Abstract
Increasing evidence indicates that developmental exposure to nonylphenol (NP) causes damage to the central nervous system (CNS). As the most unique and primary component of neuron, axon is an essential structure for the CNS function. Here, we investigated whether developmental exposure to NP affected rat axonal development in vivo and in vitro. Our results showed that developmental exposure to NP 10, 50, and 100 mg/(kg day) caused an obvious decrease in axonal length and density in the hippocampus. Developmental exposure to NP also altered the expression of CRMP-2 and p-CRMP-2, and activated Wnt-Dvl-GSK-3β cascade in the hippocampus, the crucial signaling that regulates axonal development. Even months after the exposure, impairment of axonal growth and alteration of this cascade were not fully restored. In the primary cultured neurons, 30, 50, and 70 μM NP treatment decreased axonal length and impaired axonal function. Similar to in vivo results, it also activated Wnt-Dvl-GSK-3β cascade in cultured neurons. SB-216763, a specific GSK-3β inhibitor, recovered the shortening of axon and the impairment of axonal function induced by NP. Taken together, our results support the idea that exposure to NP induces axonal injury in the developing neurons. Furthermore, the activation of Wnt-Dvl-GSK-3β cascade contributes to the axonal injury induced by NP.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CRMP-2:
-
Collapsin response mediator protein-2
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- Dvl:
-
Dishevelled
- GD:
-
Gestational day
- GSK-3β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3β
- NP:
-
Nonylphenol
- NPnEO:
-
Nonylphenol ethoxylates
- PB:
-
Placental barrier
- PND:
-
Postnatal day
- POPs:
-
Persistent organic pollutants
- p-CRMP-2:
-
Phosphorylated CRMP-2
- p-GSK-3β:
-
Phosphorylated GSK-3β
- SB:
-
SB-216763
References
Arukwe A, Thibaut R, Ingebrigtsen K, Celius T, Goksoyr A, Cravedi J (2000) In vivo and in vitro metabolism and organ distribution of nonylphenol in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquat Toxicol 49:289–304
Balakrishnan B, Thorstensen E, Ponnampalam A, Mitchell MD (2011) Passage of 4-nonylphenol across the human placenta. Placenta 32:788–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2011.07.014
Bevan CL et al (2006) The endocrine-disrupting compound, nonylphenol, inhibits neurotrophin-dependent neurite outgrowth. Endocrinology 147:4192–4204. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2006-0581
Brunelli E (2018) Histological and ultrastructural alterations of the Italian newt (Lissotriton italicus) skin after exposure to ecologically relevant concentrations of nonylphenol ethoxylates. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 60:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2018.04.007
Calafat AM, Kuklenyik Z, Reidy JA, Caudill SP, Ekong J, Needham LL (2005) Urinary concentrations of bisphenol A and 4-nonylphenol in a human reference population. Environ Health Perspect 113:391–395
Careghini A, Mastorgio AF, Saponaro S, Sezenna E (2015) Bisphenol A, nonylphenols, benzophenones, and benzotriazoles in soils, groundwater, surface water, sediments, and food: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:5711–5741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3974-5
Chou YH, Helfand BT, Goldman RD (2001) New horizons in cytoskeletal dynamics: transport of intermediate filaments along microtubule tracks. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:106–109
Ciani L, Salinas PC (2007) c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) cooperates with Gsk3beta to regulate Dishevelled-mediated microtubule stability. BMC Cell Biol 8:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2121-8-27
Ciani L, Krylova O, Smalley MJ, Dale TC, Salinas PC (2004) A divergent canonical WNT-signaling pathway regulates microtubule dynamics: dishevelled signals locally to stabilize microtubules. J Cell Biol 164:243–253. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200309096
Cole AR, Knebel A, Morrice NA, Robertson LA, Irving AJ, Connolly CN, Sutherland C (2004) GSK-3 phosphorylation of the Alzheimer epitope within collapsin response mediator proteins regulates axon elongation in primary neurons. J Biol Chem 279:50176–50180. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.c400412200
Couderc M et al (2014) Neurodevelopmental and behavioral effects of nonylphenol exposure during gestational and breastfeeding period on F1 rats. Neurotoxicology 44:237–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2014.07.002
Cunny HC, Mayes BA, Rosica KA, Trutter JA, Van Miller JP (1997) Subchronic toxicity (90-day) study with para-nonylphenol in rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 26:172–178. https://doi.org/10.1006/rtph.1997.1154
