Abstract
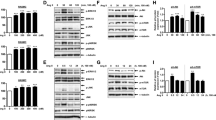
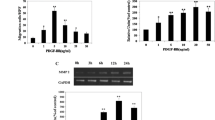
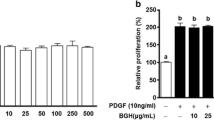
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is a potent stimulator of growth and motility of smooth muscle cells (SMCs) and fibroblasts. Abnormalities of PDGF/PDGF receptor (PDGFR) are thought to contribute to vascular diseases and malignancy. We previously showed that natural carotenoid lycopene can directly bind to PDGF-BB and affect its related functions in vascular SMCs. In this study we examined lycopene effect on PDGF-AA/-AB-induced signaling and migration in SMCs and fibroblasts. We found that lycopene inhibited PDGF-AA-induced SMC and fibroblast migration in a concentration-dependent manner. Lycopene reduced PDGF-AA signaling, including phosphorylation in PDGFR-α and its downstream protein kinases/enzymes. It also inhibited PDGF-AB-induced signaling and cell migration. However, lycopene did not affect PDGF-induced reactive oxygen species production and H2O2-induced PDGFR phosphorylation. The binding analysis revealed that lycopene but not β-carotene could directly bind to PDGF-AA in vitro and in plasma and this binding competitively inhibited lycopene interaction with PDGF-BB, suggesting that lycopene bound to PDGF-AA/-BB at a homologous/similar region within PDGF. Moreover, the docking and binding analyses predicted that the lycopene-binding region within PDGF was located at loop 2 region. Taken together, we provide here evidence that lycopene interacts with PDGF-AA/-AB and compromises their intracellular signaling, leading to a marked inhibition on PDGF-AA/-AB-induced migration in both SMCs and fibroblasts. We also predicted its binding region within PDGF and proved its anti-vascular injury effect in vivo. The results, together with our previous findings, suggest lycopene special affinity/effect for PDGF family and its possible application in prevention in vascular diseases and malignancy.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ERK:
-
extracellular matrix-regulated kinase
- PDGF:
-
platelet-derived growth factor
- PDGFR-α:
-
PDGF receptor α
- PLC-γ:
-
phospholipase C-γ
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- SMC(s):
-
smooth muscle cell(s)
References
Andersson M, Ostman A, Kreysing J, Backstrom G, Van de PM, Heldin CH (1995) Involvement of loop 2 of platelet-derived growth factor-AA and -BB in receptor binding. Growth Factors 12:159–164
Britton G (1995) Structure and properties of carotenoids in relation to function. FASEB J 9:1551–1558
Chiu YT, Chiu CP, Chien JT, Ho GH, Yang J, Chen BH (2007) Encapsulation of lycopene extract from tomato pulp waste with gelatin and poly (gamma-glutamic acid) as carrier. J Agric Food Chem 55:5123–5130
Dong J, Grunstein J, Tejada M, Peale F, Frantz G, Liang WC, Bai W, Yu L, Kowalski J, Liang X, Fuh G, Gerber HP, Ferrara N (2004) VEGF-null cells require PDGFR alpha signaling-mediated stromal fibroblast recruitment for tumorigenesis. EMBO J 23:2800–2810
El Agamey A, Lowe GM, McGarvey DJ, Mortensen A, Phillip DM, Truscott TG, Young AJ (2004) Carotenoid radical chemistry and antioxidant/pro-oxidant properties. Arch Biochem Biophys 430:37–48
Fiaschi T, Chiarugi P, Buricchi F, Giannoni E, Taddei ML, Talini D, Cozzi G, Zecchi-Orlandini S, Raugei G, Ramponi G (2001) Low molecular weight protein-tyrosine phosphatase is involved in growth inhibition during cell differentiation. J Biol Chem 276:49156–49163
Giovannucci E, Ascherio A, Rimm EB, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Willett WC (1995) Intake of carotenoids and retino in relation to risk of prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:1767–1776
Heber D, Lu QY (2002) Overview of mechanisms of action of lycopene. Exp Biol Med 227:920–923
Heldin CH, Westermark B (1999) Mechanism of action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor. Physiol Rev 79:1283–1316
Heldin CH, Ostman A, Ronnstrand L (1998) Signal transduction via platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - reviews on cancer 1378:F79–F113
Hughes AD, Clunn GF, Refson J, Moliou-Mason C (1996) Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF): actions and mechanisms in vascular smooth muscle. Gen Pharmacol: Vasc Sys 27:1079–1089
Hung C-F, Fang C-L, Liao M-H, Fang J-Y (2007) The effect of oil components on the physicochemical properties and drug delivery of emulsions: tocol emulsion versus lipid emulsion. Int J Pharm 335:193–202
Jones AV, Cross NC (2004) Oncogenic derivatives of platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:2912–2923
