W, Rosenberg H, Howard J, Williams S et al (1995) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy associated with tacrolimus in paediatric transplant patients. Lancet 345:894–896
Bányász T, Magyar J, Körtvély Á, Gy S, Szigligeti P, Papp Z, Mohácsi A, Kovács L, Nánási PP (2001) Different effects of endothelin-1 on calcium and potassium currents in canine ventricular cells. N Schmied Arch Pharmacol 363:383–390
Bányász T, Magyar J, Szentandrássy N, Horváth B, Birinyi P, Szentmiklósi J, Nánási PP (2007) Action potential clamp fingerprints of K+ currents in canine cardiomyocytes: their role in ventricular repolarization. Acta Physiol 190:189–198
Bechstein WO (2000) Neurotoxicity of calcineurin inhibitors: impact and clinical management. Transplant Proc 13:313–326
Calderón-Sánchez E, Rodriguez-Moyano M, Smani T (2011) Immunophilins and cardiovascular complications. Curr Med Chem 18:5408–5413
Christ T, Wettwer E, Ravens U (2005) Risperidone-induced action potential prolongation is attenuated by increased repolarization reserve due to concomitant block of ICa, L. (N Schmied Arch Pharmacol 371:393–400
DuBell WH, Wright PA, Lederer WJ, Rogers TB (1997) Effect of the immunosuppressant FK506 on excitation—contraction coupling and outward K+ currents in rat ventricular myocytes. J Physiol (Lond) 501:509–516
DuBell WH, Gaa ST, Lederer WJ, Rogers TB (1998) Independent inhibition of calcineurin and K+ currents by the immunosuppressant FK-506 in rat ventricle. Am J Physiol 275:H2041–H2052
DuBell WH, Lederer WJ, Rogers TB (2000) K+ currents responsible for repolarization in mouse ventricle and their modulation by FK-506 and rapamycin. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278:H886–H897
Eschenhagen T (2010) Is ryanodine receptor phosphorylation key to the fight or flight response and heart failure? J Clin Invest 120:4197–4203
Fauconnier J, Lacampagne A, Rauzier JM, Fontanaud P, Frapier JM, Sejersted OM, Vassort G, Richard S (2005) Frequency-dependent and proarrhythmogenic effects of FK-506 in rat ventricular cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288:H778–H786
Fischmeister R, DeFelice LJ, Ayer RK, Levi R, DeHaan RL (1984) Channel currents during spontaneous action potentials in embryonic chick heart sells. The action potential patch clamp. Biophys J 46:267–271
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Hondeghem LM, Katzung BG (1977) Time- and voltage-dependent interactions of antiarrhythmic drugs with cardiac sodium channels. Biochim Biophys Acta 472:373–398
Kettlewell S, Seidler T, Smith GL (2009) The effects of over-expression of the FK506-binding protein FKBP12.6 on K+ currents in adult rabbit ventricular myocytes. Pflügers Arch 458:653–660
Lam E, Martin MM, Timerman AP, Sabers C, Fleischer S, Lukas T, Abraham RT, O’Keefe SJ, O’Neill EA, Wiederrecht GJ (1995) A novel FK506 binding protein can mediate the immunosuppressive effects of FK506 and is associated with the cardiac ryanodine receptor. J Biol Chem 270:26511–26522
Magyar J, Bányász T, Szigligeti P, Körtvély Á, Jednákovits A, Nánási PP (2000) Electrophysiological effects of bimoclomol in canine ventricular myocytes. N Schmied Arch Pharmacol 361:303–310
Magyar J, Bányász T, Fülöp L, Szentandrássy N, Körtvély Á, Kovács A, Szénási G, Nánási PP (2001) Effects of the antiarrhythmic agent EGIS-7229 on calcium and potassium currents in canine ventricular myocytes. N Schmied Arch Pharmacol 363:604–611
Magyar J, Bányász T, Zs B, Pacher P, Szentandrássy N, Fülöp L, Kecskeméti V, Nánási PP (2002) Electrophysiological effects of risperidone in mammalian cardiac cells. N Schmied Arch Pharmacol 366:350–356
Magyar J, Szentandrássy N, Bányász T, Kecskeméti V, Nánási PP (2004) Effects of norfluoxetine on the action potential and transmembrane ion currents in canine ventricular cardiomyocytes. N Schmied Arch Pharmacol 370:203–210