de Anda FC, Tsai LH (2011) Axon selection: from a polarized cytoplasm to a migrating neuron. Commun Integr Biol 4:304–307. https://doi.org/10.4161/cib.4.3.14781
Debanne D, Campanac E, Bialowas A, Carlier E, Alcaraz G (2011) Axon physiology. Physiol Rev 91:555–602. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00048.2009
Desai MK, Sudol KL, Janelsins MC, Mastrangelo MA, Frazer ME, Bowers WJ (2009) Triple-transgenic Alzheimer’s disease mice exhibit region-specific abnormalities in brain myelination patterns prior to appearance of amyloid and tau pathology. Glia 57:54–65. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20734
Fukata Y et al (2002) CRMP-2 binds to tubulin heterodimers to promote microtubule assembly. Nat Cell Biol 4:583–591. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb825
Gillette R, Reilly MP, Topper VY, Thompson LM, Crews D, Gore AC (2017) Anxiety-like behaviors in adulthood are altered in male but not female rats exposed to low dosages of polychlorinated biphenyls in utero. Horm Behav 87:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2016.10.011
Grandjean P, Landrigan PJ (2006) Developmental neurotoxicity of industrial chemicals. Lancet 368:2167–2178. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69665-7
Gu W, Wang Y, Qiu Z, Dong J, Wang Y, Chen J (2018) Maternal exposure to nonylphenol during pregnancy and lactation induces microglial cell activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in offspring hippocampus. Sci Total Environ 634:525–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.329
Hu F, Xu L, Liu ZH, Ge MM, Ruan DY, Wang HL (2014) Developmental lead exposure alters synaptogenesis through inhibiting canonical Wnt pathway in vivo and in vitro. PLoS One 9:e101894. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101894
Huang YF et al (2014) Nonylphenol in pregnant women and their matching fetuses: placental transfer and potential risks of infants. Environ Res 134:143–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.07.004
Hur EM, Zhou FQ (2010) GSK3 signalling in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:539–551. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2870
Inagaki N et al (2001) CRMP-2 induces axons in cultured hippocampal neurons. Nat Neurosci 4:781–782. https://doi.org/10.1038/90476
Inoue K, Yoshimura Y, Makino T, Nakazawa H (2000) Determination of 4-nonylphenol and 4-octylphenol in human blood samples by high-performance liquid chromatography with multi-electrode electrochemical coulometric-array detection. Analyst 125:1959–1961
Jiang H, Guo W, Liang X, Rao Y (2005) Both the establishment and the maintenance of neuronal polarity require active mechanisms: critical roles of GSK-3beta and its upstream regulators. Cell 120:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.033
Jie X, Yang W, Jie Y, Hashim JH, Liu XY, Fan QY, Yan L (2010) Toxic effect of gestational exposure to nonylphenol on F1 male rats. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol 89:418–428. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdrb.20268
Jie X, Jianmei L, Zheng F, Lei G, Biao Z, Jie Y (2013a) Neurotoxic effects of nonylphenol: a review. Wien Klin Wochenschr 125:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-012-0221-2
Jie Y, Fan QY, Binli H, Biao Z, Zheng F, Jianmei L, Jie X (2013b) Joint neurodevelopmental and behavioral effects of nonylphenol and estradiol on F1 male rats. Int J Environ Health Res 23:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2012.733936
Jie Y, Xuefeng Y, Mengxue Y, Xuesong Y, Jing Y, Yin T, Jie X (2016) Mechanism of nonylphenol-induced neurotoxicity in F1 rats during sexual maturity. Wien Klin Wochenschr 128:426–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-016-0960-6
Jie Y, Pan W, Wenxia Y, Feng G, Liting H, Wenmei L, Jie X (2017) The effects of gestational and lactational exposure to nonylphenol on c-jun, and c-fos expression and learning and memory in hippocampus of male F1 rat. Iran J Basic Med Sci 20:386–391. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2017.8578
Kawaguchi S, Kuwahara R, Kohara Y, Uchida Y, Oku Y, Yamashita K (2015) Oral exposure to low-dose of nonylphenol impairs memory performance in Sprague-Dawley rats. J Toxicol Sci 40:43–53. https://doi.org/10.2131/jts.40.43
Kazemi S, Bahramifar N, Moghadamnia AA, Jorsarae SG (2016a) Detection of bisphenol A and nonylphenol in rat’s blood serum, tissue and impact on reproductive system. Electron Physician 8:2772–2780. https://doi.org/10.19082/2772
