Abstract
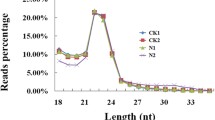
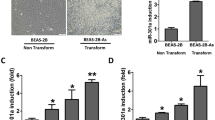
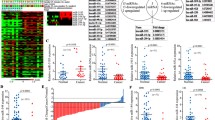
Environmental carcinogens-induced lung cancer and potential mechanisms have attracted widespread attention. Currently, microRNAs (miRNAs) have been recognized as key players in development of cancer, among which guide strand of miRNA has been well documented rather than its passenger strand (miRNA*). Our previous study showed that treatment of 0.1 nM AFB1 for 50 passages could induce malignant transformation of immortalized human bronchial epithelial cells stably expressing CYP2A13 (P50 B-2A13 cells). However, the role of miRNAs in this carcinogenic proceeding is still unclear. In present study, 36 upregulated and 27 downregulated miRNAs in P50 B-2A13 cells were first identified by miRNA microarray, and miR-138-1* was selected as a candidate miRNA by RT-qPCR and pilot experiments. Functional studies revealed that miR-138-1* could inhibit proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion of P50 B-2A13 cells. Further, target analysis and dual-luciferase reporter gene assay identified that miR-138-1* was consequentially paired with 3′-UTR of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) and decreased the luciferase activity. miR-138-1* could decrease the expressions of PDK1 and its downstream proteins in PI3K/PDK/Akt pathway but not vice versa, indicating that miR-138-1* might affect AFB1-induced malignant transformation through targeting PDK1. As predicted, interference of PDK1 showed the similar effects to miR-138-1* in the proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion of P50 B-2A13 cells. Our study demonstrated that miR-138-1* played a critical role in AFB-induced malignant transformation of B-2A13 cells by targeting PDK1. Still, the study provides a novel insight into the roles of miRNA* during carcinogenesis, particularly airborne carcinogens-induced lung cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CYP:
-
Cytochrome P450
- CYP2A13:
-
Cytochrome P450 2A13
- AFB1:
-
Aflatoxin B1
- BEAS-2B:
-
Immortalized human bronchial epithelial cells
- B-2A13:
-
BEAS-2B cells stably expressing CYP2A13
- P50 B-2A13:
-
Passage 50 B-2A13 cells with malignant transformation induced by AFB1
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- PDK1:
-
3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions
References
Aghanoori MR, Mirzaei B, Tavallaei M (2014) MiRNA molecular profiles in human medical conditions: connecting lung cancer and lung development phenomena. Aaian Pac J Cancer Prev 15(22):9557–9565
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Bayascas JR (2010) PDK1: the major transducer of PI 3-kinase actions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 346:9–29
Bedard LL, Massey TE (2006) Aflatoxin B1-induced DNA damage and its repair. Cancer Lett 241(2):174–183
Bockhorn J, Prat A, Chang YF et al (2014) Differentiation and loss of malignant character of spontaneous pulmonary metastases in patient-derived breast cancer models. Cancer Res 74(24):7406–7417
Bolleyn J, De Kock J, Rodrigues RM et al (2014) MicroRNAs as key regulators of xenobiotic biotransformation and drug response. Arch Toxicol. doi:10.1007/s00204-014-1314-7
Bunney TD, Katan M (2010) Phosphoinositide signalling in cancer: beyond PI3K and PTEN. Nat Rev Cancer 10(5):342–352
Burg WA, Shotwell OL, Saltzman BE (1981) Measurements of airborne aflatoxins during the handling of contaminated corn. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 42(1):1–11
Castellano E, Downward J (2011) RAS interaction with PI3K: more than just another effector pathway. Genes Cancer 2(3):261–274
Chang KW, Kao SY, Wu YH et al (2013) Passenger strand miRNA miR-31* regulates the phenotypes of oral cancer cells by targeting RhoA. Oral Oncol 49(1):27–33
Damiani LA, Yingling CM, Leng S et al (2008) Carcinogen-induced gene promoter hypermethylation is mediated by DNMT1 and causal for transformation of immortalized bronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Res 68:9005–9014
Ding X, Kaminsky LS (2003) Human extrahepatic cytochromes P450: function in xenobiotic metabolism and tissue-selective chemical toxicity in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:149–173
Eser S, Reiff N, Messer M et al (2013) Selective requirement of PI3K/PDK1 signaling for Kras oncogene-driven pancreatic cell plasticity and cancer. Cancer Cell 23(3):406–420
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W (2010) Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem 79:351–379
Fyffe C, Falasca M (2013) 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 as an emerging target in the management of breast cancer. Cancer Manag Res 5:271–280
Govindan R, Ding L, Griffith M et al (2012) Genomic landscape of nonsmall cell lung cancer in smokers and never-smokers. Cell 150:1121–1134
Guindon KA, Foley JF, Maronpot RR et al (2008) Failure of catalase to protect against aflatoxin B1-induced mouse lung tumorigenicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 227(2):179–183
Guindon KA, Mulder JE, Massey TE (2014) In vivo treatment with aflatoxin B1 increases DNA oxidation, base excision repair activity and 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 levels in mouse lung. Toxicology 321:21–26
He XY, Tang L, Wang SL et al (2006) Efficient activation of aflatoxin B1 by cytochrome P450 2A13, an enzyme predominantly expressed in human respiratory tract. Int J Cancer 118(11):2665–2671
Herceg Z, Lambert MP, van Veldhoven K et al (2013) Towards incorporating epigenetic mechanisms into carcinogen identification and evaluation. Carcinogenesis 34(9):1955–1967