Kim JH, Jin YR, Park BS, Kim TJ, Kim SY, Lim Y, Hong JT, Yoo HS, Yun YP (2005) Luteolin prevents PDGF-BB-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells by inhibition of PDGF beta-receptor phosphorylation. Biochem Pharmacol 69:1715–1721
Kovalenko M, Ronnstrand L, Heldin CH, Loubtchenkov M, Gazit A, Levitzki A, Bohmer FD (1997) Phosphorylation site-specific inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor autophosphorylation by the receptor blocking tyrphostin AG1296. Biochemistry 36:6260–6269
Kreysing J, Ostman A, van de Canoy PM, Backstrom G, Heldin CH (1996) Identification of three amino acid residues in the B-chain of platelet-derived growth factor with different importance for binding to PDGF alpha- and beta-receptors. FEBS Lett 385:181–184
Li G, Satyamoorthy K, Meier F, Berking C, Bogenrieder T, Herlyn M (2003) Function and regulation of melanoma-stromal fibroblast interactions: when seeds meet soil. Oncogene 22:3162–3171
Lo HM, Hung CF, Tseng YL, Chen BH, Jian JS, Wu WB (2007) Lycopene binds PDGF-BB and inhibits PDGF-BB-induced intracellular signaling transduction pathway in rat smooth muscle cells. Biochem Pharmacol 74:54–63
Majesky MW, Reidy MA, Bowen-Pope DF, Hart CE, Wilcox JN, Schwartz SM (1990) PDGF ligand and receptor gene expression during repair of arterial injury. J Cell Biol 111:2149–2158
Oefner C, D’Arcy A, Winkler FK, Eggimann B, Hosang M (1992) Crystal structure of human platelet-derived growth factor BB. EMBO J 11:3921–3926
Osornio-Vargas AR, Lindroos PM, Coin PG, Badgett A, Hernandez-Rodriguez NA, Bonner JC (1996) Maximal PDGF-induced lung fibroblast chemotaxis requires PDGF receptor-alpha. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 271:L93–L99
Pietras K, Sjoblom T, Rubin K, Heldin CH, Ostman A (2003) PDGF receptors as cancer drug targets. Cancer Cell 3:439–443
Raines EW (2004) PDGF and cardiovascular disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15:237–254
Reigstad LJ, Varhaug JE, Lillehaug JR (2005) Structural and functional specificities of PDGF-C and PDGF-D, the novel members of the platelet-derived growth factors family. FEBS J 272:5723–5741
Rissanen T, Voutilainen S, Nyyssonen K, Salonen R, Salonen JT (2000) Low plasma lycopene concentration is associated with increased intima-media thickness of the carotid artery wall. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:2677–2681
Rissanen TH, Voutilainen S, Nyyssonen K, Salonen R, Kaplan GA, Salonen JT (2003) Serum lycopene concentrations and carotid atherosclerosis: the Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study. Am J Clin Nutr 77:133–138
Sjolund M, Hedin U, Sejersen T, Heldin CH, Thyberg J (1988) Arterial smooth muscle cells express platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) A chain mRNA, secrete a PDGF-like mitogen, and bind exogenous PDGF in a phenotype- and growth state-dependent manner. J Cell Biol 106:403–413
Sundaresan M, Yu ZX, Ferrans VJ, Irani K, Finkel T (1995) Requirement for generation of H2O2 for platelet-derived growth factor signal transduction. Science 270:296–299
Tallquist M, Kazlauskas A (2004) PDGF signaling in cells and mice. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15:205–213
Venkatesan B, Ghosh-Choudhury N, Das F, Mahimainathan L, Kamat A, Kasinath BS, Abboud HE, Choudhury GG (2008) Resveratrol inhibits PDGF receptor mitogenic signaling in mesangial cells: role of PTP1B. FASEB J 22:3469–3482
Weber AA, Neuhaus T, Skach RA, Hescheler J, Ahn HY, Schror K, Ko Y, Sachinidis A (2003) Mechanisms of the inhibitory effects of epigallocatechin-3 gallate on platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced cell signaling and mitogenesis. FASEB J 18:128–130
Yu JC, Heidaran MA, Pierce JH, Gutkind JS, Lombardi D, Ruggiero M, Aaronson SA (1991) Tyrosine mutations within the alpha platelet-derived growth factor receptor kinase insert domain abrogate receptor-associated phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase activity without affecting mitogenic or chemotactic signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol 11:3780–3785
Acknowledgments
We thanked Dr. Su-Jane Wang for providing us with rat aorta. The work was supported by the research grants from Changhua Christian Hospital, Shin Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital, and the National Science Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CP., Hung, CF., Lee, SC. et al. Lycopene binding compromised PDGF-AA/-AB signaling and migration in smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts: prediction of the possible lycopene binding site within PDGF. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 381, 401–414 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-010-0501-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-010-0501-1