Kazemi S, Feizi F, Aghapour F, Joorsaraee GA, Moghadamnia AA (2016b) Histopathology and histomorphometric investigation of bisphenol A and nonylphenol on the male rat reproductive system. N Am J Med Sci 8:215–221. https://doi.org/10.4103/1947-2714.183012
Kazemi S, Khalili-Fomeshi M, Akbari A, Kani SNM, Ahmadian SR, Ghasemi-Kasman M (2018) The correlation between nonylphenol concentration in brain regions and resulting behavioral impairments. Brain Res Bull 139:190–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.03.003
Kennedy MB (2013) Synaptic Signaling in Learning and Memory Cold Spring. Harb Perspect Biol 8:a016824. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016824
Kim NH, Lee Y, Yook JI (2018) Dishevelling Wnt and Hippo. BMB Rep 51:425–426
Krylova O, Messenger MJ, Salinas PC (2000) Dishevelled-1 regulates microtubule stability: a new function mediated by glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. J Cell Biol 151:83–94
Kudo C et al (2004) Nonylphenol induces the death of neural stem cells due to activation of the caspase cascade and regulation of the cell cycle. J Neurochem 88:1416–1423
Lee CC, Jiang LY, Kuo YL, Chen CY, Hsieh CY, Hung CF, Tien CJ (2015) Characteristics of nonylphenol and bisphenol A accumulation by fish and implications for ecological and human health. Sci Total Environ 502:417–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.09.042
Litwa E, Rzemieniec J, Wnuk A, Lason W, Krzeptowski W, Kajta M (2014) Apoptotic and neurotoxic actions of 4-para-nonylphenol are accompanied by activation of retinoid X receptor and impairment of classical estrogen receptor signaling. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 144 Pt B:334–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.07.014
Litwa E, Rzemieniec J, Wnuk A, Lason W, Krzeptowski W, Kajta M (2016) RXRalpha, PXR and CAR xenobiotic receptors mediate the apoptotic and neurotoxic actions of nonylphenol in mouse hippocampal cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 156:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.11.018
Lopez-Espinosa MJ et al (2009) Nonylphenol and octylphenol in adipose tissue of women in Southern Spain. Chemosphere 76:847–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.03.063
Lu YY, Chen ML, Sung FC, Wang PS, Mao IF (2007) Daily intake of 4-nonylphenol in Taiwanese. Environ Int 33:903–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2007.04.008
Mao Z et al (2008) Chronic application of nonylphenol-induced apoptosis via suppression of bcl-2 transcription and up-regulation of active caspase-3 in mouse brain. Neurosci Lett 439:147–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2008.05.006
Mennigen JA, Thompson LM, Bell M, Tellez Santos M, Gore AC (2018) Transgenerational effects of polychlorinated biphenyls: 1. Development and physiology across 3 generations of rats. Environ Health 17:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-018-0362-5
Nixon RA, Sihag RK (1991) Neurofilament phosphorylation: a new look at regulation and function. Trends Neurosci 14:501–506
Peifer M, McEwen DG (2002) The ballet of morphogenesis: unveiling the hidden choreographers. Cell 109:271–274
Prokop A (2013) The intricate relationship between microtubules and their associated motor proteins during axon growth and maintenance. Neural Dev 8:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-8104-8-17
Raecker T, Thiele B, Boehme RM, Guenther K (2011) Endocrine disrupting nonyl- and octylphenol in infant food in Germany: considerable daily intake of nonylphenol for babies. Chemosphere 82:1533–1540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.11.065
Rice D, Barone S Jr (2000) Critical periods of vulnerability for the developing nervous system: evidence from humans and animal models. Environ Health Perspect 108(Suppl 3):511–533
Ryan TA, Reuter H, Wendland B, Schweizer FE, Tsien RW, Smith SJ (1993) The kinetics of synaptic vesicle recycling measured at single presynaptic boutons. Neuron 11:713–724
Salcedo-Tello P, Ortiz-Matamoros A, Arias C (2011) GSK3 function in the brain during development, neuronal plasticity, and neurodegeneration. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:189728. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/189728
Salinas PC (1999) Wnt factors in axonal remodelling and synaptogenesis. Biochem Soc Symp 65:101–109
Salinas PC (2005) Retrograde signalling at the synapse: a role for Wnt proteins. Biochem Soc Trans 33:1295–1298. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20051295
Shekhar S et al (2017) Detection of phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) from maternal blood plasma and amniotic fluid in Indian population. Gen Comp Endocrinol 241:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2016.05.025