Kang SM, Lee HJ (2014) MicroRNAs in human lung cancer. Exp Biol Med 239(11):1505–1513
Kensler TW, Roebuck BD, Wogan GN et al (2011) Aflatoxin: a 50-year odyssey of mechanistic and translational toxicology. Toxicol Sci 1:S28–S48
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG et al (2001) An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294(5543):858–862
Liu Y, Wang J, Wu M et al (2009) Down-regulation of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 levels inhibits migration and experimental metastasis of human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 7(6):944–954
Lujambio A, Lowe SW (2012) The microcosmos of cancer. Nature 482(7385):347–355
Markowitz SB, Levin SM, Miller A et al (2013) Asbestos, asbestosis, smoking, and lung cancer: new findings from the North American insulator cohort. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 188:90–96
Okamura K, Phillips MD, Tyler DM et al (2008) The regulatory activity of microRNA* species has substantial influence on microRNA and 3 UTR evolution. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15(4):354–363
Qiu C, Chen G, Ciu Q (2012) Towards the understanding of microRNA and environmental factor interactions and their relationships to human diseases. Sci Rep 2:318
Qiu S, Huang D, Yin D et al (2013) Suppression of tumorigenicity by microRNA-138 through inhibition of EZH2-CDK4/6-pRb-E2F1 signal loop in glioblastoma multiforme. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832(10):1697–1707
Rager JE, Bailey KA, Smeester L et al (2014) Prenatal arsenic exposure and the epigenome: altered microRNAs associated with innate and adaptive immune signaling in newborn cord blood. Environ Mol Mutagen 55(3):196–208
Senchenko VN, Liu J, Loginov W et al (2004) Discovery of frequent homozygous deletions in chromosome 3p21.3 LUCA and AP20 regions in renal, lung and breast carcinomas. Oncogene 23(34):5719–5728
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 62(1):10–29
So L, Fruman DA (2012) PI3K signalling in B- and T-lymphocytes: new developments and therapeutic advances. Biochem J 442(3):465–481
Tchana AN, Moundipa PF, Tchouanguep FM (2010) Aflatoxin contamination in food and body fluids in relation to malnutrition and cancer status in Cameroon. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7:178–188
Tellez CS, Juri DE, Do K et al (2011) EMT and stem cell-like properties associated with miR-205 and miR-200 epigenetic silencing are early manifestations during carcinogen-induced transformation of human lung epithelial cells. Cancer Res 71(8):3087–3097
Viegas S, Veiga L, Figueredo P et al (2013) Occupational exposure to aflatoxin B1 in swine production and possible contamination sources. J Toxicol Environ Health A 76(15):944–951
Wen W, Ding J, Sun W et al (2012) Cyclin G1-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition via phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling facilitates liver cancer progression. Hepatology 55:1787–1798
Williams JH, Phillips TD, Jolly PE et al (2004) Human aflatoxicosis in developing countries: a review of toxicology, exposure, potential health consequences, and interventions. Am J Clin Nutr 80(5):1106–1122
Xu C, Gui Q, Chen W et al (2011) Small interference RNA targeting tissue factor inhibits human lung adenocarcinoma growth in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 30:63
Yang J, Mani SA, Weinberg RA (2006) Exploring a new twist on tumor metastasis. Cancer Res 66(9):4549–4552
Yang JS, Phillips MD, Betel D et al (2011) Widespread regulatory activity of vertebrate microRNA* species. RNA 17:312–326
Yang XJ, Lu HY, Li ZY et al (2012) Cytochrome P450 2A13 mediates aflatoxin B1-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicology 300(3):138–148
Yang XJ, Zhang Z, Wang XC et al (2013) Cytochrome P450 2A13 enhances the sensitivity of human bronchial epithelial cells to aflatoxin B1-induced DNA damage. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 270:114–121
Yeh YM, Chuang CM, Chao KC et al (2013) MicroRNA-138 suppresses ovarian cancer cell invasion and metastasis by targeting SOX4 and HIF-1α. Int J Cancer 133(4):867–878
Yu J, Chen KS, Li YN et al (2012) Silencing of PDK1 gene expression by RNA interference suppresses growth of esophageal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 13(8):4147–4151
Yuan K, Xie K, Fox J et al (2013) Decreased levels of miR-224 and the passenger strand of miR-221 increase MBD2, suppressing maspin and promoting colorectal tumor growth and metastasis in mice. Gastroenterology 145(4):853–864
Zhang Z, Lu H, Huan F et al (2014) Cytochrome P450 2A13 mediates the neoplastic transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells at a low concentration of aflatoxin B1. Int J Cancer 134(7):1539–1548
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81372956, 81172695), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Universities (14KJA330002), 333 Advance Talents Projects of Jiangsu Province (BRA2014285), Six Talents Peak Project of Jiangsu Province (DG216D5047) and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), China.
Conflict of interest
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yun Wang and Zhan Zhang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhang, Z., Wang, H. et al. miR-138-1* regulates aflatoxin B1-induced malignant transformation of BEAS-2B cells by targeting PDK1. Arch Toxicol 90, 1239–1249 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1551-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1551-4