Maruyama M, Li BY, Chen H, Xu X, Song LS, Guatimosim S, Zhu W, Yong W, Zhang W, Bu G, Lin SF, Fishbein MC, Lederer WJ, Schild JH, Field LJ, Rubart M, Chen PS, Shou W (2011) FKBP12 is a critical regulator of the heart rhythm and the cardiac voltage-gated sodium current in mice. Circ Res 108:1042–1052
Moench C, Barreiros AP, Schuchmann M, Bittinger F, Thiesen J, Hommel G, Kraemer I, Otto G (2007) Tacrolimus monotherapy without steroids after liver transplantation—a prospective randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trial. Am J Transplant 7:1616–1623
Pacher P, Magyar J, Szigligeti P, Bányász T, Pankucsi C, Korom Z, Ungvári Z, Kecskeméti V, Nánási PP (2000) Electrophysiological effects of fluoxetine in mammalian cardiac tissues. N Schmied Arch Pharmacol 361:67–73
Rifai K, Bahr MJ, Cantz T, Klempnauer J, Manns MP, Strassburg CP (2005) Severe hearing loss after liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 37:1918–1919
Rifai K, Kirchner GI, Bahr MJ, Cantz T, Rosenau J, Nashan B, Klempnauer JL, Manns MP, Strassburg CP (2006) A new side effect of immunosuppression: high incidence of hearing impairment after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 12:411–415
Shan J, Betzenhauser MJ, Kushnir A, Reiken S, Meli AC, Wronska A, Dura M, Chen B-X, Marks AR (2010) Role of chronic ryanodine receptor phosphorylation in heart failure and β-adrenergic receptor blockade in mice. J Clin Invest 120:4375–4387
Simkó J, Szentandrássy N, Harmati G, Bárándi L, Horváth B, Magyar J, Bányász T, Lőrincz I, Nánási PP (2010) Effects of ropinirole on action potential characteristics and the underlying ion currents in canine ventricular myocytes. N Schmied Arch Pharmacol 382:213–220
Strichartz G, Cohen I (1978) Vmax as a measure of GNa in nerve and cardiac membranes. Biophys J 23:153–156
Su Z, Sugishita K, Li F, Ritter M, Barry WH (2003) Effects of FK506 on [Ca2+]i differ in mouse and rabbit ventricular myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:334–341
Szabó G, Szentandrássy N, Bíró T, Tóth IB, Czifra G, Magyar J, Bányász T, Varró A, Kovács L, Nánási PP (2005) Asymmetrical distribution of ion channels in canine and human left ventricular wall: epicardium versus midmyocardium. Pflügers Arch 450:307–316
Szentandrássy N, Bányász T, Bíró T, Szabó G, Tóth IB, Magyar J, Lázár J, Varró A, Kovács L, Nánási PP (2005) Apico-basal inhomogeneity in distribution of ion channels in canine and human ventricular myocardium. Cardiovasc Res 65:851–860
Williams R, Neuhaus P, Bismuth H, McMaster P, Pichlmayr R, Calne R, Otto G, Groth C (1996) Two-year data from the European multicentre tacrolimus (FK506) liver study. Transpl Int 9(Suppl 1):S144–S150
Winkler M, Pichlmayr R, Neuhaus P, McMaster P, Calne R, Otto G, Williams R, Bismuth H, Groth C (1994) Optimal FK 506 dosage in patients under primary immunosuppression following liver transplantation. Transpl Int 7(Suppl 1):S58–S63
Wu Y, Anderson ME (2002) Reduced repolarization reserve in ventricular myocytes from female mice. Cardiovasc Res 53:763–769
Acknowledgments
Financial support was provided by grants from the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund (OTKA-K100151, OTKA101196, OTKA-PD101171). Further support was obtained from the Hungarian Government (CNK-77855, TAMOP-4.2.1/B-09/1/KONV-2010-007 and TAMOP-4.2.2.A-11/1/KONV-2012-0045 research projects).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szabó, L., Szentandrássy, N., Kistamás, K. et al. Effects of tacrolimus on action potential configuration and transmembrane ion currents in canine ventricular cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 386, 239–246 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0823-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0823-2