Shen L, Glowacki J, Zhou S (2011) Inhibition of adipocytogenesis by canonical WNT signaling in human mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res 317:1796–1803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.05.018
Sise S, Uguz C (2017) Nonylphenol in human breast milk in relation to sociodemographic variables, diet, obstetrics histories and lifestyle habits in a Turkish population. Iran J Public Health 46:491–499
Sobolewski M, Conrad K, Allen JL, Weston H, Martin K, Lawrence BP, Cory-Slechta DA (2014) Sex-specific enhanced behavioral toxicity induced by maternal exposure to a mixture of low dose endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Neurotoxicology 45:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2014.09.008
Son JH, Shim JH, Kim KH, Ha JY, Han JY (2012) Neuronal autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Mol Med 44:89–98. https://doi.org/10.3858/emm.2012.44.2.031
Stoica R et al (2016) ALS/FTD-associated FUS activates GSK-3beta to disrupt the VAPB-PTPIP51 interaction and ER-mitochondria associations. EMBO Rep 17:1326–1342. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201541726
Tabassum H, Ashafaq M, Parvez S, Raisuddin S (2017) Role of melatonin in mitigating nonylphenol-induced toxicity in frontal cortex and hippocampus of rat brain. Neurochem Int 104:11–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2016.12.010
Tan M et al (2015) CRMP4 and CRMP2 interact to coordinate cytoskeleton dynamics, regulating growth cone development and axon elongation. Neural Plast 2015:947423. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/947423
Tiwari SK, Agarwal S, Tripathi A, Chaturvedi RK (2016) Bisphenol-A mediated inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis attenuated by curcumin via canonical Wnt pathway. Mol Neurobiol 53:3010–3029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9197-z
Tsai MS et al (2013) Neonatal outcomes of intrauterine nonylphenol exposure–a longitudinal cohort study in Taiwan. Sci Total Environ 458:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.04.039
Walker DM, Gore AC (2017) Epigenetic impacts of endocrine disruptors in the brain. Front Neuroendocrinol 44:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2016.09.002
Wegner AM, Nebhan CA, Hu L, Majumdar D, Meier KM, Weaver AM, Webb DJ (2008) N-wasp and the arp2/3 complex are critical regulators of actin in the development of dendritic spines and synapses. J Biol Chem 283:15912–15920. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m801555200
Xu G et al (2013) 2,3,7,8-TCDD induces neurotoxicity and neuronal apoptosis in the rat brain cortex and PC12 cell line through the down-regulation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Neurotoxicology 37:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2013.04.005
Yoshimura T, Kawano Y, Arimura N, Kawabata S, Kikuchi A, Kaibuchi K (2005) GSK-3beta regulates phosphorylation of CRMP-2 and neuronal polarity. Cell 120:137–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.012
Yoshimura T, Arimura N, Kawano Y, Kawabata S, Wang S, Kaibuchi K (2006) Ras regulates neuronal polarity via the PI3-kinase/Akt/GSK-3beta/CRMP-2 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 340:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.11.147
Zhang L, Cao Y, Hao X, Zhang Y, Liu J (2015) Application of the GREAT-ER model for environmental risk assessment of nonylphenol and nonylphenol ethoxylates in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:18531–18540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5352-3
Zhao J, Qu Y, Wu J, Cao M, Ferriero DM, Zhang L, Mu D (2013) PTEN inhibition prevents rat cortical neuron injury after hypoxia-ischemia. Neuroscience 238:242–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.02.046
Zhou FQ, Snider WD (2005) Cell biology. GSK-3beta and microtubule assembly in axons. Science 308:211–214
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, China (Grant number: 201602865), Program for Liaoning Innovative Research Team in University (Grant number: LT2015028), and Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (Grant number: XLYC1807225).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
204_2019_2536_MOESM1_ESM.tif
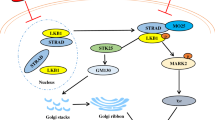
Supplementary material 1 (TIFF 7994 kb). Schematic overview of involvement of Wnt-Dvl-GSK-3β cascade in NP-induced axonal injury
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., You, M., Chai, W. et al. Developmental exposure to nonylphenol induced rat axonal injury in vivo and in vitro. Arch Toxicol 93, 2673–2687 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02536-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02536-0